Pretest self-assessment question
A 23-year-old patient with her first depression has the S/S genotype for the SERT gene, the Del/Del alleles for the D2 receptor gene, the Val/Val alleles for the COMT gene, the T/T alleles for the MTHFR gene, and the A/A alleles for the CACNA1C gene. She also had a brain fMRI completed and it shows that her right insular cortex was hypoactive. Based only on these genetic results and neuroimaging findings, what treatment might be preferred for this patient?
A. SSRI
B. An atypical antipsychotic
C. Lithium
D. NDRI like bupropion
E. A noradrenergic TCA like desipramine
F. A mood stabilizer like lamotrigine
G. A folate-boosting product such as L-methylfolate
H. CBT
 Patient evaluation on intake
Patient evaluation on intake
 Psychiatric history
Psychiatric history
There is no premorbid psychiatric history
This is her first MDE
There has been no prior psychotropic drug treatment before this hospitalization for suicidal thinking
There are no other comorbid psychiatric disorders present
 Social and personal history
Social and personal history
Graduated college with a business degree and has a good job as a manager in a local company
This job is going very well and with minimal stress
She is in a long-term relationship with a supportive boyfriend
There are no financial concerns
Her upbringing was relatively stress free and her parents are supportive
Denies any drug or alcohol misuse
 Medical history
Medical history
Denies acute medical problems
Takes no medications
 Family history
Family history
There is no family history of psychiatric disorder
 Question
Question
Based on this patient’s history and current symptom profile, testing of which of the following might be useful?
SLC6A4 (SERT) gene
COMT gene
MTHFR gene
Calcium channel, voltage-dependent L-type alpha, 1c subunit (CACNA1C) gene
D2 receptor gene (DRD2)
fMRI of the insular cortex
 Attending physician’s mental notes: initial evaluation
Attending physician’s mental notes: initial evaluation
This patient is asking for a precise answer as to what type of treatment will “help her the most, the fastest, and harm her the least”
– All antidepressants are equal per regulatory agencies
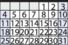
– Her genetic testing is daunting in that she has the bad alleles for every gene (see Table 30.1)
She is less likely to respond to SSRI and may have more side effects
Her high-activity COMT will degrade DA more completely
She may be vulnerable to more cognitive depressive symptoms
She is less likely to respond to atypical antipsychotic augmentation
She may experience many recurring depressive episodes
Testing of any of these genes may provide information that could be considered in the management of this patient
This patient is homozygous for (158 Val/Val, 472 G/G)
May indicate individuals with depression who are more likely to experience associated cognitive symptoms such as slowness of information processing, difficulty with executive functioning, and problem solving
– DRD2, -141C insertion/deletion (rs1799732)
This patient is heterozygous for T/T
The T allele may indicate individuals with depression who are more likely to experience associated cognitive symptoms, especially in those who also express the Val variant of the COMT gene
As this is her index depressive episode, treating her to remission quickly and avoiding relapses and recurrences is the primary goal, similar to an index episode of schizophrenia or mania
It seems that no medication is an ideal choice and genetic testing really has failed to guide prescribing toward a clear, concise choice of antidepressant
Testing via fMRI suggests depression exists when the DLPFC is hypoactive and the limbic system is hyperactive
– This patient has this typical depression finding in her limbic area, which may help aid in diagnosis but does not help in treatment selection
– This patient also has a novel finding that her right insular cortex is hypoactive
Initial studies suggest that this hypoactivity predicts a response to CBT but not SSRI
Alternatively, if hyperactivity were detected, then response to SSRI is favored and CBT would likely be ineffective
 Case outcome: initial visit
Case outcome: initial visit
No psychotherapy is offered outside core therapeutic skills, support, and education
No prescription is issued
She is deemed to be a low suicide risk and should be amenable to outpatient therapy
She is given advice about many medication and psychotherapy types to consider
The patient states that she wants you to “pick the treatment with the greatest likelihood of helping her in the short term and with the least chance of harming her”
In considering the potential future of psychopharmacology, the patient has a brain fMRI study completed. It is normal except that her right insula is noted to be hypoactive, the DLPFC is hypoactive, and the limbic system is hyperactive
In considering the potential future of psychopharmacology, the patient has her saliva sample/cheek swab analyzed
Like the previous two cases, red alleles in Table 30 are considered risky for depressive symptoms and drug responses
The patient is tested for these five genes and her results are shown in the table
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree



