Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Key Facts
Terminology
Synonyms
Loeffler syndrome
Definition
Patchy pulmonary infiltrates characterized by presence of eosinophils as main inflammatory component
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Parasites
Ingestants and inhalants
Fungal infections
Drug toxicity
Unknown etiology
Clinical Issues
Presentation
Simple (Loeffler syndrome)
Tropical
Chronic
Acute
Treatment
Depends on etiology of process
Prognosis
Most patients follow a recovery process
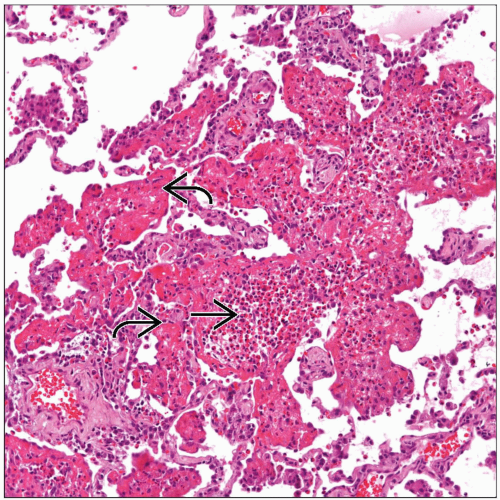
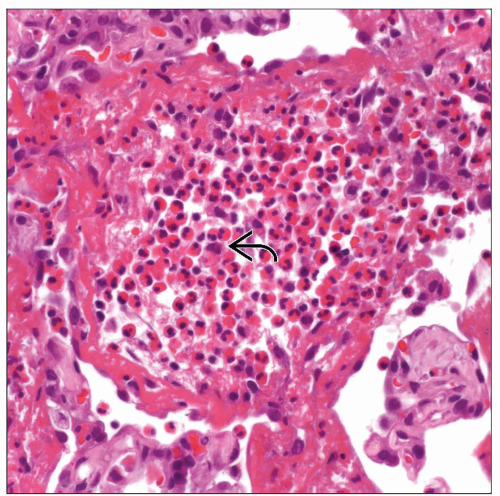
Microscopic Pathology
Histological Features
Filling of alveolar spaces by eosinophils and macrophages
Intraalveolar acellular exudate
Eosinophilic intraalveolar necrosis may be present
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Loeffler syndrome
Definitions
Patchy pulmonary infiltrates characterized by the presence of eosinophils as the main inflammatory component
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Causes
Parasites
Ascaris
Filariasis
Strongyloides
Toxocara
Ingestants and inhalants
L-tryptophan
Cocaine
Fungal infections
Aspergillus
Candida
Curvularia
Drug toxicity
Antibiotics
Unknown etiology
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Gender
Females are more commonly affected in chronic phase
Presentation
Symptomatology will depend on type of process
Simple (Loeffler syndrome)
Self-limited
Fleeting pulmonary infiltrates
Tropical
Fever
Cough
Dyspnea
Chronic
Fever
Chills
Dyspnea
Weight loss
History of asthma
Acute
Fever
Marked respiratory difficulty
Laboratory Tests
Peripheral eosinophilia in chronic phase
Elevated IgE in serum in chronic phase
Natural History
Eosinophilic pneumonia can present in 4 different forms
Simple (Loeffler syndrome)
Tropical
Chronic
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree