19 Environmental medicine
Heat
• Heat acclimatization. This occurs over several weeks. The sweat volume increases and the sweat salt content falls. Increased evaporation of sweat results in a reduced TCore.
• Heat cramps. Painful muscle cramps, usually in the legs, occur in fit people during exercise in hot weather. They respond to combined salt and water replacement, and in the acute stage to stretching and muscle massage. TCore remains normal.
• Heat illness (heat exhaustion). At any environmental temperature (especially with TEnv of > 25°C), and with a high humidity, exercise in clothes that inhibit sweating can cause an elevation in TCore in less than 15 mins. Heat illness with a TCore > 37°C causes weakness, cramps and syncope, and may progress to heat injury.
Cold
Hypothermia
• Hypothermia can occur when TEnv is below 8°C with inadequate heating and clothing. Drugs, e.g. hypnotics, alcohol, hypothyroidism or intercurrent illness also contribute. The elderly have diminished ability to sense cold and also have little insulating fat. Neonates and infants become hypothermic rapidly because of a relatively large surface area in proportion to subcutaneous fat.
• Hypothermia often occurs in climbers, skiers and polar travellers, and in wartime. Wet, cold conditions with wind chill, physical exhaustion, injuries and inadequate clothing are contributory.
• Serious hypothermia can develop following immersion for more than 1 hour in water temperatures of 15–20°C. In water temperatures below 12°C limbs rapidly become numb and weak. Recovery takes place gradually, often taking several hours.
Diagnosis
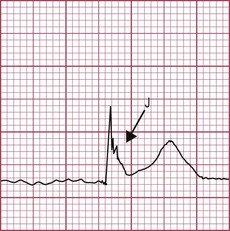
Bradycardia with ‘J’ waves (rounded waves above the isoelectric line at the junction of the QRS complex and ST segment (Fig. 19.1)) is pathognomonic of hypothermia. Prolongation of PR and QT intervals and of the QRS complex also occurs. Ventricular dysrhythmia (tachycardia/fibrillation) or asystole is the usual cause of death.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree