1–4 cups
1–2.5 cups
3–10 servings
2–3 cups
2–7 ounce-equivalents
Well-moistened fish. Eggs.
Soft or mashed beans.
Meat, fish, or egg salads without celery/onion chunks
Hot dogs, bacon. Meats with thick hard breading. Dry or tough meats. Dry fish or fish with bones. Crunchy peanut butter.
Tough legumes.
Use sparingly
Table 3.2 Mechanical Soft
Suggested Menu Plan for Mechanical Soft Diet
| Breakfast |
| ½ c. orange juice 1 egg ½ c. oatmeal 1 slice whole wheat toast 1 tsp. jelly 1 tsp. soft margarine 1 c. fat-free milk Hot beverage Sugar, pepper (optional) |
| Lunch |
| 2 oz. roasted chicken, ground ½ c. mashed potatoes with gravy ½ c. mixed vegetables, tender 1 oz. wheat roll 1 tsp. soft margarine 1 c. fat-free milk Water |
| Supper |
| 2 oz. tuna on 2 slices whole wheat bread, 2 tsp mayonnaise ½ c. tomatoes, chopped 1 c. leafy greens, shredded 1 Tbsp. salad dressing ½ c. fruit cocktail 1 c. fat-free milk Water |
| Snack Ideas |
| ½ c. cantaloupe, soft, bite size pieces ½ c. vegetable juice 3 graham squares |
PUREED DIET
Use
The Pureed Diet is designed for residents with severe chewing difficulties. This diet is appropriate for residents with poor dentition or general debility or weakness.
Adequacy
The suggested food plan includes foods in amounts that will provide the DRIs recommended by the National Academy of Sciences for the adult, if the patient consumes the proper amount and variety.
Diet Principles
1. The Pureed Diet is designed to permit easy swallowing and requires minimal or no chewing.
2. The General Diet or other appropriate diet is modified in consistency by pureeing or modifying foods to a smooth consistency.
3. To improve appearance and appetite appeal, foods may be slurried (moistening foods and retaining their shape).
4. Individuals vary in their abilities to handle different puree consistencies. Thickeners or thinning liquids are useful in adapting pureed foods to individual needs.
5. It is most important to individualize or adjust it to the tolerance of the resident.
Table 3.3 Pureed Diet
| Food for the Day | ||
| Food Category | Recommended | Avoid |
| Vegetables 1–4 cups | Pureed vegetables. Vegetable juices. | All raw vegetables. All vegetables that are not pureed. |
| Fruits 1–2.5 cups | Pureed fruits. Fruit juice and nectars. Raw, ripe banana—mashed | Dried fruits. Coconut. Raw fruit except bananas. |
| Grains 3–10 ounce-equivalents | Pureed or slurried breads, rolls, muffins. Plain crackers, if crushed. Cracker or bread crumbs. Cooked cereals. Milk toast. Pureed pastas and rice. | Any with seeds, nuts, dried fruits, coconut. Popcorn. Wild rice. |
| Milk Products 2–3 cups | Fat-free or low-fat milk, fat-free or low-fat, nondairy milks (soy, almond, rice), low-fat yogurt and cottage cheese, low-fat or part-skim cheeses. | Any with nuts, seeds, pieces of fruit |
| Protein Foods 2–3 servings (total 2–7 ounce-equivalents) | Pureed meats, scrambled eggs. Hummus or pureed lentils/legumes. Moistened tofu. | Meat, fish, poultry, legumes or lentils that are not pureed. |
| Oils, Solid Fats, Added Sugars Use sparingly | Most fats present no problem, for example butter, margarine, oils, mayonnaise. Plain puddings, custards, cheese cake, plain ice cream, sherbet, yogurt, gelatin. Plain cakes and cookies soaked in milk or juice. | Any with nuts, olives, coconut, bacon or other coarse or chunky pieces. Pastries, pies; any with nuts, coconut, raisins. |
| Fluids | All | No restrictions. Need to evaluate any with lumps, chunks, or seeds. |
Table 3.4 Pureed Diet
Suggested Menu Plan for Pureed Diet
| Breakfast |
| ½ c. orange juice 1 egg, scrambled ½ c. oatmeal 1 serving bread crumbs pureed in egg 1 tsp. jelly 1 tsp. soft margarine 1 c. fat-free milk Hot beverage Sugar, pepper (optional) |
| Lunch |
| 2 oz. roasted chicken, pureed ½ c. mashed potatoes with gravy 1 serving mixed vegetables, pureed 1 serving bread crumbs pureed in meat 1 tsp. soft margarine 1 c. fat-free milk Water |
| Supper |
| 2 oz. tuna, 2 slices wheat bread and 2 tsp mayonnaise, pureed 2 slices tomato, 1 cup leafy green salad and 1 Tbsp. salad dressing, pureed ½ c. fruit cocktail, pureed 1 c. fat-free milk Water |
| Snack Ideas |
| ½ c. cantaloupe, pureed ½ c. vegetable juice 1 muffin, soaked |
NATIONAL DYSPHAGIA DIETS*
LEVEL 1: DYSPHAGIA PUREED DIET
Description
This diet consists of pureed, homogenous, and cohesive foods. Food should be “pudding-like.” No coarse textures, raw fruits or vegetables, nuts, and so forth are allowed. Any foods that require bolus formation, controlled manipulation, or mastication are excluded.
Rationale
This diet is designed for people who have moderate to severe dysphagia, with poor oral phase abilities and reduced ability to protect their airway. Close or complete supervision and alternate feeding methods may be required.
Table 3.5 Liquid Consistency

Food Textures for NDD Level 1: Dysphagia Pureed
Table 3.6 Dysphagia Pureed
| Food Groups | Recommended | Avoid |
| Beverages | Any smooth, homogenous beverages without lumps, chunks, or pulp. Beverages may need to be thickened to appropriate consistency. If thin liquids allowed, also may have: Milk, juices, coffee, tea, sodas, carbonated beverages, alcoholic beverages, nutritional supplements. Ice chips. | Any beverages with lumps, chunks, seeds, pulp, etc. |
| Breads | Commercially or facility-prepared pureed bread mixes, pregelled slurried breads, pancakes, sweet rolls, Danish pastries, French toast, etc., that are gelled through entire thickness of product. | All other breads, rolls, crackers, biscuits, pancakes, waffles, French toast, muffins, etc. |
| Cereals Cereals may have just enough milk to moisten. | Smooth, homogenous, cooked cereals such as farina-type cereals. Cereals should have a “pudding-like” consistency. If thin liquids allowed, also may have: Enough milk or cream with cereals to moisten; they should be blended in well. | All dry cereals and any cooked cereals with lumps, seeds, chunks. Oatmeal. |
| Desserts | Smooth puddings, custards, yogurt, pureed desserts and soufflés. If thin liquids allowed, also may have: Frozen malts, yogurt, milk shakes, eggnog, nutritional supplements, ice cream, sherbet, plain regular or sugar-free gelatin. | Ices, gelatins, frozen juice bars, cookies, cakes, pies, pastry, coarse or textured puddings, bread and rice pudding, fruited yogurt. These foods are considered thin liquids and should be avoided if thin liquids are restricted: Frozen malts, milk shakes, frozen yogurt, eggnog, nutritional supplements, ice cream, sherbet, regular or sugar-free gelatin, or any foods that become thin liquid at either room (70°F) or body temperature (98°F). |
| Fats | Butter, margarine, strained gravy, sour cream, mayonnaise, cream cheese, whipped topping. Smooth sauces such as white sauce, cheese sauce or hollandaise sauce. | All fats with coarse or chunky additives. |
| Fruits | Pureed fruits or well-mashed fresh bananas. Fruit juices without pulp, seeds, or chunks (may need to be thickened to appropriate consistency if thin liquids are restricted). If thin liquids allowed, also may have: Unthickened fruit juices. | Whole fruits (fresh, frozen, canned, dried). |
| Meats and Meat Substitutes | Pureed meats. Braunschweiger. Soufflés that are smooth and homogenous. Softened tofu mixed with moisture. Hummus or other pureed legume spread. | Whole or ground meats, fish, or poultry. Nonpureed lentils or legumes. Cheese, cottage cheese. Peanut butter, unless pureed into foods correctly. Nonpureed fried, scrambled, or hard-cooked eggs. |
| Potatoes and Starches | Mashed potatoes or sauce, pureed potatoes with gravy, butter, margarine, or sour cream. Well-cooked pasta, noodles, bread dressing, or rice that have been pureed in a blender to smooth, homogenous consistency. | All other potatoes, rice, noodles. Plain mashed potatoes, cooked grains. Nonpureed bread dressing. |
| Soups | Soups that have been pureed in a blender or strained. May need to be thickened to appropriate viscosity. If thin liquids allowed, also may have: Broth and other thin, strained soups. | Soups that have chunks, lumps, etc. |
| Vegetables | Pureed vegetables without chunks, lumps, pulp, or seeds. Tomato paste or sauce without seeds. Tomato or vegetable juice (may need to be thickened to appropriate consistency if juice is thinner than prescribed liquid consistency). If thin liquids allowed, also may have: Thin tomato or vegetable juices. | All other vegetables that have not been pureed. Tomato sauce with seeds, thin tomato juice. |
| Miscellaneous | Sugar, artificial sweetener, salt, finely ground pepper, and spices. Ketchup, mustard, BBQ sauce and other smooth sauces. Honey, smooth jellies. Very soft, smooth candy such as truffles. If thin liquids allowed, also may have: Smooth chocolate candy with no nuts, sprinkles, etc. | Coarsely ground pepper and herbs. Chunky fruit preserves and seedy jams. Seeds, nuts, sticky foods. Chewy candies such as caramels or licorice. |
LEVEL 2: DYSPHAGIA MECHANICALLY ALTERED CHARACTERISTICS
Description
This level consists of foods that are moist, soft-textured, and easily formed into a bolus. Meats are ground or are minced no larger than ¼-inch pieces; they are still moist, with some cohesion. All foods from NDD Level 1 are acceptable at this level.
Rationale
This diet is a transition from the pureed textures to more solid textures. Chewing ability is required. The textures on this level are appropriate for individuals with mild to moderate oral or pharyngeal dysphagia. Patients should be assessed for tolerance to mixed textures. It is expected that some mixed textures are tolerated on this diet.
Table 3.5 Liquid Consistency

Food Textures for NDD Level 2: Dysphagia Mechanically Altered
(Includes all foods on NDD Level 1: Dysphagia Pureed in addition to the foods listed here.)
Table 3.7 Dysphagia Mechanically Altered
| Food Groups | Recommended | Avoid |
| Beverages | All beverages with minimal amounts of texture, pulp, etc. (Any texture should be suspended in the liquid and should not precipitate out.) (May need to be thickened, depending on liquid consistency recommended.) If thin liquids allowed, also may have: Milk, juices, coffee, tea, sodas, carbonated beverages, alcoholic beverages if allowed, nutritional supplements. Ice chips. | |
| Breads | Soft pancakes, well moistened with syrup or sauce. Pureed bread mixes, pregelled or slurried breads that are gelled through entire thickness. | All others |
| Cereals Cereals may have ¼ cup milk or just enough milk to moisten if thin liquids are restricted. The moisture should be well-blended into food. | Cooked cereals with little texture, including oatmeal. Slightly moistened dry cereals with little texture such as corn flakes, Rice Krispies®, Wheaties®, etc. Unprocessed what bran stirred into cereals for bulk. Note: if thin liquids are restricted, it is important that all of the liquid is absorbed into the cereal. If thin liquids allowed, also may have: Milk or cream for cereals. | Very coarse cooked cereals that may contain flax seed or other seeds or nuts. Whole-grain dry or coarse cereals. Cereals with nuts, seeds, dried fruit and/or coconut. |
| Desserts | Pudding, custard. Soft fruit pies with bottom crust only. Crisps and cobblers without seeds or nuts and with soft breading or crumb mixture. Canned fruit (excluding pineapple). Soft, moist cakes with icing or “slurried” cakes. Pregelled cookies or soft, moist cookies that have been “dunked” in milk, coffee, or other liquid. If thin liquids allowed, also may have: Ice cream, sherbet, malts, nutritional supplements, frozen yogurt, and other ices. Plain gelatin or gelatin with canned fruit, excluding pineapple. | Dry, coarse cakes and cookies. Anything with nuts, seeds, coconut, pineapple, or dried fruit. Breakfast yogurt with nuts. Rice or bread pudding. These foods are considered thin liquids and should be avoided if thin liquids are restricted: Frozen malts, milk shakes, frozen yogurt, eggnog, nutritional supplements, ice cream, sherbet, regular or sugar-free gelatin, or any foods that become thin liquid at either room (70°F) or body temperature (98°F). |
| Fats | Butter, margarine, cream for cereal (depending on liquid consistency recommendations), gravy, cream sauces, mayonnaise, salad dressings, cream cheese, cream cheese spreads with soft additives, sour cream, sour cream dips with soft additives, whipped toppings. If thin liquids allowed, also may have: Cream for cereal. | All fats with coarse or chunky additives. |
| Fruits | Soft drained canned or cooked fruits without seeds or skin. Fresh soft/ripe banana. Fruit juices with small amount of pulp. If thin liquids are restricted, fruit juices should be thickened to appropriate viscosity. If thin liquids allowed, also may have: Thin fruit juices. Watermelon without seeds. | Fresh or frozen fruits. Cooked fruit with skin or seeds. Dried fruits. Fresh, canned, or cooked pineapple. |
| Meats, Meat Substitutes, and Entrees Meat pieces should not exceed ¼ inch cube and should be tender. | Moistened ground or cooked meat, poultry, or fish. Moist ground or tender meat may be served with gravy or sauce. Casseroles without rice. Moist macaroni and cheese, well-cooked pasta with meat sauce, tuna-noodle casserole, soft, moist lasagna. Moist meatballs, meat loaf, or fish loaf. Protein salads such as tuna or egg without large chunks, celery, or onion. Cottage cheese, smooth quiche without large chunks. Poached, scrambled, or soft-cooked eggs (egg yolks should not be “runny” but should be moist and mashable with butter, margarine, or other moisture added to them). (Cook eggs to 160°F or use pasteurized eggs for safety.) Soufflés may have small soft chunks. Tofu. Well-cooked, slightly mashed, moist legumes such as baked beans. All meats or protein substitutes should be served with sauces, or moistened to help maintain cohesiveness in the oral cavity. | Dry meats, tough meats (such as bacon, sausage, hot dogs, bratwurst). Dry casseroles or casseroles with rice or large chunks. Cheese slices and cubes. Peanut butter. Hard-cooked or crisp fried eggs. Sandwiches. Pizza. |
| Potatoes and Starches | Well-cooked, moistened, boiled, baked, or mashed potatoes. Well-cooked shredded hash brown potatoes that are not crisp. (All potatoes need to be moist and in sauces.) Well-cooked noodles in sauce. Spaetzel or soft dumplings that have been moistened with butter or gravy. | Potato skins and chips. Fried or French-fried potatoes. Rice. |
| Soups | Soups with easy-to-chew or easy-to-swallow meats or vegetables: particle sizes in soups should be <½ inch. (Soups may need to be thickened to appropriate consistency, if soup is thinner than prescribed liquid consistency). If thin liquids allowed, also may have: All soups except those noted in Avoid column. | Soups with large chunks of meat and vegetables. Soups with rice, corn, peas. |
| Vegetables | All soft, well-cooked vegetables. Vegetables should be <½ inch. Should be easily mashed with a fork. | Cooked corn and peas. Broccoli, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, asparagus, or other fibrous, nontender or rubbery cooked vegetables. |
| Miscellaneous | Jams and preserves without seeds, jelly. Sauces, salsas, etc., that may have small tender chunks <½ inch. Soft, smooth chocolate bars that are easily chewed. | Seeds, nuts, coconut, sticky foods. Chewy candies such as caramel and licorice. |
LEVEL 3: DYSPHAGIA ADVANCED DIET
Description
This level consists of food of nearly regular textures with the exception of very hard, sticky, or crunchy foods. Foods still need to be moist and should be in bite-size pieces at the oral phase of the swallow.
Rationale
This diet is a transition to a regular diet. Adequate dentition and mastication are required. The textures of this diet are appropriate for individuals with mild oral or pharyngeal phase dysphagia. Patients should be assessed for tolerance of mixed textures. It is expected that mixed textures are tolerated on this diet.
Table 3.5 Liquid Consistency

Food Textures for NDD Level 3: Dysphagia Advanced
Table 3.8 Dysphagia Advanced
| Food Groups | Recommended | Avoid |
| Beverages | Any beverages, depending on recommendations for liquid consistency. If thin liquids allowed, also may have: Milk, juices, coffee, tea, sodas, carbonated beverages, alcoholic beverages, nutritional supplements. Ice chips. | |
| Breads | Any well-moistened breads, biscuits, muffins, pancakes, waffles, etc. Need to add adequate syrup, jelly, margarine, butter, etc, to moisten well. | Dry bread, toast, crackers, etc. Tough, crusty breads such as French bread or baguettes. |
| Cereals Cereals may have ¼ cup milk or just enough milk to moisten if thin liquids are restricted. | All well-moistened cereals. | Coarse or dry cereals such as shredded wheat or All Bran®. |
| Desserts | All others except those on Avoid list. If thin liquids allowed, also may have: Malts, milk shakes, frozen yogurts, ice cream, and other frozen desserts. Nutritional supplements, gelatin, and any other desserts of thin liquid consistency when in the mouth. | Dry cakes, cookies that are chewy or very dry. Anything with nuts, seeds, dry fruits, coconut, pineapple. These are considered thin liquids and should be avoided if thin liquids are restricted: Frozen malts, milk shakes, frozen yogurt, eggnog, nutritional supplements, ice cream, sherbet, regular or sugar-free gelatin or any foods that become thin liquid at either room (70°F) or body temperature (98°F). |
| Fats | All other fats except those on Avoid list. | All fats with coarse, difficult-to-chew, or chunky additives such as cream-cheese spread with nuts or pineapple. |
| Fruits | All canned and cooked fruits. Soft, peeled fresh fruits such as peaches, nectarines, kiwi, mangos, cantaloupe, honeydew, watermelon (without seeds). Soft berries with small seeds such as strawberries. If thin liquids allowed, also may have: Any fruit juices. | Difficult-to-chew fresh fruits such as apples or pears. Stringy, high-pulp fruits such as papaya, pineapple, or mango. Fresh fruits with difficult-to-chew peels such as grapes. Uncooked dried fruits such as prunes and apricots. Fruit leather, fruit roll-ups, fruit snacks, dried fruits. |
| Meats, Meat Substitutes, and Entrees | Thin-sliced, tender, or ground meats and poultry. Well-moistened fish. Eggs prepared any way. Yogurt without nuts or coconut. Casseroles with small chunks or meat, ground meats, or tender meats. | Tough, dry meats and poultry. Dry fish or fish with bones. Chunky peanut butter. Yogurt with nuts or coconut. |
| Potatoes and Starches | All, including rice, wild rice, moist bread dressing, and tender, fried potatoes. | Tough, crisp-fried potatoes. Potato skins. Dry bread dressing. |
| Soups | All soups except those on the Avoid list. Strained corn or clam chowder. (May need to be thickened to appropriate consistency if soup is thinner than prescribed liquid consistency). If thin liquids allowed, also may have: All thin soups except those on the Avoid list. Broth and bouillon. | Soups with tough meats. Corn or clam chowders. Soups that have large chunks of meat or vegetables >1 inch. |
| Vegetables | All cooked, tender vegetables. Shredded lettuce. | All raw vegetables except shredded lettuce. Cooked corn. Nontender or rubbery cooked vegetables. |
| Miscellaneous | All seasonings and sweeteners. All sauces. Nonchewy candies without nuts, seeds, or coconut. Jams, jellies, honey, preserves. | Nuts, seeds, coconut. Chewy caramel or taffy-type candies. Candies with nuts, seeds, or coconut. |
NATIONAL DYSPHAGIA DIET (NDD) LIQUID CONSISTENCY LEVELS
Clients with swallowing difficulty can often handle thickened beverages better than normal thin fluids such as water, milk, or coffee. However, not everyone needs thickened liquids. Speech and occupational therapists use the following terms and measurement of thickness, or viscosity, to prescribe the appropriate consistency for liquids based on individual needs.
Definitions of Terms Used for Thickened Liquids
Table 3.9 Viscosity Borders and Ranges for Thickened Liquids
© 2003, American Dietetic Association. Table used with permission
| Thin | 1–50 cP |
| Nectar-like | 51–350 cP |
| Honey-like | 351–1,750 cP |
| Spoon-thick | >1,750 cP |
*cP = Centipoise, the term for the measure of viscosity
Foods that are naturally nectar-like and do not require modification include:
Fruit nectars such as apricot and pear nectar
Tomato juice
Buttermilk
Some manufacturers now put the viscosity measurement on their product labels. Avoid any liquid that changes thickness (viscosity) at room temperature (70°F) or body temperature (98°F). Examples include some nutritional supplements, milkshakes, eggnog, ice cream, and gelatin. A variety of commercial thickeners are available to modify liquids’ consistencies. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to obtain the desired thickness.
Table 3.10 Sample Menu Plan for National Dysphagia Diets
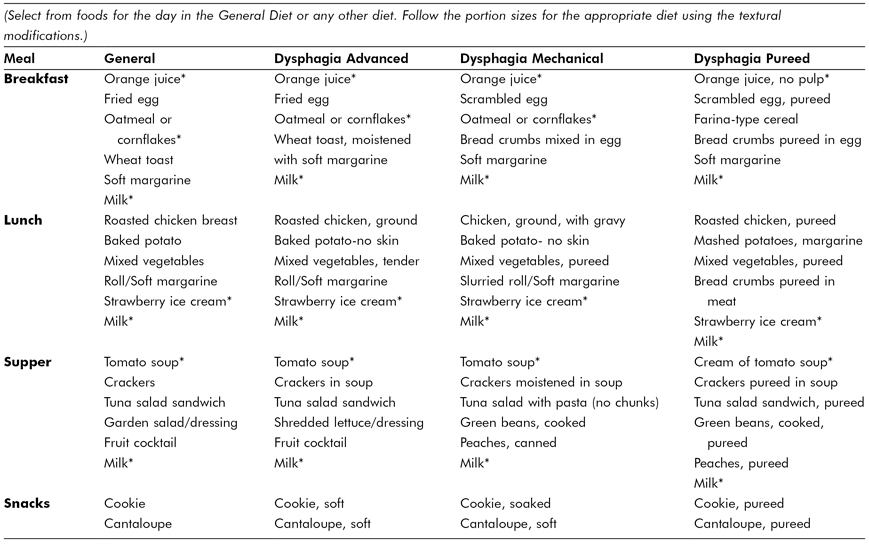
*If thin liquids restricted, thicken to appropriate consistency
Food and Beverage Preparation Tips
Thickeners for Consistency Altered Foods
A variety of methods and special products are available to prepare a wide range of food consistencies. Thickeners for pureed foods and liquids include:
- For pureed foods:
- Commercial food thickeners, bread and cracker crumbs, instant potato flakes, instant infant cereal, and instant pudding mixes are good nutritious thickeners.
- For liquids:
- Commercial thickeners, instant pudding mix, and instant potato flakes are acceptable thickeners. Yogurt, applesauce, and puddings are also acceptable, however they increase the volume of the products considerably; these may not be good choices for persons with poor appetite. Prethickened beverages are available.
- Addition of thickening agents, irrespective of type, to orally ingested fluids does not significantly alter the absorption rate of water from the gut. Client acceptance is always a concern. Introducing a new thickened beverage such as lemon-flavored thickened water or thickened fruit juice may be more acceptable than offering thickened coffee or milk, which would have a different mouth feel than is usually expected with those flavors.
- Commercial thickeners, instant pudding mix, and instant potato flakes are acceptable thickeners. Yogurt, applesauce, and puddings are also acceptable, however they increase the volume of the products considerably; these may not be good choices for persons with poor appetite. Prethickened beverages are available.
Preparation of Texture Altered Foods
Because diminished appetite is often present in individuals requiring texture modification, it is of utmost importance that the food be prepared to enhance its natural flavor. Every attempt should be made to make the food as palatable as possible. Minimize the total volume necessary to provide nutritional adequacy. Serve the food at the proper temperature. The foods should be served as separate entities and on attractive dishes with an appetizing presentation.
Use a food processor to achieve the desired consistency. Foods with a variety of consistencies can be prepared with the addition of very little liquid. The traditional blender usually requires more liquids, which dilutes nutrient density and increases the volume of foods.
Soaking or moistening recognizable foods in liquids, gravies, and slurries helps maintain their appeal. A slurry is a combination of a commercial thickener, common thickeners, or gelatin, with such liquids as milk, juice, or broth, and can be obtained by using 1 to 4 tablespoons of thickener or gelatin to 2 cups of liquid.
Cookies and cakes without nuts and chips can be soaked in milk. Bread or biscuits soaked in gravy or pancakes soaked in syrup or slurry are often well tolerated. A slurry can also be used to moisten and soften such foods as bread, cakes, cookies, or crackers. In addition, it is used to gel pureed foods. This allows an individual to consume food items that are not routinely part of the puree texture modification. Before serving a dry, crumbly food with added slurry, be sure the slurry soaks through the entire thickness of the food.
Method for Determining the Portion Sizes of Consistency Altered Foods
Foods often change in volume when they have been modified in consistency and texture. To ensure that nutritional adequacy is maintained, the following guidelines may be used when several portions of a consistency altered food are needed. Puree is used in this example.
1. Measure out desired number of servings into container for pureeing. Puree the food. Add any necessary thickener or liquid to obtain desired consistency. In most cases, it is desirable to maintain or increase the caloric value of consistency altered foods. When thinning foods use liquids that add to the nutritional value as well as the flavor of foods. Appropriate liquids include milk, fruit or vegetable juice, broth, gravy, cream sauce, and liquid nutrient supplements. Plain water is not recommended for thinning.
2. Measure the volume of the food after it has been pureed.
3. Divide the total volume of the pureed food by the original number of portions. This is the new portion size. Note: Some foods may have a smaller, rather than larger, portion after pureeing.
4. After dividing portions, foods must be reheated or chilled to serving temperature per Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) guidelines.



