Cutaneous Keratocyst
David Cassarino, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
NBCCS cutaneous cyst/Gorlin-Goltz syndrome
Rare cutaneous cyst showing features identical to oral keratocysts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Most cases are associated with NBCCS
Rare cases not associated with NBCCS also reported
Microscopic Pathology
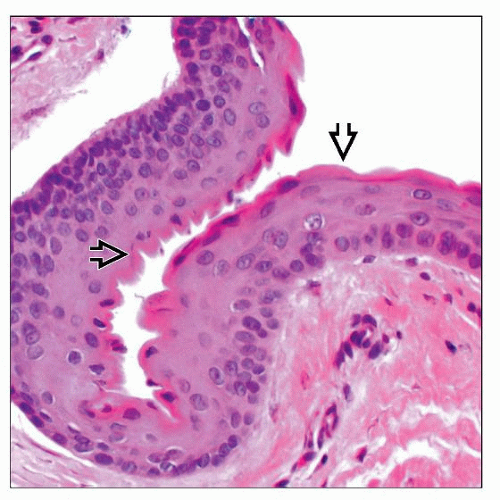
Dermal-based cystic proliferation lined by 2-5 cell layers of bland squamous cells
Typically shows corrugated eosinophilic lining (cuticle) on luminal surface
No evidence of follicular or sebaceous differentiation (unlike steatocystoma)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Steatocystoma, epidermoid (epidermal inclusion) cyst
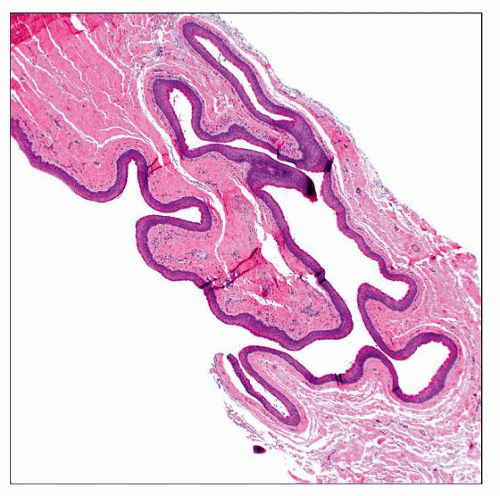 Scanning magnification view of a cutaneous keratocyst shows an undulating squamous epithelium lining the irregularly shaped cystic spaces. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS)/Gorlin-Goltz syndrome-associated cutaneous cyst
Definitions
Rare cutaneous cyst showing features identical to oral keratocysts, often associated with NBCCS
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Genetic
Most cases are associated with NBCCS (Gorlin-Goltz syndrome: Multiple cutaneous basal cell carcinomas, odontogenic keratocysts of the jaw, palmar and plantar pits, rare medulloblastomas, and skeletal abnormalities)
Mutations for NBCCS in PTCH1 gene on chromosome 9q22.3-q31, which encodes a receptor for the Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway
Rare cases not associated with NBCCS also reported
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree