Epi-myoepithelial Carcinoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Adenomyoepithelioma, epithelial-myoepithelial tumor, epithelial-myoepithelial tumor of unknown malignant potential, pneumocytic adenomyoepithelioma
Clinical Issues
Cough
Chest pain
Hemoptysis
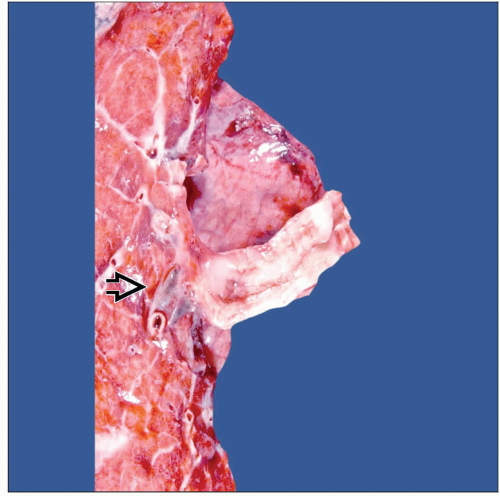
Macroscopic Features
Endobronchial tumor
2.5-5 cm in greatest dimension
Microscopic Pathology
Tubular
Epithelial, glandular
Glandular with inner epithelial layer and outer myoepithelial layer
Solid
Ancillary Tests
CK-PAN
S100
Top Differential Diagnoses
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
Mixed tumor (pleomorphic adenoma)
Adenocarcinoma
Diagnostic Checklist
Tubular structures with inner epithelial layer and outer layer of clear myoepithelial cells
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Epi-myoepithelial carcinoma (EMC)
Synonyms
Adenomyoepithelioma
Epithelial-myoepithelial tumor
Epithelial-myoepithelial tumor of unknown malignant potential
Pneumocytic adenomyoepithelioma
Definitions
Salivary gland-type tumor with epithelial and myoepithelial component
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Origin of this tumor similar to other tumors of salivary gland type; may be from endobronchial glands
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Unusual occurrence as primary lung neoplasm
No more than 15-20 cases reported in literature
Site
Invariably a central tumor
Presentation
Cough
Shortness of breath
Hemoptysis
Fever
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Lobectomy
Pneumonectomy
Prognosis
Good
Tumor has potential to metastasize
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Endobronchial tumor
Rare tumor
Size
2.5-5 cm in greatest dimension
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Glandular with inner epithelial layer and outer myoepithelial layer
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Tubular
Solid
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Epithelial, glandular
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunohistochemistry
Can highlight inner epithelial and outer myoepithelial layers
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
In small biopsies
Very difficult or impossible to differentiate
Both tumors show myoepithelial differentiation
Cylindromatous pattern is more common in adenoid cystic carcinoma
In resected specimens
Presence of bi-layer of cells forming glandular component is more common in adenoid cystic carcinoma
Areas of cylindromatous pattern is more common in adenoid cystic carcinoma
Presence of intraglandular mucoid material is more common in adenoid cystic carcinoma
Presence of glandular structures with internal layer (epithelial) and external layers of clear cells (myoepithelial cells) is classic for EMC
Mixed Tumor (Pleomorphic Adenoma)
EMC lacks presence of mesenchymal components
Cartilage
Bone
Prominent chondromyxoid background
Bi-layer showing inner epithelial + outer clear cell layer of myoepithelial cells is characteristic of P-EMC
Adenocarcinoma
No bilayer of epithelial and myoepithelial cells
Tumor cells may or may not be arranged in glands
Tumor cells may have malignant cytological features
DIAGNOSTIC CHECKLIST
Pathologic Interpretation Pearls
Tubular structures with inner epithelial layer and outer layer of clear myoepithelial cells
GRADING
Low-Grade Carcinoma
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree