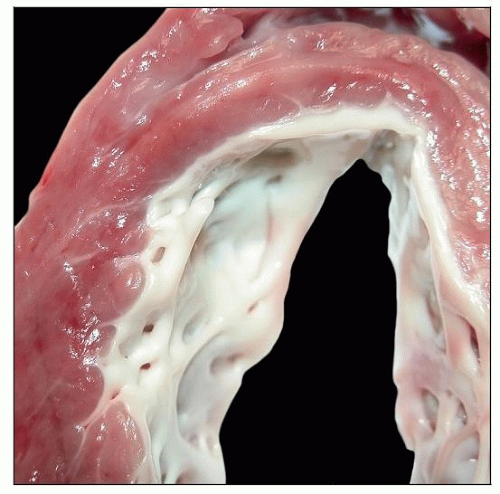
Endocardial Fibroelastosis
Monica P. Revelo, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Porcelain-like thickening of ventricular endocardium by layers of collagen and elastic fibers
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Endocardial fibroelastosis (EFE) should be regarded as endocardial response to a variety of stimuli rather than a specific disease entity
Clinical Issues
Unexplained congestive heart failure in infants
Left ventricle hypertrophy/dilatation
Exclusion of other structural abnormalities or injury
Microscopic Pathology
Thickened endocardium with collagen and elastic fiber deposition
Generally unremarkable myocardium
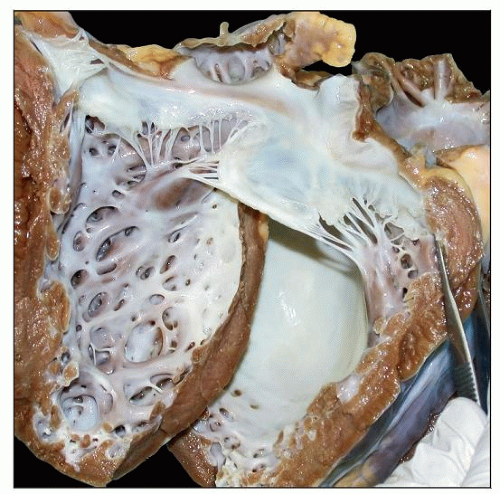 Gross specimen shows left ventricle with white opaque thickened endocardium and flat trabeculae. The mitral valve is normal. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Endocardial fibroelastosis (EFE)
Synonyms
Infantile dilated cardiomyopathy
Definitions
Porcelain-like thickening of ventricular endocardium by layers of collagen and elastic fibers
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
General Consideration
EFE is an endocardial response to a variety of stimuli rather than a specific disease entity
Putative causes and associations include
Myocarditis (viral, bacterial)
Lysosomal storage diseases
Immunologic diseases
X-linked cardiomyopathy, recessive form
Mitochondrial cardiomyopathy
Pre- and postnatal left ventricular outflow tract obstruction
Congenital malformations
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree