Endometriosis
Sharon K. Bihlmeyer, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Diagnosis requires 2 of 3 findings
Glands, stroma, or hemorrhage
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Unopposed estrogen therapy increased risk of malignancy in endometriosis
Clinical Issues
Affects intestinal tract in 15-37% of women with pelvic endometriosis
Present with abdominal pain or abdominal mass
May present with bowel obstruction or perforation
Often eventually require hysterectomy
Treat with hormonal suppressive therapy
Endometrial glands have malignant potential
Endometrioid adenocarcinoma and Müllerian adenosarcoma
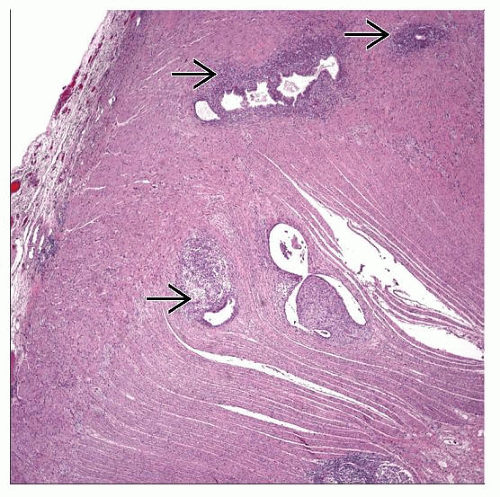
Macroscopic Features
Involves sigmoid, rectosigmoid colon, or rectum in 70-85%
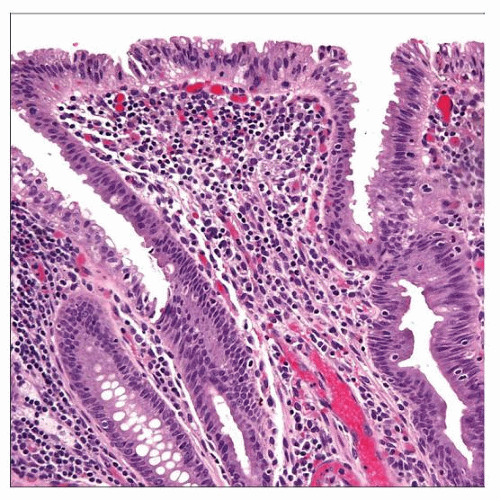
Microscopic Pathology
Endometrioid glands embedded in endometrial stroma
Columnar epithelium-lining glands
Stroma composed of densely packed small fusiform cells
Marked concentric smooth muscle hyperplasia and hypertrophy
CD10 marks normal, ectopic, and neoplastic endometrial stromal cells
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Endometrial glands and stroma outside of uterus
Diagnosis requires 2 of 3 findings
Glands, stroma, or hemorrhage
Endosalpingiosis is endometriosis without stroma (just glands lined by ciliated tubal-type epithelium)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Developmental Anomaly
Theory: Endometriosis due to Müllerian rests outside of uterus
Rests develop with hormonal stimulation
Theory: Backwash of uterine contents through fallopian tubes (retrograde menstruation)
Backwash → deposits outside of uterus, which develop into endometriosis
Environmental Exposure
Unopposed estrogen therapy increases risk of malignancy in endometriosis
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Affects 2-22% of asymptomatic women
Incidence in women with dysmenorrhea is 40-60%
Affects intestinal tract in 15-37% of women with pelvic endometriosis
Age
Reproductive age
Peaks at age 40
Postmenopausal
Gender
Women
Presentation
Abdominal pain
Deep mass
Hematochezia
Bowel obstruction
Bowel perforation
May be asymptomatic
Natural History
May cause bowel perforation, more commonly seen in pregnancy
Bowel obstruction may ensue
Usually associated with infertility
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Surgical management for perforation or obstruction usually requires partial colectomy
Laparoscopic approaches with superficial or partial-thickness excisions
Often eventually require hysterectomy
Adjuvant therapy
Norgestrel intrauterine device
Drugs
Hormonal suppressive therapy
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and oral contraceptives are initial approach
Progestins
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists
Prognosis
May be difficult to preserve fertility
Endometrial glands have malignant potential
May have glandular atypia
Hyperplasia
Endometrioid adenocarcinoma and Müllerian adenosarcoma
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Double contrast barium enema shows extrinsic mass effect with mucosal fine crenulation
Thickened bowel wall with stenotic lumen
May have mural cysts
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree