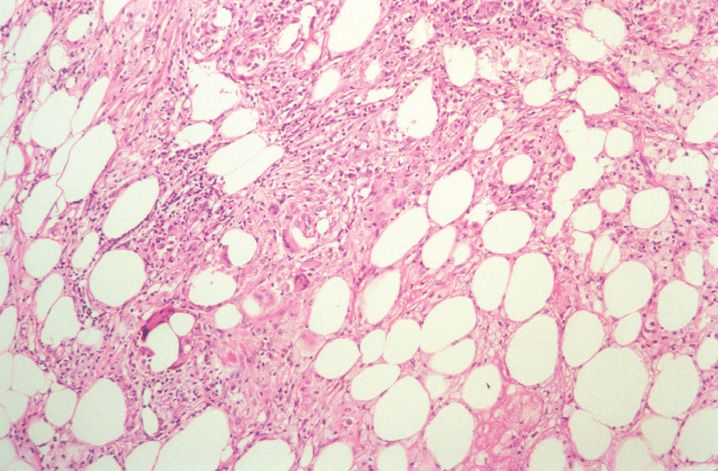
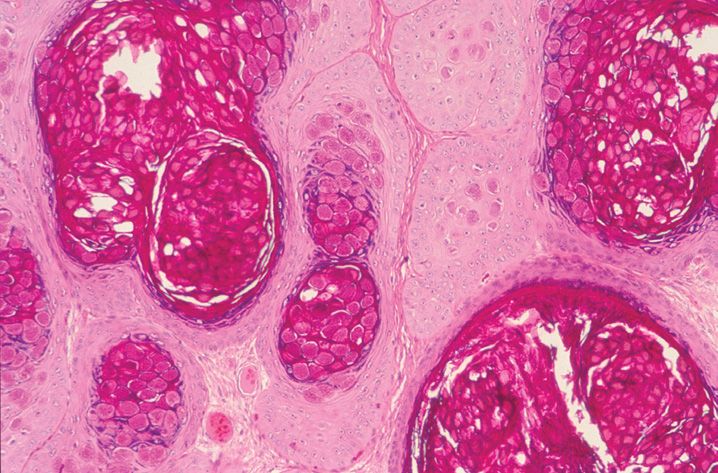
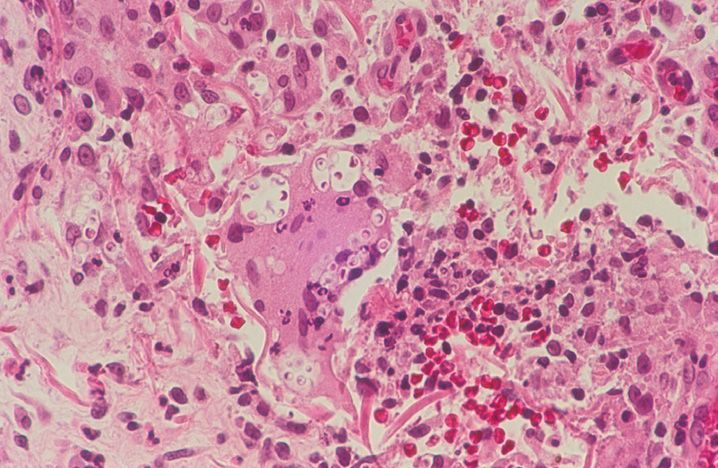
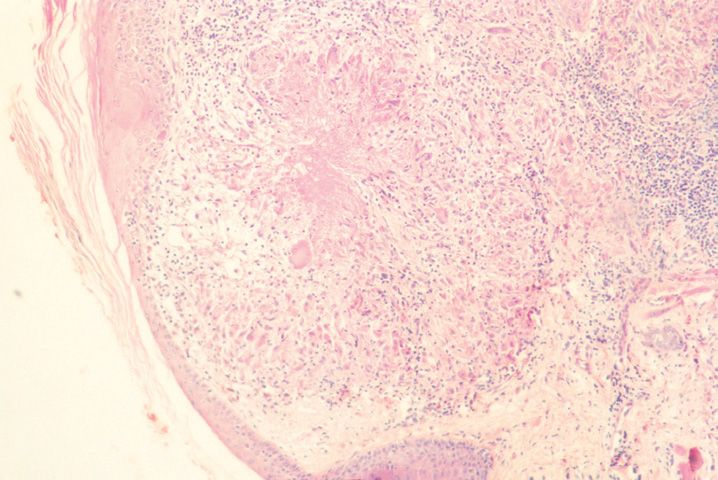
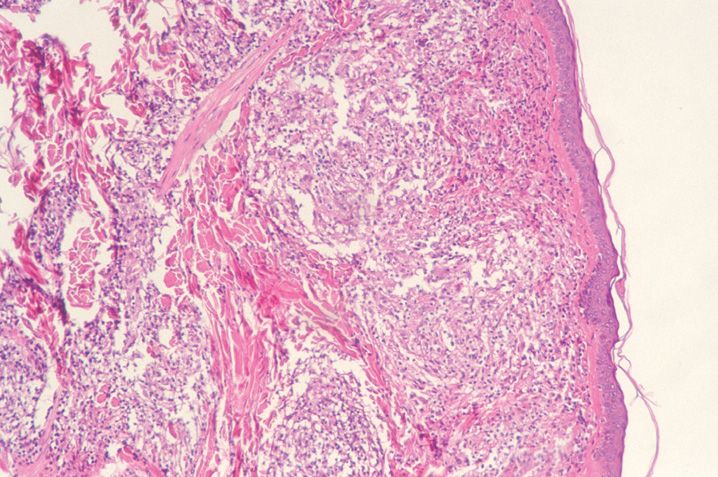
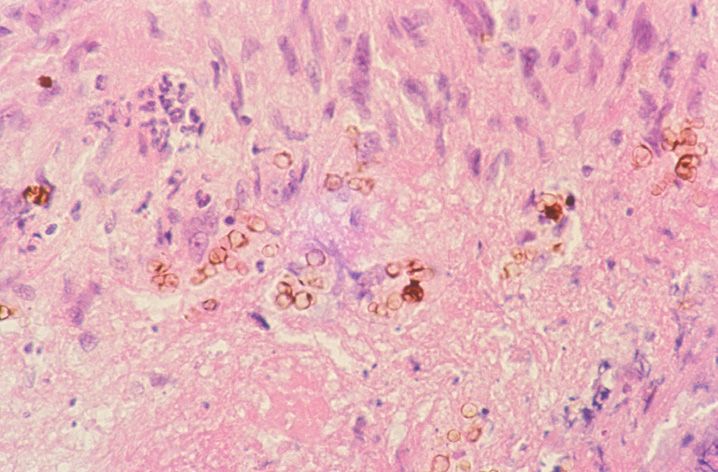
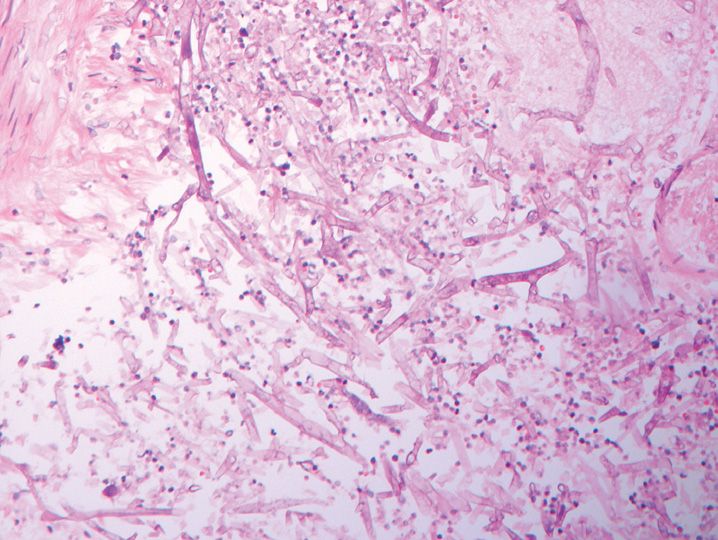
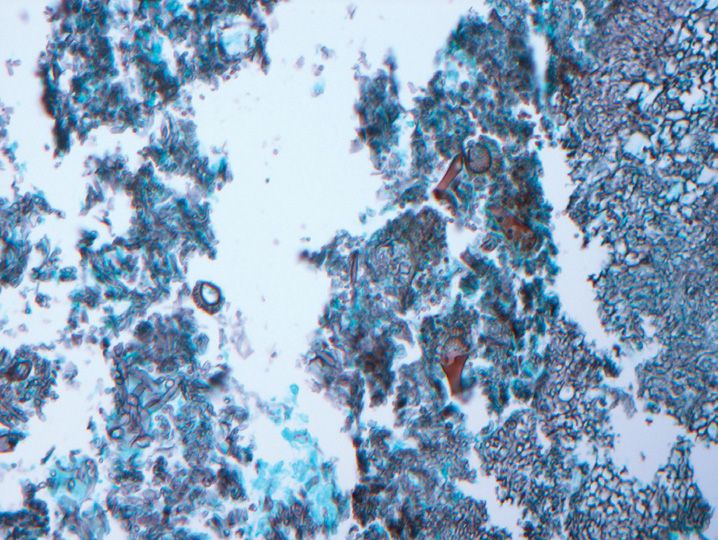
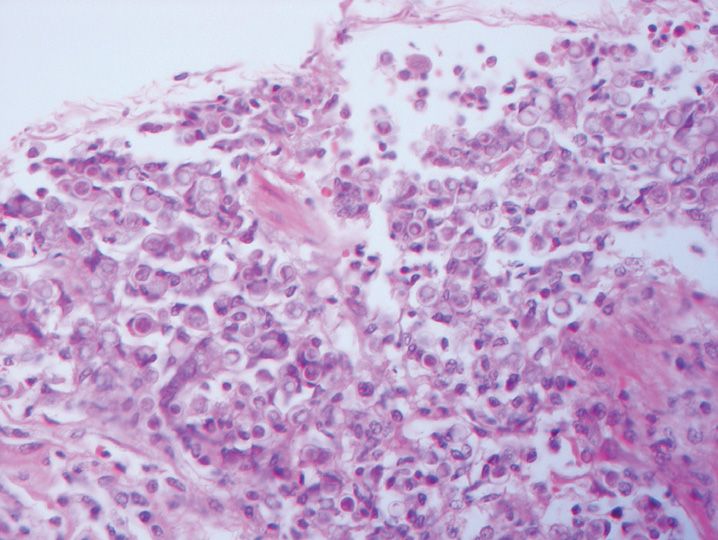
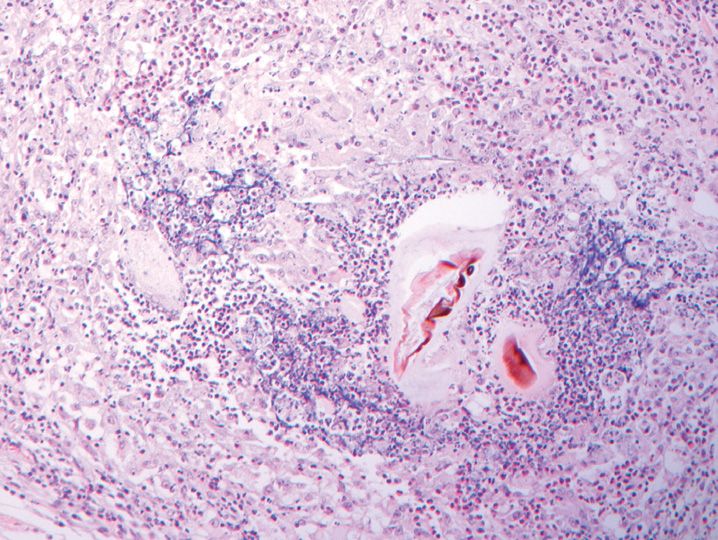
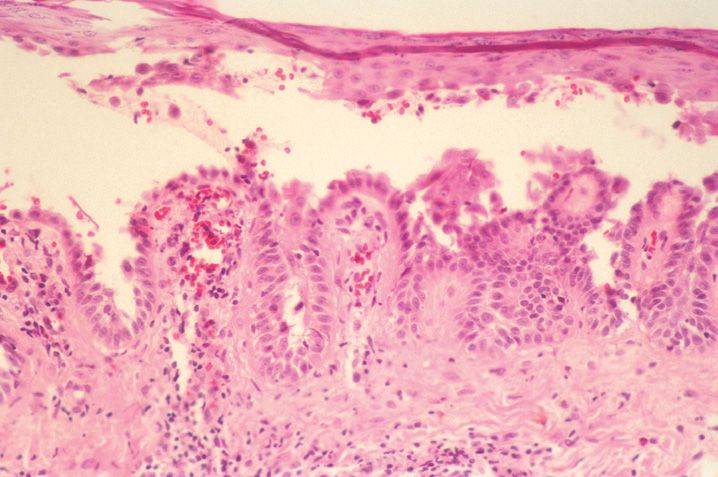
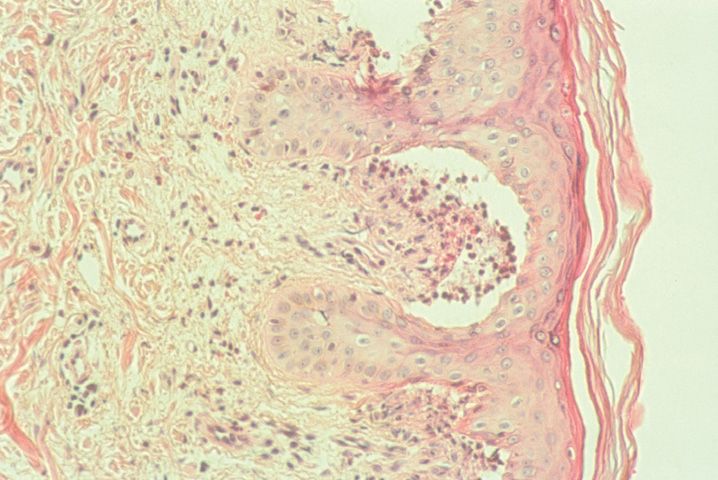
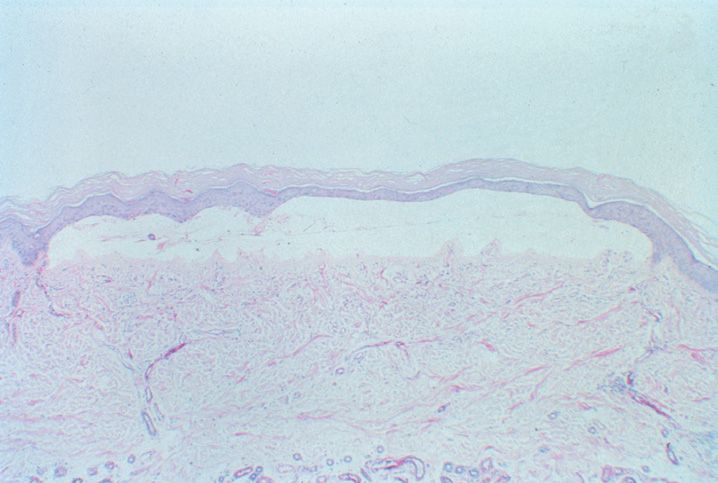
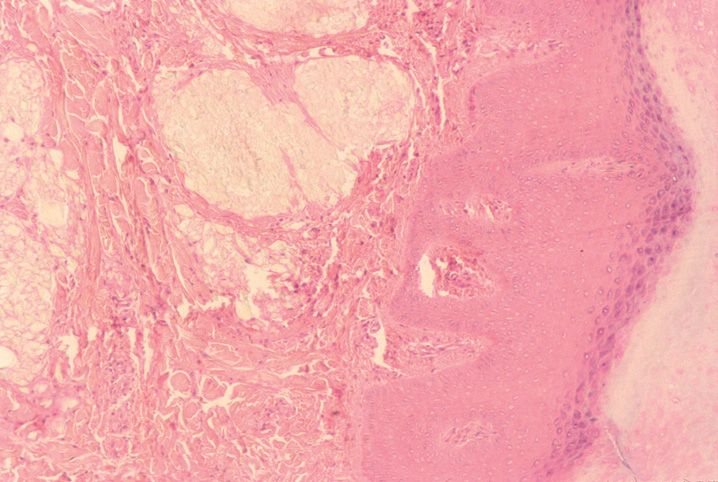
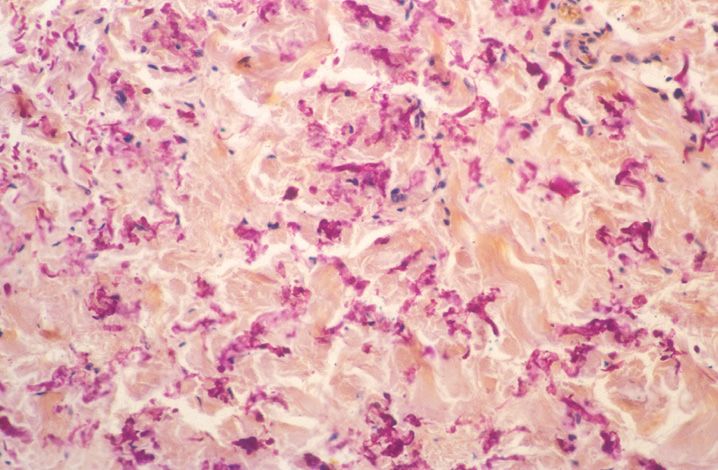
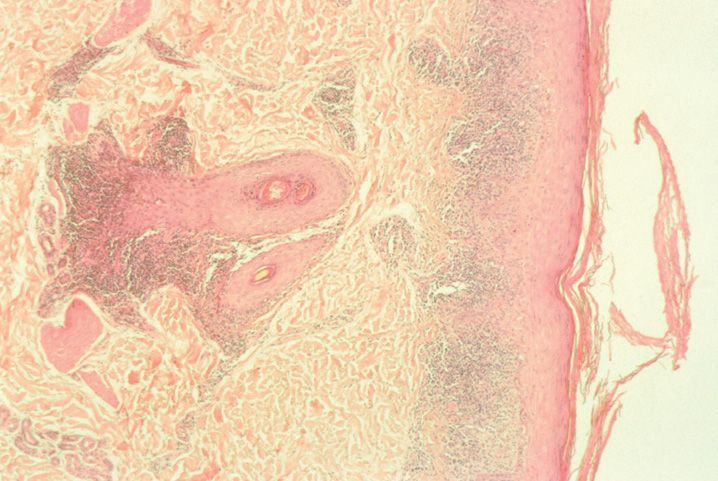
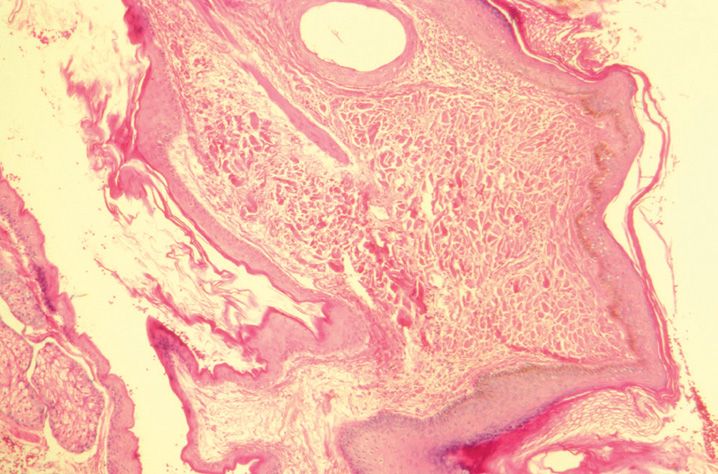
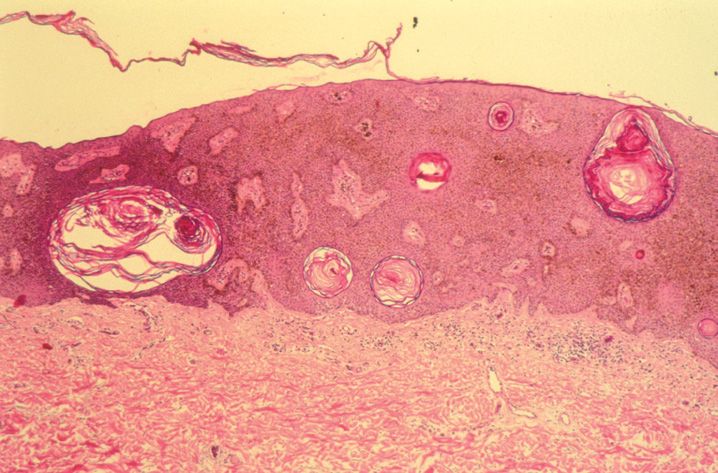
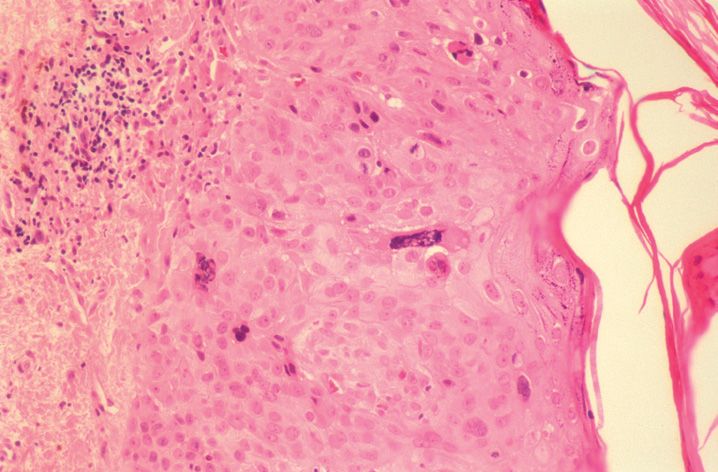
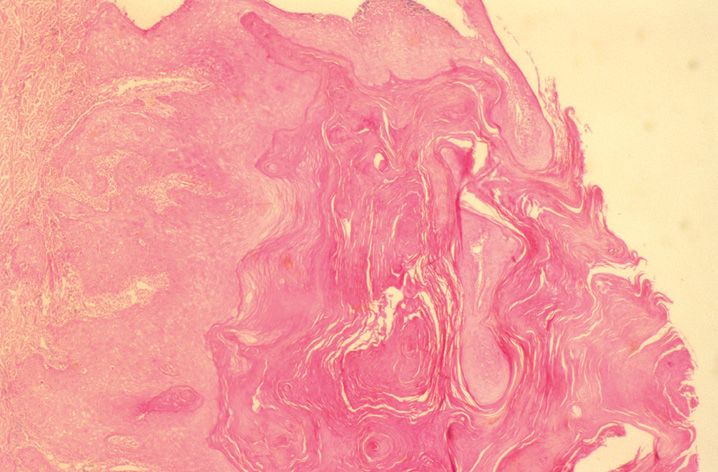
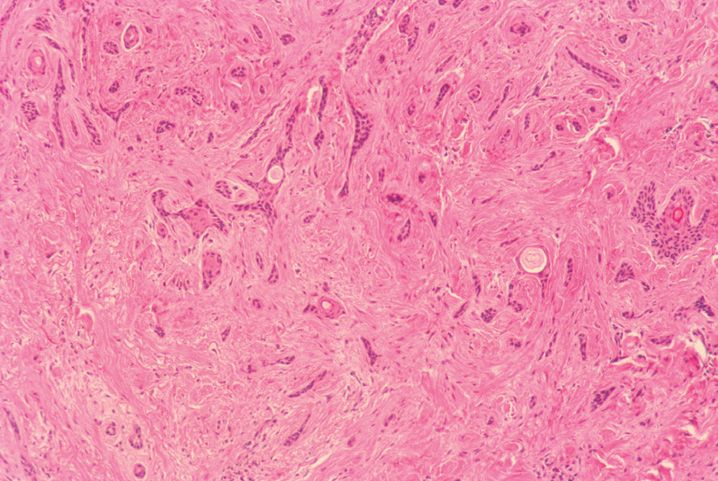
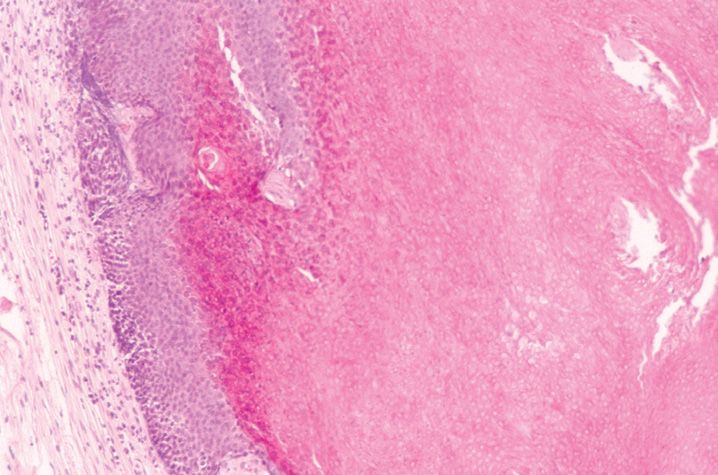
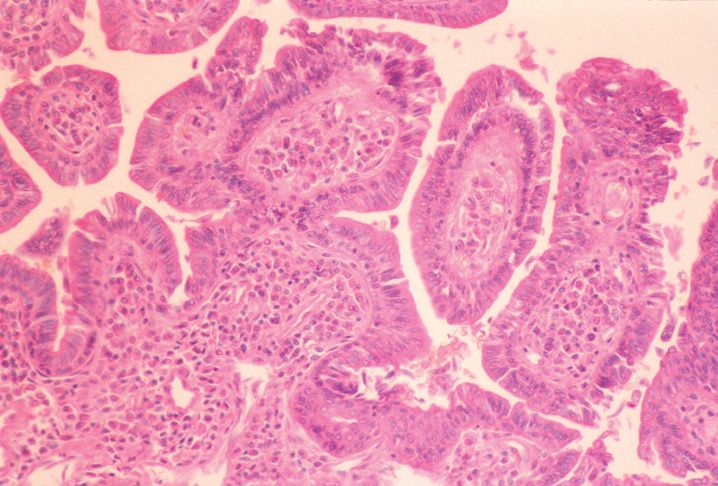
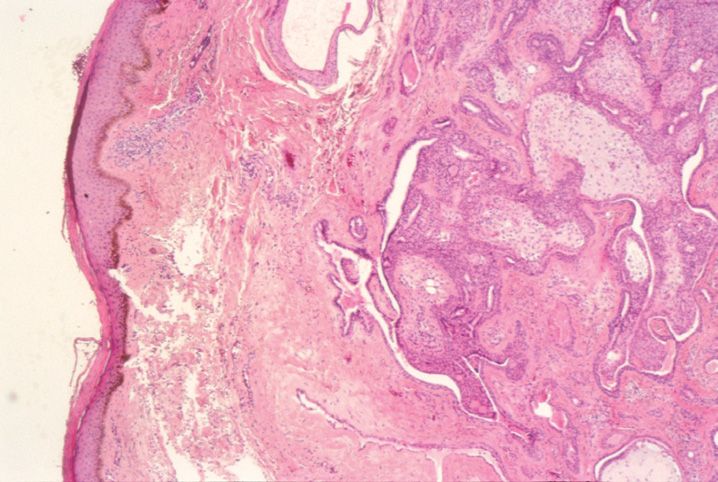
FIGURE 10-1
(A) Erythema multiforme
(B) Lichen planus
(C) Lichen sclerosis
(D) Lupus erythematosus
(E) Mycosis fungoides
15. All of the following histologic features may be seen in the setting of lupus erythematosus involving the skin except
(A) Civatte bodies
(B) Epidermal atrophy
(C) Hyperkeratosis and follicular plugging
(D) Interface dermatitis
(E) Perivascular chronic inflammation
16. All of the following are features typical of dermatomyositis except
(A) Associated with malignancy
(B) Gottron papules
(C) Max-Joseph spaces
(D) Perifascicular muscle atrophy
(E) Violaceous poikiloderma
17. A 26-year-old bone marrow transplant patient presents with erythematous macules on the face and hands about 6 weeks after transplantation.!y A diagnosis of acute graft versus host disease is being entertained. A biopsy shows vacuolar epidermal alterations with necrotic keratinocytes and subepidermal microvesicles. The lesion is best characterized as which grade?
(A) Grade 0
(B) Grade 1
(C) Grade 2
(D) Grade 3
(E) Grade 4
18. Which of the following least likely presents with granulomatous dermatitis?
(A) Granuloma annulare
(B) Leprosy
(C) Necrobiosis lipoidica
(D) Pityriasis lichenoides
(E) Sarcoid
19. A 9-year-old presents with multiple small papules and plaques. On biopsy, palisaded granulomas with increased Alcian blue positive interstitial mucin and eosinophils are seen. The best diagnosis for this entity is which of the following?
(A) Dermatofibroma
(B) Granuloma annulare
(C) Necrobiosis lipoidica
(D) Rheumatoid nodule
(E) Sarcoid
20. Kaposi sarcoma is associated with infection by which of the following human herpes viruses (HHV)?
(A) HHV-1
(B) HHV-2
(C) HHV-6
(D) HHV-8
(E) HHV-12
21. A 46-year-old woman with a history of rheumatoid arthritis presents with tender, nonpruritic erythematous plaques on the head and neck. Biopsy of one of the neck lesions shows a dense neutrophilic infiltrate in the dermis with edema and minimal vascular damage. The most likely diagnosis is which of the following?
(A) Cellulitis
(B) Dermatitis herpetiformis
(C) Polymorphous light eruption
(D) Sweet syndrome
(E) Vasculitis
22. Urticaria can be a manifestation of all of the following exposures except
(A) Basal cell carcinoma
(B) Parasitic infection
(C) Radiocontrast media
(D) Shellfish consumption
(E) Sun exposure
23. Erythema migrans is associated with which of the following conditions?
(A) Lyme disease
(B) Lymphoma
(C) Poxvirus exposure
(D) Rheumatoid arthritis
(E) Syphilis infection
24. All of the following are findings associated with plasmacytosis mucosae except
(A) A monoclonal kappa or lambda population is present
(B) Cells stain with CD138 antibody
(C) Includes Zoon balanitis
(D) There is minimal cytologic atypia
(E) Usually presents as a solitary lesion
25. Morphea on the scalp and trunk are associated with which of the following entities?
(A) Chronic graft versus host disease
(B) Dermatomyositis
(C) Lupus erythematosus
(D) Rheumatoid arthritis
(E) Scleroderma
26. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is typically associated with which of the following conditions
(A) Oncocytomas of the kidney
(B) Polycystic kidney disease
(C) Renal cell carcinoma
(D) Renal transplantation
(E) von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
27. Comedones are associated with which of the following organisms?
(A) No organism is associated with comedones
(B) Propionibacterium acnes
(C) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
(D) Staphylococcus aureus
(E) Staphylococcus epidermidis
28. Eosinophilic folliculitis is associated with which of the following viral infections?
(A) CMV
(B) Hepatitis A
(C) Hepatitis B
(D) HIV
(E) HTLV I
29. Rosacea is marked by central facial erythema that can be exacerbated by all of the following except
(A) Exercise
(B) Hot drinks
(C) Peanuts
(D) Spicy foods
(E) Sunlight
30. All of the following are associated with a neutrophilic lobular panniculitis except
(A) Alpha-1-antitrypsin
(B) Arthropod bite reaction
(C) Infection
(D) Pancreatic fat necrosis
(E) Ruptured folliculitis
31. The most common form of panniculitis is represented by which of the following?
(A) Erythema nodosa
(B) Lipodystrophy
(C) Lupus profundus
(D) Sarcoidosis
(E) Scleroderma
32. All of the following are true regarding lupus profundus except
(A) Alcian blue stain highlights stromal mucin
(B) It is a form of lymphocytic lobular panniculitis
(C) May contain lymphoid follicles
(D) Most cases have a clonal T cell population
(E) Presents as an erythematous tender nodule or plaque
33. Erythema induratum represents a form of lobular panniculitis associated with which of the following?
(A) Leukemia
(B) Polyarteritis nodosa
(C) Rosai–Dorfman disease
(D) Sarcoidosis
(E) Tuberculosis
34. The findings in this biopsy shown in Figure 10-2 are best described as which of the following?
(A) Interface dermatitis
(B) Nodular fasciitis
(C) Panniculitis
(D) Spongiotic dermatitis
(E) Vasculitis
35. Bowenoid papulosis is most commonly associated with which HPV type?
(A) Type 1
(B) Type 2
(C) Type 4
(D) Type 10
(E) Type 16
36. An 8-year-old presents with a centrally umbilicated, pearly papule. The biopsy shown in Figure 10-3 is most consistent with an infection by which of the following organisms?
(A) Cytomegalovirus
(B) Herpes simplex virus type II
(C) Polyoma virus
(D) Poxvirus
(E) Varicella zoster
37. Intracytoplasmic eosinophilic inclusions, known as Guarnieri bodies, are associated with which of the following?
(A) Epstein–Barr versus infection
(B) Milker nodules
(C) Molluscum contagiosum
(D) Polyoma virus infection
(E) Varicella zoster infection
38. A 19-year-old male presents with fever, stomatitis, and oval vesicles with an erythematous rim on the hands and feet. A diagnosis of hand-foot-and-mouth disease is made. The most likely etiology is which of the following organisms?
(A) BK virus
(B) Cowpox
(C) Coxsackie virus
(D) Enterovirus 17
(E) Monkeypox
39. An immunocompromised a 62-year-old male presents with multiple ulcerated lesions. One of the lesions is biopsied and shown in Figure 10-4. The best diagnosis for this lesion is an ulcer due to which of the following?
(A) Blastomycosis
(B) Candida
(C) Chromomycosis
(D) Cryptococcus
(E) Fusarium
40. Ecthyma is caused most commonly by which of the following organisms?
(A) Group A Streptococcus
(B) Group B Streptococcus
(C) Staphylococcus aureus
(D) Staphylococcus epidermidis
(E) Streptococcus pneumoniae
41. A 62-year-old male presents with pruritic reddish-brown patches in the axillae. A diagnosis of erythrasma is being entertained clinically. Which of the following organisms is most likely responsible for the clinical lesions, if this is the correct diagnosis?
(A) Candida albicans
(B) Corynebacterium minutissimum
(C) Group B Streptococcus
(D) Staphylococcus aureus
(E) Streptococcus pyogenes
42. Rickettsialpox skin infection caused by Rickettsia akari is transmitted by the bite of which vector?
(A) Flea
(B) Louse
(C) Mite
(D) Mosquito
(E) Tick
43. All of the following are true regarding lymphogranuloma venereum except
(A) Can be treated with antibiotics
(B) Caused by Calymmatobacterium granulomatis
(C) Initially presents with a painless vesicle, papule or ulcer
(D) May histologically show areas of necrosis
(E) Patients may develop fistulae and strictures
44. The lesion shown in Figure 10-5 was excised from a 42-year-old male who presented with a partially ulcerated nodule on the right arm. A Fite stain shows occasional positive staining organisms. The most likely etiology is which of the following?
(A) Actinomyces
(B) Klebsiella
(C) Mycobacteria
(D) Mycoplasma
(E) Nocardia
45. New cases of this disease (in Question 44) are most likely to be encountered where in the United States?
(A) Alaska
(B) California
(C) Florida
(D) Maine
(E) Texas
46. All of the following are features of lepromatous leprosy except
(A) Can involve peripheral nerves
(B) Cutaneous lesions are often symmetric and poorly demarcated
(C) Frequently involves the trunk or extremities
(D) Associated with an increased incidence of vitiligo
(E) Occurs in patients with a poor immune response
47. Fish tank granuloma is associated with infection by which of the following organisms?
(A) Mycobacterium bovis (M. bovis)
(B) M. haemophilum
(C) M. leprae
(D) M. marinum
(E) M. ulcerans
48. A 62-year-old diabetic woman with poor oral hygiene recently had two teeth pulled. She subsequently develops ulcerated and draining nodules on the face and neck. The most likely diagnosis is which of the following?
(A) Actinomycosis
(B) Botryomycosis
(C) Cat scratch disease
(D) Cryptococcosis
(E) Nocardiosis
49. The lesion shown in Figure 10-6 arises in a 69-year-old male with a history of leukemia and recent bone marrow transplant. M. leprae is cultured and responds to treatment. The pathology best fits with which of the following?
(A) Erythema nodosum leprosum
(B) Histoid leprosy
(C) Lepromatous leprosy
(D) Lucio phenomenon
(E) Tuberculoid leprosy
50. The presence of necrotizing granulomatous inflammation on a skin biopsy in the setting of an infection by Treponema pallidum is characteristic of which of the following?
(A) Condyloma lata
(B) Initial infection with syphilis
(C) Primary syphilis
(D) Secondary syphilis
(E) Tertiary syphilis
51. All of the following dermatophytosis-associated organisms are typically transmitted from human to human (anthropophilic) except
(A) Epidermophyton floccosum
(B) Microsporum gypseum
(C) Trichophyton concentricum
(D) Trichophyton mentagrophytes interdigitale
(E) Trichophyton rubrum
52. The clinical differential diagnosis of tinea pedis includes all of the following lesions except
(A) Allergic contact dermatitis
(B) Candidiasis
(C) Erythema nodosum
(D) Impetigo
(E) Interdigital erythrasma
53. All of the following are true regarding tinea versicolor except
(A) Caused by Malassezia furfur
(B) Cultured on blood agar plate
(C) Epidermis may show hyperkeratosis and acanthosis
(D) Mostly involves upper trunk or arms
(E) Well-demarcated macules and patches
54. All of the following are dematiaceous fungi that may be responsible for causing phaeohyphomycosis infection except
(A) Alternaria
(B) Bipolaris
(C) Cladosporium
(D) Pityrosporum
(E) Wangiella
55. The lesion illustrated in Figure 10-7 is most likely caused by which of the following organisms?
(A) Alternaria
(B) Curvularia
(C) Fonsecaea
(D) Sporothrix
(E) Leishmania
56. A “Mariner’s wheel” type of budding is characteristic of infection by which of the following yeast?
(A) Alterneria
(B) Blastomyces
(C) Coccidioides
(D) Cryptococcus
(E) Paracoccidioides
57. Which of the following clinical conditions are associated with the lesion illustrated in Figure 10-8?
(A) Crohn disease
(B) Diabetes
(C) Emphysema
(D) Hemochromatosis
(E) Renal failure
58. All of the following are true regarding the lesion illustrated in Figure 10-9 except
(A) Acute angle branching hyphae
(B) Fruiting bodies are commonly seen in skin lesions
(C) Granulomatous inflammation
(D) Increased risk in burn victims
(E) Vascular invasion common
59. The sandfly serves as a vector for the transmission of which of the following infections?
(A) Amebiasis
(B) Leishmaniasis
(C) Lobomycosis
(D) Rhinosporidiosis
(E) Schistosomiasis
60. A 27-year-old woman presents with a rosacea-like eruption. Follicular dilation with inflammation is seen on a biopsy. Organisms consistent with Demodex are seen. The organism represents which of the following?
(A) Fly larvae (myiasis)
(B) Fungus
(C) Louse
(D) Mite
(E) Parasite
61. All of the following are true regarding scabies infestation of the skin except
(A) Eosinophil infiltrates
(B) Highly infectious
(C) Necrotizing granulomatous inflammation
(D) Preferentially involves interdigital and flexural areas
(E) Pruritic lesions
62. A 64-year-old male presents with a verrucous, crusted nodule. A biopsy is taken and shown in Figure 10-10. The best diagnosis is which of the following?
(A) Blastomycosis
(B) Coccidioidomycosis
(C) Cryptococcosis
(D) Histoplasmosis
(E) Paracoccidioidomycosis
63. A 19-year-old sustains head trauma during a camping trip. She develops an ulcerated lesion on her right lower leg. The lesion is biopsied and shown in Figure 10-11. The best diagnosis is which of the following?
(A) Cimicosis
(B) Myiasis
(C) Pediculosis
(D) Scabies
(E) Tick bite
64. A 59-year-old female who recently travelled to India presents with white papules and nodules with a central black dot and erythematous halo on the feet. She liked to take long walks on the beaches. The most likely diagnosis is which of the following?
(A) Cimicosis
(B) Pediculosis
(C) Spider bites
(D) Tick bites
(E) Tungiasis
65. A 6-year-old from Central America presents with subcutaneous nodules and a history of black fly bites. The nodules are most likely due to which of the following?
(A) Cysticercosis
(B) Dirofilaria
(C) Onchocerciasis
(D) Protothecosis
(E) Schistosomiasis
66. In entertaining a diagnosis of cutaneous vasculitis, the optimal time for a skin biopsy is how many hours after the appearance of the lesion?
(A) 12 hours
(B) 36 hours
(C) 60 hours
(D) 1 week
(E) None. It cannot be diagnosed on a biopsy
67. All of the following represent small vessel, neutrophilic, immune complex-mediated vasculitides of the skin except
(A) Cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis
(B) Erythema elevatum diutinum
(C) Henoch–Schönlein purpura
(D) Rickettsial infection
(E) Urticarial vasculitis
68. All of the following are likely clinical manifestations of a small vessel vasculitis except
(A) Limb claudication
(B) Purpura
(C) Splinter hemorrhage
(D) Urticaria
(E) Vesiculobullous lesions
69. All of the following are chronic signs of healed lesions associated with cutaneous vasculitis except
(A) Endarteritis obliterans
(B) Intimal proliferation
(C) Intraluminal fibrin thrombi
(D) Neovascularization of vessel adventitia
(E) Onion-skinning or lamination of vessel walls
70. All of the following represent type IV delayed hypersensitivity-mediated vasculitides except
(A) Chronic graft versus host disease
(B) Cryoglobulinemic vasculitis
(C) Dego disease
(D) Giant cell arteritis
(E) Sneddon syndrome
71. The most common immunoreactant found in blood vessels by direct immunofluorescent (DIF) studies in the setting of cutaneous vasculitis is which of the following?
(A) C3
(B) C5
(C) IgA
(D) IgG
(E) IgM
72. Predominant IgM vascular deposits on a skin biopsy are most suggestive of which of the following?
(A) Churg–Strauss syndrome
(B) Cryoglobulinemic vasculitis
(C) Henoch–Schönlein purpura
(D) Lupus erythematosus vasculitis
(E) Wegener granulomatosis (granulomatosis with polyangiitis)
73. A patient with cutaneous vasculitis accompanied by ocular disease most likely has which of the following?
(A) Henoch–Schönlein purpura
(B) Microscopic polyangiitis
(C) Polyarteritis nodosa
(D) Urticarial vasculitis
(E) Wegener granulomatosis (granulomatosis with polyangiitis)
74. A 62-year-old woman with a diagnosis of cutaneous vasculitis has a positive pANCA test. Which of the following diagnoses is least likely?
(A) Churg–Strauss syndrome
(B) Microscopic polyangiitis
(C) Polyarteritis nodosa
(D) Rheumatoid vasculitis
(E) Wegener granulomatosis (granulomatosis with polyangiitis)
75. The most common group of malignancies associated with paraneoplastic vasculitis includes which of the following?
(A) Breast carcinomas
(B) Leukemias
(C) Lung carcinomas
(D) Lymphoproliferative disorders
(E) Melanomas
76. In which of the following conditions is acantholysis due to loss of cell-to- cell contact between keratinocytes the mechanism of blister formation?
(A) Acute allergic contact dermatitis
(B) Bullous pemphigoid
(C) Heat
(D) Pemphigus
(E) Polymorphous light eruption
77. All of the following conditions are associated with corneal or subcorneal blister formation in the skin except
(A) Bullous impetigo
(B) Pemphigus foliaceus
(C) Pemphigus vulgaris
(D) Pustular psoriasis
(E) Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
78. Miliaria in neonates is due to which of the following?
(A) Blockage of apocrine ducts
(B) Blockage of eccrine ducts
(C) Hair follicle plugging
(D) Infection
(E) Overproduction of sebaceous glands
79. Bullous impetigo is associated with a superficial infection by which of the following organisms?
(A) Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus)
(B) S. epidermidis
(C) S. saprophyticus
(D) S. hemolyticus
(E) S. hominis
80. In which of the following conditions is IgG antibody directed against desmoglein I and not desmoglein 3?
(A) Acropustulosis of infancy
(B) Darier disease
(C) Pemphigus foliaceus
(D) Pemphigus vulgaris
(E) Polymorphous light eruption
81. All of the following are true regarding Darier disease except
(A) Biopsy shows acantholysis and dyskeratosis
(B) Can appear as greasy, brown crusted, keratotic papules
(C) Corps ronds may be seen
(D) May involve the oral mucosa
(E) X-linked disorder
82. The biopsy shown in Figure 10-12 is from the axilla of a 49-year-old male with flaccid blisters. DIF studies are negative. Several family members have the same disease. The best diagnosis for this condition is which of the following?
(A) Grover disease
(B) Hailey–Hailey disease
(C) Herpetic dermatitis
(D) IgA pemphigus
(E) Pemphigus foliaceus
83. Cicatricial pemphigoid can be distinguished from epidermolysis bullosa acquisita by which of the following?
(A) Clinical presentation
(B) Direct immunofluorescence
(C) Indirect immunofluorescence
(D) Location of the bullae
(E) Salt split skin test
84. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis may be drug induced. The most common drug that has been associated with this disorder is which of the following?
(A) Corticosteroids
(B) Penicillin
(C) Proprandol
(D) Sulfapyridine
(E) Vancomycin
85. The biopsy shown here in Figure 10-13 is from a 26-year-old male who presented with pruritic grouped papules and vesicles on the elbows, knees, and neck. By DIF, granular IgA deposits are seen in the dermal papillae. Which of the following disorders are associated with this condition?
(A) Crohn disease
(B) Gluten-sensitive enteropathy
(C) Hepatitis C infection
(D) HIV infection
(E) Oral ulcers
86. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita is an immune-mediated bullous disorder associated with autoimmune antibodies to which of the following?
(A) Type I collagen
(B) Type II collagen
(C) Type V collagen
(D) Type VI collagen
(E) Type VII collagen
87. A 28-year-old woman presents with blisters that develop on exposure to sunlight. A biopsy of one of the hand lesions is shown in Figure 10-14. All of the following are true regarding the disorder except
(A) Associated with marked eosinophilic dermal infiltrates
(B) Causes subepidermal blistering
(C) Hyaline deposits around papillary dermal vessels
(D) May see IgG deposits at the dermoepidermal junction
(E) Rigid papillae at the blister base may be seen
88. Localized or pretibial myxedema is associated with which of the following conditions?
(A) Acromegaly
(B) Hypercortisolism
(C) Hyperthyroidism
(D) Hypercortisolism
(E) Hypothyroidism
89. The lesion illustrated in Figure 10-15 from the finger of a 58-year-old male is best diagnosed as which of the following?
(A) Gout
(B) Ochronosis
(C) Pilomatricoma
(D) Pseudogout
(E) Rheumatoid nodule
90. All of the following are risk factors for the development of the condition in Question 89 except
(A) Alcohol
(B) Family history
(C) Gender
(D) Smoking
(E) Thiazide diuretic use
91. All of the following are true regarding the condition illustrated in Figure 10-16 except
(A) Affects elastic fibers in the eye and cardiovascular systems
(B) Autosomal-recessive condition
(C) Findings present at birth
(D) Mutations of the ABCC6 gene
(E) Presents as yellowish papules
92. The presence of numerous café-au-lait macules is associated with which of the following conditions?
(A) Carney complex
(B) Neurofibromatosis type I
(C) Neurofibromatosis type II
(D) Tuberous sclerosis
(E) von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
93. Which of the following drugs is least likely to result in hyperpigmentation of the skin?
(A) Amiodarone
(B) Clofazimine
(C) Corticosteroids
(D) Imipramine
(E) Minocycline
94. All of the following are true regarding vitiligo except
(A) Associated with Graves disease
(B) Decreased melanin pigment
(C) Decreased number of intraepidermal melanocytes
(D) No gender predilection
(E) Present at birth
95. Hypopigmented macules known as ash-leaf spots are associated with which of the following conditions?
(A) Carney complex
(B) Neurofibromatosis type I
(C) Neurofibromatosis type II
(D) Tuberous sclerosis
(E) von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
96. All of the following conditions are nonscarring forms of alopecia except
(A) Alopecia areata
(B) Androgenetic alopecia
(C) Lupus erythematosus
(D) Senescent baldness
(E) Trichotillomania
97. Approximately what percent of hair are in the telogen or resting phase?
(A) 10%
(B) 25%
(C) 50%
(D) 75%
(E) 90%
98. A 46-year-old male presents with a balding patch marked by follicular hyperkeratosis. A biopsy is taken and shown in Figure 10-17. The best diagnosis is which of the following?
(A) Lichen planopilaris
(B) Loose anagen hair syndrome
(C) Pressure-induced alopecia
(D) Traction alopecia
(E) Trichotillomania
99. Which of the following cysts is the most common of all cutaneous cysts?
(A) Dermoid cyst
(B) Follicular cyst of infundibular type
(C) Sebaceous duct cyst
(D) Trichilemmal cyst
(E) Verrucous cyst
100. Which of the following cysts is associated with Gardner syndrome and Gorlin syndrome?
(A) Epidermoid cyst
(B) Infundibular cyst
(C) Milium
(D) Pilar cyst
(E) Steatocystoma
101. All of the following are true regarding the cutaneous cyst shown here in Figure 10-18 except
(A) Cysts have a granular layer
(B) Located in the dermis
(C) May have a autosomal-dominant inheritance pattern
(D) Most commonly affects the trunk
(E) Often presents as multiple cysts
102. The most common location for dermoid cysts of the skin is which of the following?
(A) Chest
(B) Lower back
(C) Nose
(D) Periorbital region
(E) Scalp
103. The lesion illustrated here in Figure 10-19 arose on the back of a 64-year-old male. It is best diagnosed as which of the following?
(A) Actinic keratosis
(B) Epidermal nevus
(C) Seborrheic keratosis
(D) Squamous cell carcinoma
(E) Verruca vulgaris
104. All of the following may arise in the background of a seborrheic keratosis except
(A) Basal cell carcinoma
(B) Bowen disease
(C) Melanoma
(D) Nevus
(E) Pilomatricoma
105. The lesion illustrated here in Figure 10-20 in this 69-year-old male is best classified as which of the following?
(A) Actinic keratosis
(B) Benign keratosis
(C) Lentigo maligna
(D) Seborrheic keratosis
(E) Squamous cell carcinoma in situ
106. Which of the following is not a risk factor for the development of invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the skin?
(A) Arsenic
(B) Impetigo
(C) Organ transplantation
(D) Ultraviolet radiation
(E) Xeroderma pigmentosum
107. All of the following are unfavorable pathologic parameters in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma except
(A) Degree of stromal inflammatory response
(B) Depth >4 mm invasion
(C) Lymphovascular invasion
(D) Poor differentiation
(E) Width >2 cm
108. Which of the following immunomarkers is least likely to be positive in squamous cell carcinoma?
(A) 34βE12
(B) CAM 5.2
(C) Cytokeratins 5/6
(D) EMA
(E) p63
109. A 76-year-old male presents with a rapidly growing nodule with rolled borders and a central keratin plug on the right arm. The lesion is excised and shown here in Figure 10-21. The best diagnosis for the lesion is which of the following?
(A) Bowen disease
(B) Keratoacanthoma
(C) Seborrheic keratosis
(D) Squamous cell carcinoma
(E) Verruca vulgaris
110. The lesion in Question 109 is associated with which of the following conditions?
(A) Cowden disease
(B) Epidermal nevus syndrome
(C) Gorlin syndrome
(D) Muir–Torre syndrome
(E) Tuberous sclerosis
111. All of the following features are consistent with a desmoplastic trichoepithelioma (Figure 10-22) versus a sclerosing basal cell carcinoma except
(A) Keratin cyst formation
(B) Minimal cytologic atypia
(C) Minimal mitotic activity
(D) More apoptotic bodies
(E) Papillary mesenchymal bodies present
112. Which of the following skin lesions is associated with Cowden syndrome?
(A) Basal cell carcinoma
(B) Pilomatricoma
(C) Syringoma
(D) Trichoblastoma
(E) Trichilemmoma
113. All of the following are true regarding the lesion shown in Figure 10-23 except
(A) Calcifications are commonly found
(B) Familial occurrence associated with myasthenia gravis
(C) Majority arise in the first 2 decades of life
(D) Stains positively with beta-catenin
(E) Usually presents as multifocal lesions
114. Which of the following markers will generally stain basal cell carcinoma and not adenoid cystic carcinoma?
(A) Ber-EP4
(B) CAM 5.2
(C) Cytokeratin 7
(D) EMA
(E) S-100 protein
115. The lesion shown in Figure 10-24 is most likely to be located where on the body?
(A) Arms
(B) Face
(C) Inguinal region
(D) Toes
(E) Trunk
116. The lesion illustrated in Figure 10-25 was excised from the neck of a 62-year-old male. The best diagnosis is which of the following?
(A) Benign mixed tumor
(B) Cylindroma
(C) Microcystic adnexal carcinoma
(D) Poroma
(E) Spiradenoma
117. The lesion shown in Figure 10-26 presented in a 76-year-old male in the scrotal area. The lesion demonstrates positive staining with CAM 5.2 and is negative for S-100 protein. The best diagnosis for this lesion is which of the following?
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree