Congenital Surfactant Deficiency
Billie Fyfe, MD
Eileen McKay, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Variable patterns of acute and chronic diffuse lung disease in neonates, children, and rarely adults due to genetic disorders of surfactant synthesis and homeostasis
Clinical Issues
Presentation varies by defect
SFTPB mutations: SP-B deficiency and ABCA3 gene mutations respiratory failure in term infants
ABCA3 mutation rarely presents later
SFTPC mutations: More variable clinical presentation extending into childhood and even adulthood
NKX2-1 mutations: Brain-thyroid-lung syndrome
Microscopic Pathology
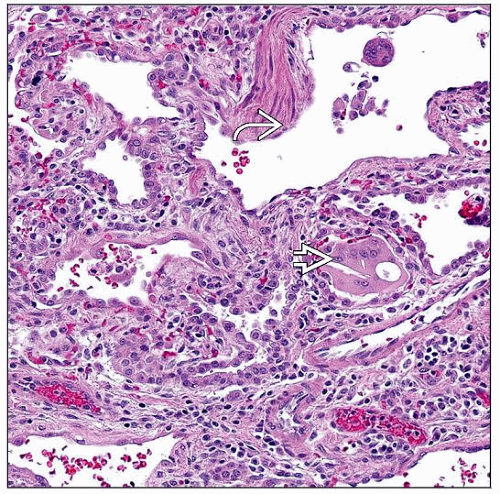
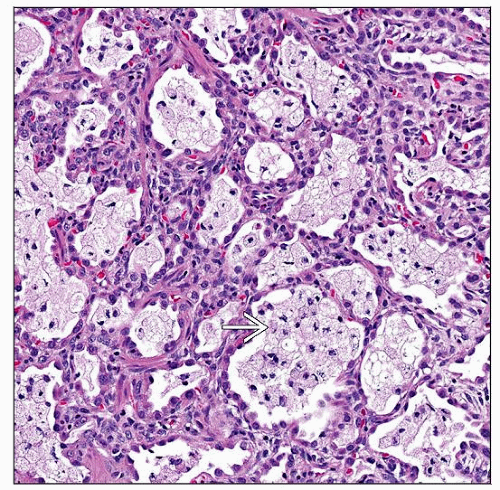
Mixture of patterns of lung injury in all mutations makes light microscopy nonspecific for individual mutation
Alveolar proteinosis change (intraalveolar accumulation of PAS[+] material)
Desquamative interstitial pneumonitis change (intraalveolar collections of macrophages)
Nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis change (alveolar septal fibroblastic proliferation, fibrosis, and chronic inflammation)
Ancillary Tests
Ultrastructure may be more indicative of disease type than light microscopy and is indicated in cases of unexplained respiratory failure in infants
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Surfactant dysfunction disorder
Congenital alveolar proteinosis
Often used incorrectly as a synonym
Proteinosis histology not specific to surfactant dysfunction and is one of many histologic patterns seen in this disease
Definitions
Variable patterns of acute and chronic diffuse lung disease in neonates, children, and rarely adults related to genetic disorders of surfactant synthesis and homeostasis
Mutations identified in surfactant protein B gene (SFTPB), surfactant protein C gene (SFTPC), ATP-binding cassette A3 transporter protein gene (ABCA3), and NKX2-1 gene (TTF1)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Normal Surfactant Homeostasis
Synthesized, packaged, and secreted by type 2 pneumocytes via lamellar bodies, surfactant reduces surface tension at air-liquid interface in the alveoli
Surfactant proteins B (SP-B) and C (SP-C) interact with surfactant phospholipids to aid organization, spreading, and stability of surfactant
SP-B also important for processing proSP-C to SP-C
ABCA3 aids translocation of substances (especially lipids) across cell membranes
Expressed on outer membrane of lamellar bodies
Thought to play a role in maturation of lamellar bodies
TTF-1 protein important for lung development and expression of SP-B, SP-C, and ABCA3
Inheritance Patterns and Mutations
SFTPB mutations: Autosomal recessive
Gene localized on chromosome 2
> 30 loss of function mutations leading to partial or complete absence of SP-B
Most common mutation (70% of cases) is GAA substitution for C in codon 121 (a.k.a. 121ins2)
Carrier frequency: 1 per 1,000 people in general population
Loss of SP-B → improper SP-C processing with accumulation of proSP-C in type 2 pneumocytes and alveoli contributing to surfactant dysfunction and clinical disease
SFTPC mutations: Autosomal dominant with variable penetrance and sporadic (55%) mutations
Gene localized on chromosome 8
> 35 dominantly expressed mutations leading to misfolded proSP-C that accumulates in type 2 pneumocytes
Leads to misfolded protein response, cell stress injury, and apoptosis
Most common mutation (25% of cases) is threonine for isoleucine in codon 73 (a.k.a. I73T)
ABCA3 mutations: Autosomal recessive
Gene localized on chromosome16
> 70 recessive mutations
NKX2-1 mutations: Autosomal dominant
Gene localized on chromosome 14
Gene deletions and point mutations identified