Cutaneous Rhabdomyosarcoma
Khin Thway, BSc, MBBS, FRCPath
Key Facts
Terminology
Malignant soft tissue tumor that shows variable differentiation toward skeletal muscle
3 main subtypes
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (ARMS)
Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS)
Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma
Clinical Issues
Rare at cutaneous sites
May be primary or secondary
ERMS: Most common subtype; most in children < 10 years
ARMS: Adolescents and younger adults; highly aggressive tumor
Pleomorphic RMS: Older adults; aggressive tumor
Microscopic Pathology
ERMS
Sheets and loose fascicles of spindle and ovoid cells
Complex karyotypes by cytogenetics
ARMS
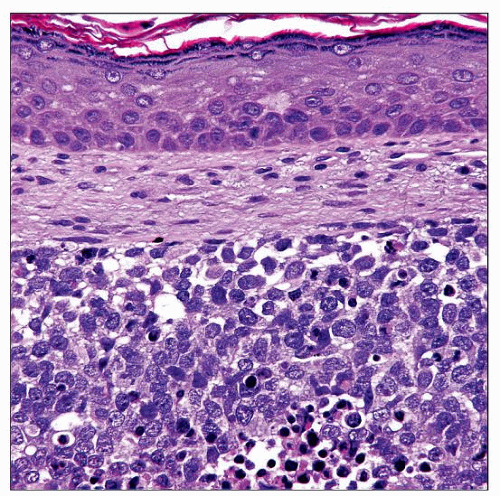
Sheets of small and medium-sized round cells; central dyscohesion resembling pulmonary alveoli
Characteristic PAX-FOXO1 gene fusions in most
Pleomorphic RMS
Malignant fibrous histiocytoma/pleomorphic sarcoma-like morphology with marked anaplasia
All RMS can have rhabdomyoblasts in variable numbers and stages of differentiation
Most frequently seen in ERMS
All RMS express desmin and at least focal myogenin
Expression usually most widespread in ARMS
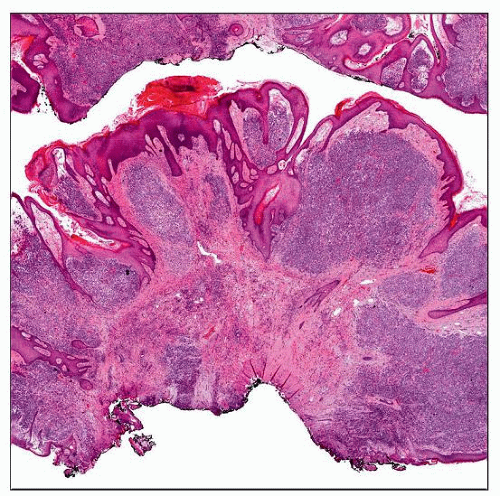 This cutaneous RMS from the ear is a polypoidal tumor with extensive infiltration of the dermis by hypercellular sheets of fairly uniform, small, hyperchromatic, ovoid cells. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS)
Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS)
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (ARMS)
Definitions
Malignant tumor showing variable differentiation toward skeletal muscle
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Unknown
Cell of origin still unknown
Possible candidate cells include muscle stem cells and multipotent mesenchymal stem cells
Often occurs in sites lacking skeletal muscle
May occur in association with inherited syndromes
e.g., Beckwith-Wiedemann
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rhabdomyosarcomas are most frequent soft tissue sarcomas in children and young adults
Occurrence in skin is rare
May occur as metastasis from primary site
May very rarely occur as primary cutaneous lesion
ARMS, ERMS, and pleomorphic RMS may all occur as primary neoplasms in the skin
ERMS is most common RMS subtype
Represents 60-70% of RMS
Alveolar RMS
Approximately 30% of RMS
Pleomorphic RMS
Rarer amongst pleomorphic sarcomas
Age
RMS occurs most often in children and young adults
Cutaneous RMS occurs mostly in children (including congenitally and in infants) and young people
However, can occur in all age groups
ERMS generally affects youngest population
Typically < 10 years
ARMS
Adolescents and young adults
Pleomorphic RMS
Older adults
Spindle cell RMS
Rare variant in children and adolescents; rarely adults
Gender
M = F
Site
May occur at any cutaneous site
Including head and neck, trunk, extremities
Small numbers arise as heterologous elements of other skin tumors
e.g., within congenital melanocytic nevi
e.g., in Merkel cell carcinoma
Embryonal RMS
Most common soft tissue sites include head and neck, pelvis (including genitourinary region), and bile duct
Trunk and limbs less frequently involved than in ARMS
Alveolar RMS
Extremities, trunk, head and neck
Spindle cell RMS
Paratesticular region, head and neck
Pleomorphic RMS
Extremities
Presentation