Cutaneous Gamma-Delta T-cell Lymphoma
Aaron Auerbach, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
T-cell lymphoma of mature γδ cells
Separately classified from SPTCL in WHO (2008)
Clinical Issues
Hemophagocytic syndrome in 45%
Poor prognosis
Treated with multiagent chemotherapy
Macroscopic Features
Skin nodules with ulceration
Microscopic Pathology
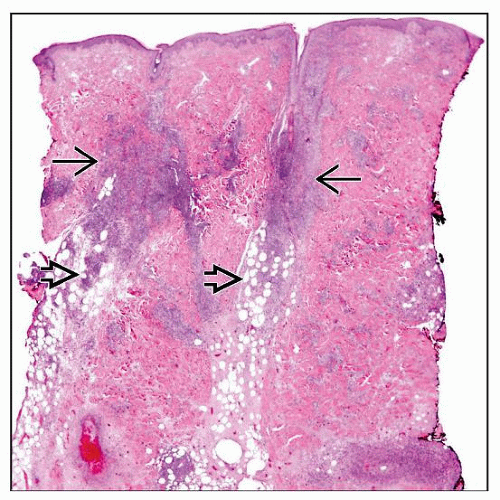
3 patterns of disease: Epidermotropic, dermal, and subcutaneous
Malignant T cells rim around adipocytes
Prominent karyorrhexis/apoptosis and angioinvasion
Ancillary Tests
Immunohistochemistry: TCRδ1(+), βF1(−), CD56(+), CD4(−), CD8(−), EBER(−), cytotoxic markers (+)
T-cell receptor gene rearrangement
Top Differential Diagnoses
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma
Panniculitis, but not in dermis or epidermis; lacks ulceration; TCRδ1(−), βF1(+)
Much better prognosis than CGDTCL
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified
Lupus profundus panniculitis
Similar inflammation in the subcutis in panniculitic pattern
Lobular panniculitis, but contains plasma cells and germinal centers, unlike CGDTCL
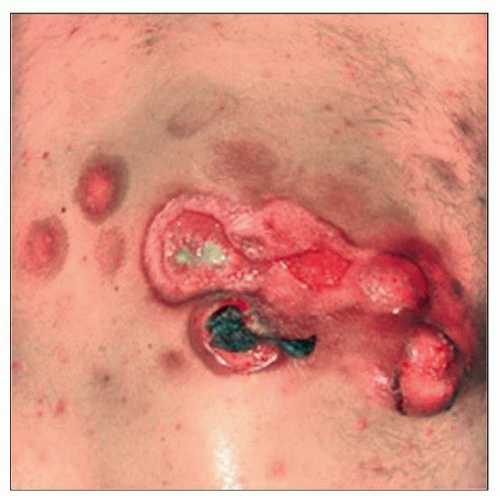 Cutaneous γδ T-cell lymphoma shows a large raised lesion with ulcer and satellite lesions. (Courtesy C. Sander, MD.) |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Cutaneous gamma-delta T-cell lymphoma (CGDTCL)
Synonyms
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma with γδ cells
Definitions
T-cell lymphoma arising in the skin, which is composed of cytotoxic γδ T cells
Does not include subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma composed of αβ cells
May encompass mucocutaneous γδ cell T-cell lymphoma, but further study is needed
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Immunosuppression or Dysregulation of T Cells
Found in many of the patients
Chronic Antigenic Stimulation
Speculative, but possibly involved in pathogenesis
Cell of Origin
γδ T cells
Involved with mucosal and epithelial immune system function
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare tumor, < 100 cases reported in literature
< 1% of all cutaneous T-cell lymphomas
Age
Commonly adults
Gender
No gender preponderance
Site
Mostly extremities
Sometimes mucosal sites, where normal γδ T cells are found
Metastasis common
Spread to lungs, liver, kidneys, oral mucosa, and brain
Usually not in bone marrow, lymph node, or spleen
Presentation
1 or multiple skin lesions
Patches or plaques due to epidermal infiltrates
Tumors or nodules due to dermal infiltrates
± ulcerated epidermis
Hemophagocytic syndrome (HPS) may be present in 45% of cases
More often in subcutaneous lesions
Related to release of cytotoxic molecules
Laboratory Tests
Cytopenias
↑ liver function tests
Treatment
Adjuvant therapy
Multiagent chemotherapy ± radiotherapy
Poor response to allogenic stem cell transplant
Prognosis
Poor prognosis
5-year survival: ˜ 11%
Subcutaneous disease is a poor prognostic indicator
Better prognosis if only disease in dermis or epidermis
HPS is a poor prognostic indicator
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
3 patterns of disease
Epidermotropic
Ranges from mild to marked
Can mimic mycosis fungoides or pagetoid reticulosis
Dermal
More dermal and epidermal involvement typically present than in subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma
Subcutaneous
Lobules mostly involved
Septae less frequently involved and represents secondary spilling of T cells from lobules
Subcutis involvement can appear identical to subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma of αβ cells, including rimming of fat cells
Often more than 1 pattern of disease in a patient
Different patterns of disease in a single biopsy or in different biopsies
Malignant T cells with nuclear atypia, hyperchromasia
Frequent necrosis/apoptosis and vascular invasion
Necrosis may be caused by released cytotoxic molecules
↑ reactive histiocytes
Vacuolated foamy cytoplasm from imbibed material/lipid
With erythrophagocytosis or cytophagocytosis
Cytologic Features
Medium to large T cells with coarse, hyperchromatic-staining chromatin, sometimes vesicular nuclei, and variably prominent nucleoli
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunohistochemistry
T-cell antigens (CD2, CD3, CD5, CD7) positive
May lose 1 or more T-cell antigens
Most cases: CD4(−)/CD8(−)
Few cases: CD4(−)/CD8(+)
TCRδ1(+), βF1(−)
If TCRδ1 antibody is unavailable, βF1 can be used instead
Negative βF1 may serve to assume γδ cell origin
CD56 usually positive, unlike subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree