Fibrous Obliteration
Scott R. Owens, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Fibrosing process → loss of normal mucosal and lymphoid structures, may occlude appendiceal lumen
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Many associated with neural proliferations (“neuromas”)
Clinical Issues
Frequent finding in both incidental appendectomies and in patients with other diseases
Frequency increases with age
Microscopic Pathology
Lumen replaced by collagenous tissue, often with myxoid background
Appendiceal lymphoid tissue undergoes atrophy and disappears
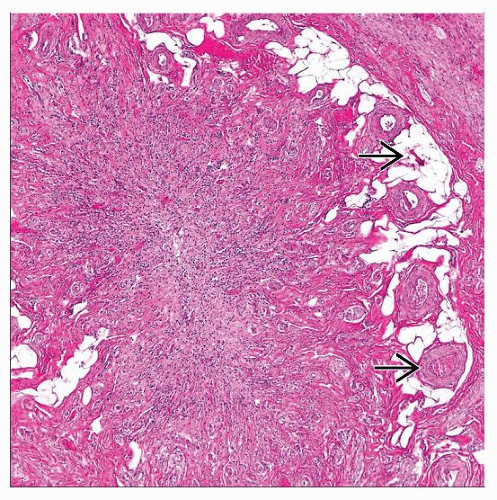
 Hematoxylin & eosin shows appendiceal tip with fibrous obliteration. Note the total loss of luminal space and mucosa. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Fibrous obliteration (FO)
Synonyms
Distal fibrous occlusion
Definitions
Fibrosing process → loss of normal mucosal and lymphoid structures, may occlude appendiceal lumen
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Idiopathic
Possibly proliferative in origin
Many associated with neural proliferations (“neuromas”)
Uncertain whether this causes fibrosis or results from it
Mast cells may be involved
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Frequent incidental finding in appendectomies and in patients with other diseases
Age
Frequency increases with age
Usually found in older individuals, but occasionally seen in young patients
Presentation
Incidental finding