Diffuse Pulmonary Lymphangiomatosis
Monica P. Revelo, MD, PhD
Brandon T. Larsen, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Rare disease characterized by proliferation of lymphatic vessels and smooth muscle cells along lymphatic routes in visceral pleura, bronchovascular bundles, and interlobular septa
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Congenital disease due to abnormal lymphatic system development
Clinical Issues
Mean age at presentation: 8.5 years
No gender predilection
Localized to lung or chest
Widespread distribution involving spleen, bones (e.g., ribs, vertebrae, humerus, femur), liver, and skin
Microscopic Pathology
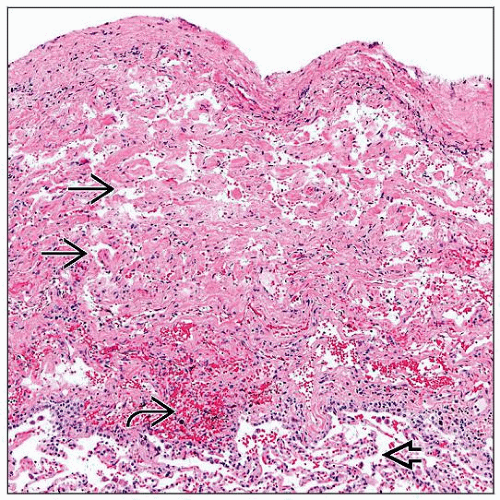
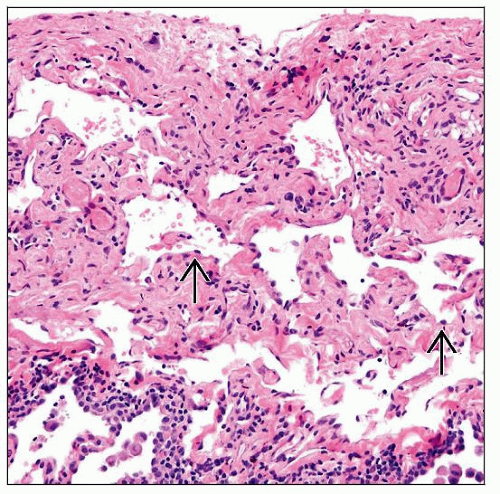
Anastomosing lymphatic channels in pleura, interlobular septa, bronchovascular bundles
Thickening of pleura, interlobular septa, and bronchovascular bundles
Lymphatic channels filled with chyle
Smooth muscle fascicles in periphery of lymphatic channels
Ancillary Tests
CD31 and D2-40 stains highlight endothelial lining of lymphatic channels
Top Differential Diagnoses
Diffuse pulmonary lymphangiectasia
Lymphangioma
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Diffuse pulmonary lymphangiomatosis (DPL)
Definitions
Rare disease characterized by proliferation of lymphatic vessels and smooth muscle fascicles along preexisting lymphatic routes in visceral pleura, bronchovascular bundles, and interlobular septa
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Developmental Anomaly
Congenital disease due to abnormal lymphatic system development
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Mean at presentation: 8.5 years
May manifest at birth and rarely in adults
Gender
No predilection
Site
Localized to lung or chest
Widespread distribution involving spleen, bones (e.g., ribs, vertebrae, humerus, femur), liver, and skin
Presentation
Dyspnea
Cough
Hemoptysis
Chest pain
Milky sputum
Pleural effusions
Mediastinal enlargement
Laboratory Tests
Pulmonary functional tests demonstrate
Mixed pattern obstructive/restrictive
Restrictive pattern only
Natural History
Progressive condition leading to end-stage respiratory failure
Treatment
Options, risks, complications
Definitive treatment is not available; palliative measurements and adjuvant therapies are used
Surgical approaches
Pleurocentesis
Pleurodesis
Pleurectomy
Ligation of thoracic duct
Transplantation
Drugs
Interferon alpha
Glucocorticoids
Propranolol
Radiation
For localized disease
Prognosis
Poor; causes of death include respiratory failure, infections, and chylus effusions
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
Chest x-ray shows mediastinal enlargement
Peribronchial expansion
Increased interstitial markings
Chylous pleural/pericardial effusions
Multifocal cystic bone lesions with porous soap or honeycomb texture
CT Findings
Thickening of interlobular septa and bronchovascular bundles
Ground-glass opacities
Pleural thickening and effusions
Diffuse fluid infiltration of mediastinal soft tissue
Increased mediastinal/hilar nodes
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree