Cystadenocarcinoma (Papillary)
Lester D. R. Thompson, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Malignant epithelial salivary gland neoplasm characterized by predominantly cystic growth with intraluminal papillae
Clinical Issues
Slowly growing, painless swelling or compressible mass
Usually a tumor of older age (6th decade)
Parotid is most commonly affected (˜ 70%)
Complete surgical excision
Excellent overall prognosis (indolent, low grade)
Microscopic Pathology
Partially circumscribed and encapsulated
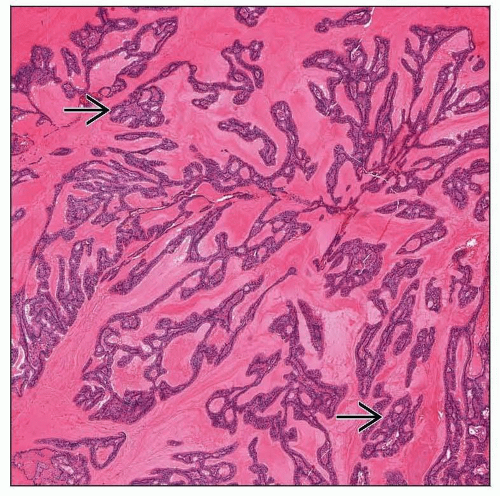
Prominent cystic appearance
Haphazard cysts, sometimes filled with mucin
Cysts may be back to back or show limited fibrous connective tissue stroma
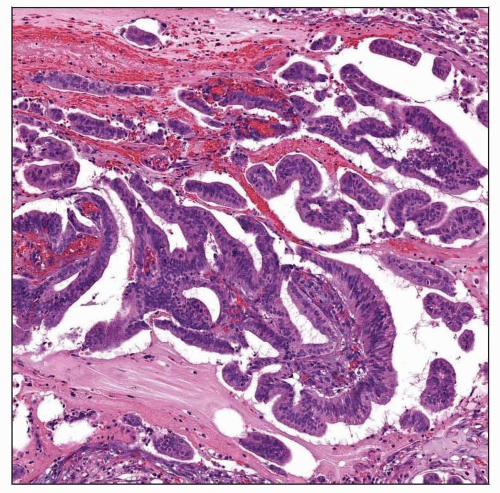
Papillary growth is almost always present
Papillae vary from single simple projections with delicate fibrovascular cores to complex, arborizing structures filling the lumen
Cysts and papillae lined by small and large cuboidal to columnar cells
Cells are cytologically bland
Mitotic figures are uncommon
Tumor-associated lymphoid proliferation (TALP) is frequently present
Top Differential Diagnoses
Cystadenoma, acinic cell carcinoma (papillary-cystic variant), mucoepidermoid carcinoma, salivary duct carcinoma, polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Low-grade papillary adenocarcinoma
Definitions
Malignant epithelial salivary gland neoplasm characterized by predominantly cystic growth with intraluminal papillae
Malignant counterpart of cystadenoma
Lacks specific histopathologic features of other salivary carcinomas with cystic growth
A few cases are not papillary
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare (< 1%)
Age
Wide range at presentation (20-86 years)
Mean: 6th decade
˜ 75% of patients are > 50 years old
Gender
Equal gender distribution
Site
Parotid is most commonly affected (˜ 70%)
Minor salivary glands (˜ 25%)
Order of frequency: Buccal mucosa, lips, palate, floor of mouth, tongue, retromolar region
Presentation
Slowly growing, painless swelling or mass
Tumors may be compressible
Palate tumors may erode bone and extend into nasal cavity/paranasal sinuses
Symptoms present for long duration (mean: 4 years)
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete surgical excision
Wide excision for minor salivary glands
Prognosis
Excellent overall prognosis (indolent, low grade)
Approaching 100% 5-year survival
Recurrences are uncommon (˜ 10%)
Develop up to 10 years after primary
Lymph node metastases are uncommon (˜ 10%)
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES