37 Excitation–contraction coupling in skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle
Skeletal muscle
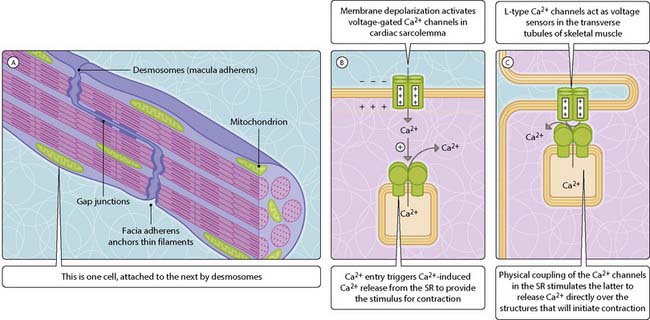
In skeletal muscle, the Ca2+ for contraction comes from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ stores. At the A–I band junction, a regular structure of tubules, known as a triad, is formed that consists of two SR tubules, called terminal cisternae, separated by a deep invagination of the plasma membrane, called a transverse tubule or t-tubule. The release of Ca2+ is triggered by electrical activity in the sarcolemma (muscle plasma membrane) (Fig. 3.37.1C).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree