8
Doses in children
Doses based on age
The BNF uses ranges:
- First month (neonate)
- Up to 1 year (infant)
- 1 to 6 years would be a dose for a child from 1 year up to their 6th birthday.
- 6 to 12 years
In the BNF for Children a number of different ranges are stated depending on the medication.
Doses based on body weight
Many drugs are potent and the dose of such drugs will take into account the body weight of the person receiving the drug. This is particularly important for children. Unless the age is specified, the term ‘child’ in the BNF includes those who are 12 years and under. Children’s doses are expressed in a number of different ways. The doses are usually given for age ranges and can be given as an amount of drug to be given, or the amount of drug to be given can be related to the body weight in kg or body surface area in m2 of the child or adult. The way that children respond to drugs is different from the adult response. This is particularly true of neonates and both the BNF and the BNF for Children advise care in calculating doses for neonates. The advice also states that ‘for most drugs the adult maximum dose should not be exceeded’. The example given is if a drug has a dose of 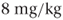 and a maximum dose of 300 mg a 10-kg child would be given 80 mg but a child weighing 40 kg should receive 300 mg and not 320 mg. It also advises that in overweight children it may be more appropriate to calculate the dose from the ideal weight for a child of that age and height to avoid giving higher doses than required.
and a maximum dose of 300 mg a 10-kg child would be given 80 mg but a child weighing 40 kg should receive 300 mg and not 320 mg. It also advises that in overweight children it may be more appropriate to calculate the dose from the ideal weight for a child of that age and height to avoid giving higher doses than required.
Average body weights appear both in the BNF and in the BNF for Children as well as information about average heights. The information related to average weights and heights has been reproduced in Table 8.1 and it can be seen that the average man is considered to have a body weight of 68 kg and the average woman to have a body weight of 58 kg, although there will be considerable variation about these average weights. The body weights of children can also be obtained from Table 8.1. For example, a 6-month-old child with an average body weight would weigh 7.6 kg and a 5-year-old child with an average body weight would weigh 18 kg. If the child’s age is not given in the table, it is usual to estimate the body weight using the weights on either side of the age of the child or to take into account the height of the child. For example, the body weight of a 4-year-old child would be estimated to be between that of a 3 year old and that of a 5 year old, i.e. about 16 kg.
Table 8.1 Age and related body weight and height
| Age | Ideal body weight (kg) | Height (cm) |
| Full-term neonate | 3.5 | 51 |
| 1 month | 4.3 | 55 |
| 2 months | 5.4 | 58 |
| 3 months | 6.1 | 61 |
| 4 months | 6.7 | 63 |
| 6 months | 7.6 | 67 |
| 1 year | 9 | 75 |
| 3 years | 14 | 96 |
| 5 years | 18 | 109 |
| 7 years | 23 | 122 |
| 10 years | 32 | 138 |
| 12 years | 39 | 149 |
| 14-year-old boy | 49 | 163 |
| 14-year-old girl | 50 | 159 |
| Adult male | 68 | 176 |
| Adult female | 58 | 164 |
If a baby is born prematurely then calculations of age will have to take into consideration chronological age together with the number of weeks’ gestation at birth and are beyond the scope of this book.
The calculation of a dose based on body weight may produce a value that does not correspond to an available dosage form. Example 8.1 illustrates such a situation.



