Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma
Laura Webb Lamps, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Botryoid rhabdomyosarcoma is most common pediatric neoplasm of extrahepatic biliary tree
Macroscopic Features
More common in biliary tree than gallbladder
Grape-like gelatinous masses in lumen of bile duct
Microscopic Pathology
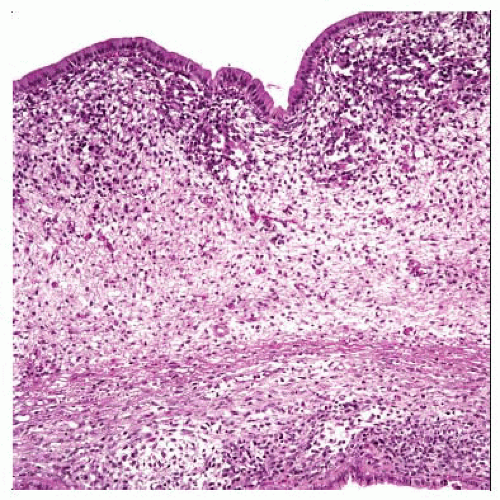
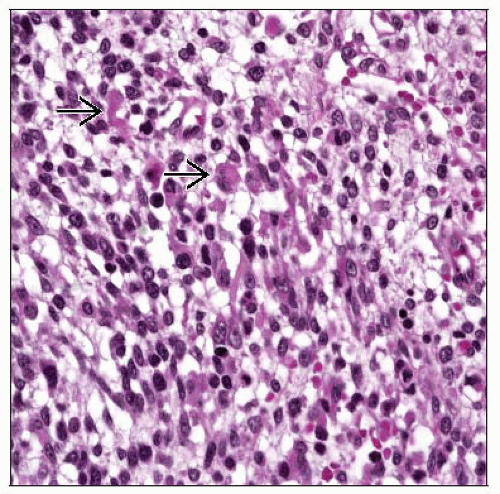
Resembles botryoid-type embryonal RMS elsewhere in the body
Tumor cells densely packed beneath single layer of biliary epithelium to form characteristic “cambium layer”
Newer myogenic markers such as myogenin, MYOD1 very helpful
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS)
Definitions
Primary rhabdomyosarcoma, embryonal type, arising in biliary tree or gallbladder
Botryoid rhabdomyosarcoma is most common neoplasm of extrahepatic biliary tree in childhood
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Most frequently described in children, in extrahepatic biliary tree
Range: 16 months to 11 years; mean age: 4.5 years
Occasionally seen in adults
Usually in gallbladder (rather than biliary tree) of elderly patients
Gender
No gender predilection
Presentation
Signs of progressive biliary obstruction