Cytomegalovirus
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
One of the most common opportunistic infections in AIDS and organ transplant patients
Diagnosis of CMV pneumonia is based on evaluation of lung biopsy or bronchoalveolar lavage specimens
Disseminated CMV infection can cause pneumonitis, hepatitis, adrenalitis, encephalitis, leukopenia, and other systemic manifestations
Microscopic Pathology
Cytopathic effects of CMV involve both nucleus and cytoplasm of infected cells and lead to cytomegaly
Can infect a large variety of cell types in lung, including pneumocytes, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages
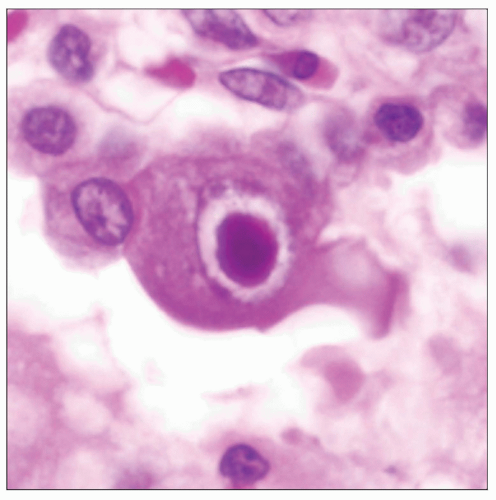
Intranuclear inclusions in CMV are larger than cytoplasmic inclusions and may measure up to 20 µm in diameter
Nuclear inclusions are usually basophilic, round to oval, and show a peripheral halo with accentuation of nuclear membrane
Cytoplasmic inclusions are basophilic to eosinophilic and smaller than intranuclear inclusions (1-3 µm in diameter)
Ancillary Tests
Anti-CMV antibodies by immunoperoxidase technique are sensitive and specific for the organisms
DNA in situ hybridization for CMV is another sensitive and reliable method for identification of the organisms
 Histologic appearance of CMV pneumonitis in an immunosuppressed patient shows interstitial inflammation with a few alveolar lining cells containing the characteristic viral intranuclear inclusions. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Definitions
Infection of the lung caused by cytomegalovirus
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
CMV is a double-stranded DNA herpesvirus with an icosahedral capsid that contains 120 capsomeres
Measures 120 to 200 nm and has an envelope derived from the nuclear membrane
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
One of the most common opportunistic infections in AIDS and organ transplant patients
Age
Seen in congenital, perinatal, childhood and adult age groups
Presentation
CMV pneumonitis causes fever, nonproductive cough, and shortness of breath with hypoxemia
Diagnosis of CMV pneumonia is based on evaluation of lung biopsy or bronchoalveolar lavage specimens
Presence of CMV in blood, urine, or sputum is not evidence of CMV pneumonia; tissue confirmation is required for diagnosis
Serologic demonstration of CMV infection is not sufficient for diagnosis of CMV pneumonia; tissue confirmation is required
Natural History
Primary infection can occur in utero or shortly after birth and is generally asymptomatic, leading to latent status
Immune deficiency or immunosuppression causes CMV to reactivate and disseminate
Reactivation may lead to minimal disease or be symptomatic to fulminant depending on degree of immunodeficiency
CMV can cause a variety of infections that affect multiple organs, including liver, lung, CNS, lymph nodes, etc.
Disseminated CMV infection can cause pneumonitis, hepatitis, adrenalitis, encephalitis, leukopenia, and other systemic manifestations
Treatment
Drugs
Ganciclovir, foscarnet, and intravenous immunoglobulin
Prognosis
CMV pneumonia can be fatal in immunosuppressed patients
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree