Diffuse Alveolar Damage
Key Facts
Terminology
Acute inflammatory reaction involving endothelial and epithelial cells of the alveolus
Clinical Issues
Nonspecific histologic pattern of acute lung injury that may occur in wide variety of clinical settings
Idiopathic cases are designated acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP) or Hamman-Rich syndrome
Clinical syndrome associated with DAD is known as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
About 50% of patients may undergo spontaneous resolution with supportive therapy
High overall mortality (˜ 50% of patients)
Surviving patients may recover normal lung function or go on to develop interstitial fibrosis
Microscopic Pathology
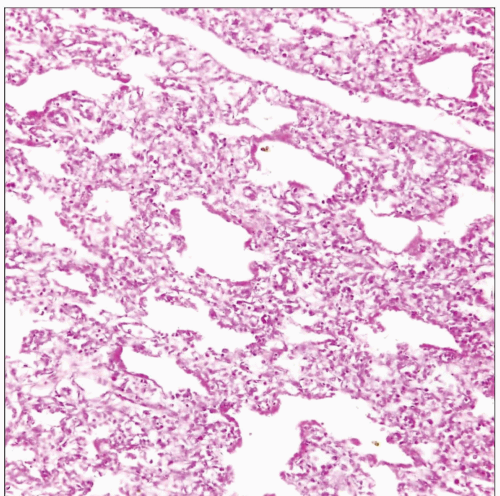
Early, acute phase characterized by capillary congestion, edema, and intraalveolar hemorrhage
Formation of hyaline membranes (pink fibrinous material lining alveolar walls) is hallmark of acute phase
Interstitial inflammatory exudates (lymphocytes, plasma cells, and histiocytes)
Organizing phase shows proliferation of type II pneumocytes with cytologic atypia
Fibroblastic proliferation forms fibrinous intraalveolar plugs of granulation tissue reminiscent of organizing pneumonia
Dense interstitial fibrosis with widening of alveolar septa is seen in late stages
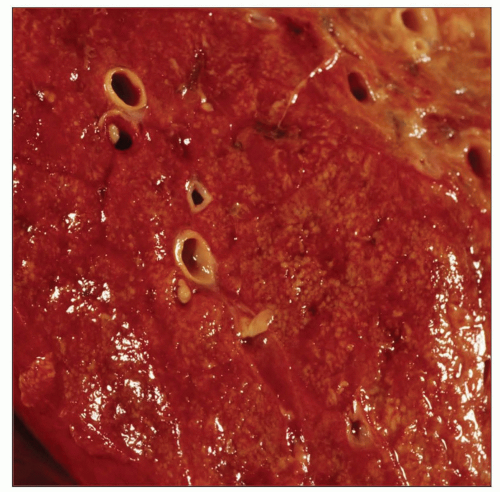 Gross appearance of the lung on cut surface in a patient with diffuse alveolar damage shows beefy red, congested, and edematous parenchyma. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Diffuse alveolar damage (DAD)
Synonyms
Acute respiratory distress syndrome, shock lung, post-perfusion lung, hyaline membrane disease
Definitions
Acute inflammatory reaction involving endothelial and epithelial cells of alveolus
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Can result from variety of lung injuries
Bacterial and viral infection
Drugs and inhaled toxins
Shock, trauma, burns
Sepsis
Allograft rejection
Radiation
Collagen vascular disease
Idiopathic
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
18-50 persons per 100,000 population per year
Age
Children to adults
Presentation
Tachypnea and rapidly progressive dyspnea
Hypoxemia (PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 200)
Respiratory failure with noncardiogenic pulmonary edema
Natural History
Nonspecific histologic pattern of acute lung injury that may occur in wide variety of clinical settings
Idiopathic cases are designated acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP) or Hamman-Rich syndrome
Clinical syndrome associated with DAD is known as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
Rapid clinical onset, usually within 24-48 hours of precipitating event
About 50% of patients may undergo spontaneous resolution with supportive therapy
Oxygen therapy and mechanical ventilation may play significant role in causing development of tissue injury
Treatment
Supportive therapy using mechanical ventilation with low tidal volumes
Treatment of underlying precipitating condition (e.g., infection, shock, etc.)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree