Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma
Key Facts
Terminology
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EH)
Synonym: Intravascular bronchioloalveolar tumor (IVBT)
Clinical Issues
Incidence
Unusual tumor in lung
Appears to be more common in young adults; age range: 7-72 years
More common in women
Symptoms
Cough
Dyspnea
Pleuritic pain
Asymptomatic
Presentation
Bilateral pulmonary infiltrates
Treatment
There is no specific treatment
Top Differential Diagnoses
Angiosarcoma
Usually shows high mitotic count
May also show areas of necrosis
Shows more nuclear atypia
Metastatic carcinoma
Shows positive staining for epithelial markers (keratins and EMA/MUC1)
Negative for vascular markers (FVIIIRAg, CD31, and CD34)
Metastatic chordoma
Also negative for vascular markers (CD31, CD34)
Negative history of chordoma elsewhere
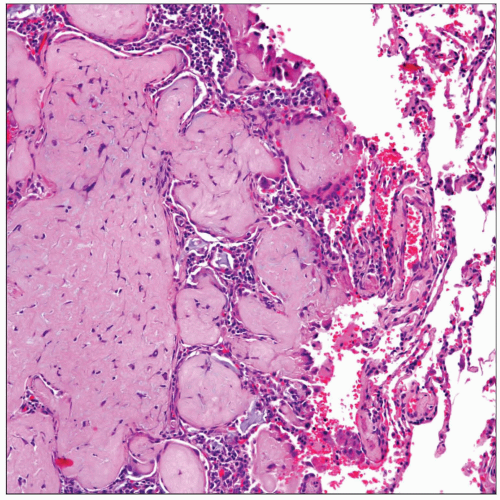 Classical presentation of epithelioid hemangioendothelioma in the lung. Note the presence of a nodule replacing lung parenchyma and infiltrating alveolar spaces. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EH)
Synonyms
Intravascular bronchioloalveolar tumor (IVBT)
Definitions
Vascular neoplasm of low- to intermediate-grade malignancy
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Vascular origin from precursor mesenchymal cells
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Tumor is unusual in lung
Age
Appears to be more common in young adults; however, age may range from 7-72 years old
Gender
More common in women
Site
Usually bilateral pulmonary infiltrates
Presentation
Cough
Shortness of breath
Pleuritic pain
Asymptomatic
Treatment
There is no specific treatment
Radiation and chemotherapy can be attempted
Steroids have been tried
Prognosis
Unpredictable
Spontaneous regression can occur
Protracted course may follow
Aggressive course with fatal outcome may occur
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Bilateral pulmonary infiltrates
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Multiple nodules replacing normal lung parenchyma
Nodules are soft or may be mucoid in consistency
Size
Nodules may measure from a few mm to 2-3 cm
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
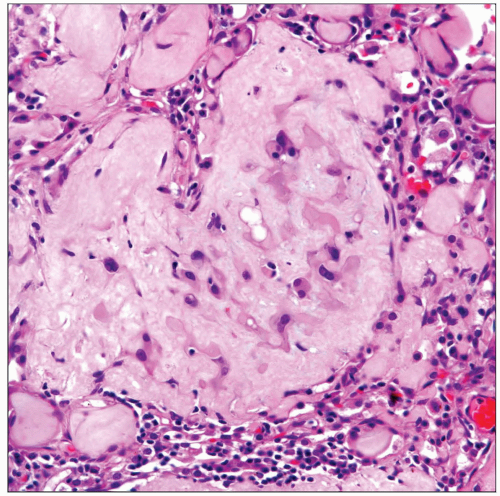
Multiple pulmonary nodules
Nodules in different phases of development
Prominent chondromyxoid background
Epithelioid cells embedded in chondromyxoid background
Low mitotic count
Signet ring cell-like cellular appearance
Cluster of tumor cells in polypoid intraalveolar pattern
Extravasated red cells
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Chondromyxoid
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Epithelioid
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree