EXAMINATION
Have patient in lithotomy position, draped for minimal exposure.
Obtaining Vaginal Smears and Cultures
Vaginal specimens are obtained while the speculum is in place in the vagina but after the cervix and its surrounding tissue have been inspected. Collect specimens as indicated for a Papanicolaou (Pap) smear, sexually transmitted disease screening, and wet mount. Label the specimen with the patient’s name and a description of the specimen (e.g., cervical smear, vaginal smear, and culture). Be sure to follow standard precautions for the safe collection of human secretions.
Pap Smear
Brushes and brooms are now being used in conjunction with or instead of the conventional spatula to improve the quality of cells obtained. The cylindric-type brush (e.g., a Cytobrush) collects endocervical cells only. First, collect a sample from the ectocervix with a spatula. Insert the longer projection of the spatula into the cervical os. Rotate it 360 degrees, keeping it flush against the cervical tissue. Withdraw the spatula, and spread the specimen on a glass slide. A single light stroke with each side of the spatula is sufficient to thin out the specimen over the slide. Fix the specimen and label as ectocervical. Then introduce the brush device into the vagina, and insert it into the cervical os until only the bristles closest to the handle are exposed. Slowly rotate one half to one full turn. Remove and prepare the slide. A single light stroke with each side of the spatula is sufficient to thin out the specimen over the slide. Fix the specimen and label as ectocervical. Then introduce the brush device into the vagina, and insert it into the cervical os until only the bristles closest to the handle are exposed. Slowly rotate one half to one full turn. Remove and prepare the endocervical smear by rolling the brush with moderate pressure across a glass slide. Fix the specimen and label as endocervical. Alternatively, both specimens can be placed on a single slide.
The broom-type brush is used for collecting ectocervical and endocervical cells at the same time. The broom has flexible plastic bristles, which are reported to cause less blood spotting after the examination. Introduce the brush into the vagina, and insert the central long bristles into the cervical os until the lateral bristles bend fully against the ectocervix. Maintain gentle pressure, and rotate the brush by rolling the handle between the thumb and forefinger three to five times to the left and right. Withdraw the brush, and transfer the sample to a glass slide with two single “paint” strokes. Apply first one side of the bristle, then turn the brush over, and paint the slide again in exactly the same area. Apply fixative and label as the ectocervical and endocervical specimen.
For the liquid preparation technology, using the broom-type device, insert the central bristles of the broom into the endocervical canal deep enough to allow the shorter bristles to fully contact the ectocervix. Push gently, and rotate the broom clockwise five times. Rinse the broom into the solution vial by pushing the broom into the bottom of the vial 10 times, forcing the bristles apart. As a final step, swirl the broom vigorously to further release material. Discard the collection device. Alternatively, deposit the broom end of the device directly into the collection vial. With any collection device, be sure to follow the manufacturer’s and laboratory instructions to collect and preserve the specimen appropriately. Close the vial tightly to prevent leakage and loss of the sample during transport. The liquid sample is also used to test for the HPV virus.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


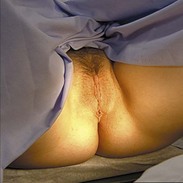
 Characteristics
Characteristics Pubic hair
Pubic hair
 Labia majora
Labia majora
 Size and length
Size and length Urethral orifice
Urethral orifice Vaginal introitus
Vaginal introitus
 Skin characteristics
Skin characteristics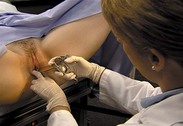
 Color
Color
 Position
Position Size
Size Shape
Shape Surface characteristics
Surface characteristics

