Dirofilariasis
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Caused by Dirofilaria immitis
Dirofilariasis is more common in dogs
Humans are accidental hosts
Clinical Issues
Uncommon infectious condition
Can occur at any age, and infection has been described in children and adults
More common in adults
May be more common in males than in females
As it occurs in dogs, worms lodge in the heart but die before reaching maturity
Worms pass into pulmonary arteries
Peripheral lung lesions are by far more common
Clinical presentation
Cough
Dyspnea
Wheezing
Chest pain
Fever
Laboratory findings
Eosinophilia may be present in 10-15% of patients
Treatment
Complete surgical resection is curative
Microscopic Pathology
Histological features
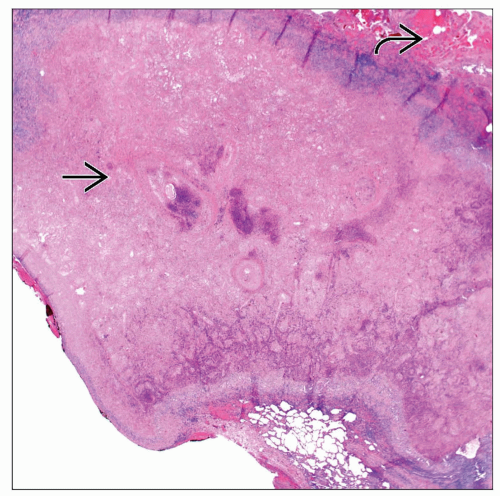
Well-demarcated necrotic nodule
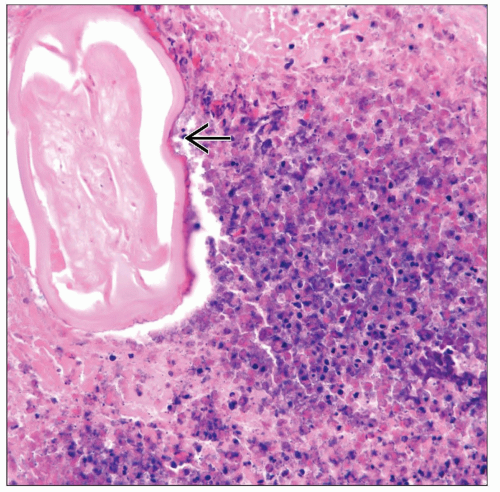
Intravascular presence of nonviable worms
Worms may be present in necrotic tissue and not in vessels
Prominent inflammatory reaction
Nonnecrotizing granulomas may be present
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Infectious condition caused by helminth
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Caused by Dirofilaria immitis
Dirofilariasis is more common in dogs
Humans are accidental hosts
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Uncommon infectious condition
Age
Can occur at any age, and infection has been described in children and adults
More common in adults
Gender
May be more common in males than in females
Ethnicity
No ethnic predilection
Site
Worms lodge in the heart but die before reaching maturity
Worms pass into pulmonary arteries
Right lung appears to be more commonly involved
Peripheral lung lesions are by far more common
Central lung lesions are unusual
Presentation
Symptoms
Cough
Dyspnea
Wheezing
Chest pain
Fever
Some patients may be asymptomatic
Laboratory Tests
Eosinophilia may be present in about 10-15% of patients
Natural History
Not associated with immunosuppression
In some cases, it is associated with history of previous malignancy
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete surgical resection is curative
Prognosis
Excellent
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
May present as single or multiple lung nodules
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Well-circumscribed necrotic nodule of soft consistency ± hemorrhage
Sections to Be Submitted
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree