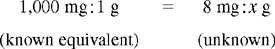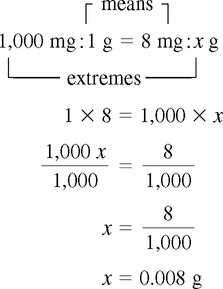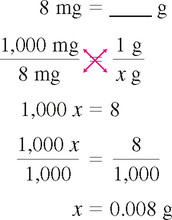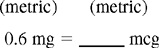CHAPTER 8 After reviewing this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Convert a unit of measure to its equivalent within the same system 2. Convert approximate equivalents among the metric, apothecary, and household systems of measure Moving the decimal point is discussed in Chapter 6. Because the metric system is based on the decimal system, conversions within the metric system can be done easily by moving the decimal point. This method cannot be applied in the apothecary or household system because decimal points are not used in either system. Remember the two rules in moving decimal points: Using ratio and proportion is one of the easiest ways to make conversions, whether within the same system or between systems. The basics on how to state ratios and proportions and how to solve them when looking for one unknown are presented in Chapter 4. To make conversions using ratio and proportion, a proportion must be set up that expresses a numerical relationship between the two systems. A proportion may be written in colon format or as a fraction when making conversions. Regardless of the format used, there are some basic rules to follow when using this method. 1. Note that conversion is going from smaller to larger; thus division or moving the decimal point to the left is indicated. 2. Note that the unit is going from milligrams to grams, thus changing by a factor of 1,000. 3. The decimal point will be moved three places to the left to complete this conversion: 8 mg = 0.008 g. Dimensional analysis is a conversion method that has been used in chemistry and other sciences and will be discussed in more detail in Chapter 16. Dimensional analysis involves manipulation of units to get the desired unit. This method can be used for conversion in all systems. As with other methods discussed, you must know the conversion factor (equivalent). 1. Identify the unit you are converting to. 2. Write the conversion factor so that the desired unit is in the denominator, and write the unit in the successive numerator to match the previous unit of measure in the previous denominator. 3. Cancel the alternate denominator/numerator units to leave the unit desired (being calculated).
Converting Within and Between Systems
METHODS OF CONVERTING
Moving the Decimal Point
Using Ratio and Proportion
Example:
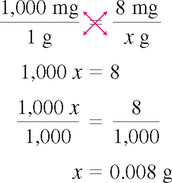
CONVERTING WITHIN THE SAME SYSTEM
DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Converting Within and Between Systems

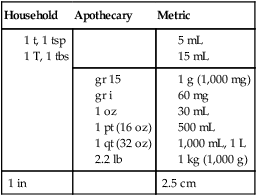
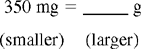
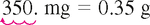
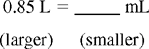
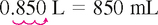
 Practice Problems
Practice Problems