Familial Juvenile Hyperuricemic Nephropathy
Shane M. Meehan, MBBCh
Key Facts
Terminology
Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial disorder with chronic renal failure and hyperuricemia
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Mutations of uromodulin (UMOD) gene (on chromosome 16p12) in ˜ 30%
Clinical Issues
Early hyperuricemia with precocious gout
Reduced urinary uric acid and UMOD
Chronic renal failure by 20 years
End-stage renal failure by age 30-60
Microscopic Pathology
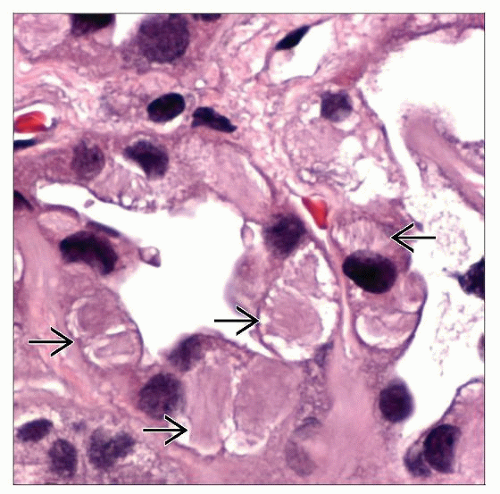
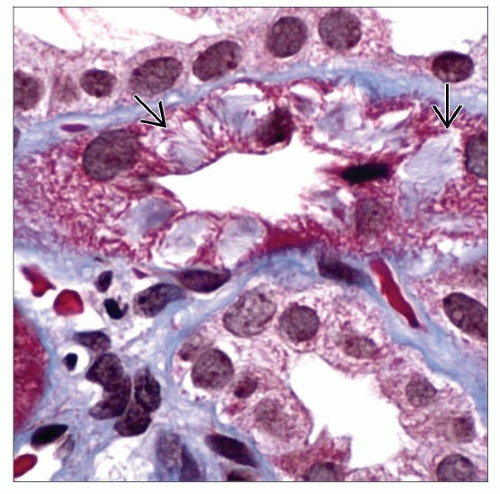
Tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis with inclusions in TALH
Lamellated bundles of ER and dilated ER by EM
UMOD cytoplasmic aggregates in TALH by IHC
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Familial juvenile hyperuricemic nephropathy (FJHN)
Synonyms
Uromodulin (Tamm-Horsfall protein) storage disease
Uromodulin-associated nephropathy
Medullary cystic disease type 2
Familial glomerulocystic disease variant
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree