Congenital Nephrotic Syndrome of the Finnish Type
Helen Liapis, MD
Joseph Gaut, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Finnish nephropathy (FN)
Occurs in neonates up to 3 months of age and is due to mutations in nephrin (NPHS1) gene
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Mutations in NPHS1 gene encoding nephrin
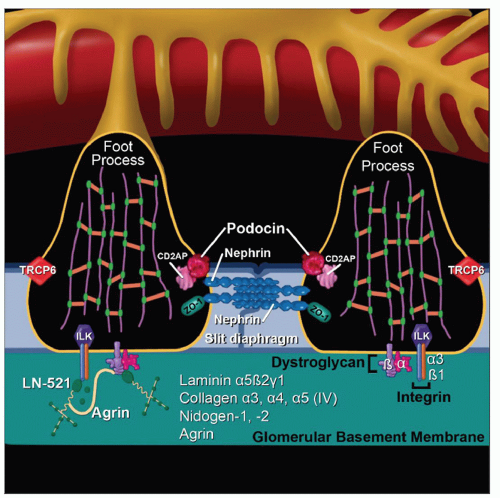
Nephrin is major structural protein of slit diaphragm, important for its formation and maintenance
Absent or mutant nephrin results in absent slit diaphragms and massive proteinuria
Clinical Issues
Presents at birth or shortly after (< 3 months of age) with massive proteinuria and steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome
Prognosis depends on nature of NPHS1 mutation
Autosomal recessive inheritance
Ancillary Tests
Mutational analysis of NPHS1 on chromosome 19
Staining for nephrin protein expression
Top Differential Diagnoses
Podocin deficiency
Early diffuse mesangial sclerosis (DMS)
Idiopathic or associated with Pierson syndrome or WT1 mutations (Denys-Drash)
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Finnish nephropathy (FN)
Synonyms
Microcystic kidney disease
Definitions
Steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome in neonates up to 3 months of age due to mutations in nephrin (NPHS1) gene
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Genetics
Autosomal recessive disease
Homozygous mutation in NPHS1
Maps to chromosome 19q13.1
Encodes protein nephrin
Transmembrane protein of immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily with 8 extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains with N-glycosylated sites
N-glycosylation is important for protein folding, formation of slit diaphragm, and localization in GBM
Forms “zipper” structure of slit diaphragm described by Karnovsky
Over 70 mutations have been identified in Finland and elsewhere around the world
Fin-major
Frameshift mutation in chromosome 19q13.1 leading to absent slit diaphragms and no nephrin protein expression
Fin-minor
Nonsense mutations in exon 26 produce a truncated or nonfunctioning nephrin
Compound heterozygous NPHS1 mutations are rare
May present as adult onset focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)
Heterozygotes with 1 normal NPHS1 allele (carriers) are normal post birth
In utero may have transient deficiency of nephrin during podocytogenesis
Can lead to false-positive α-fetoprotein (AFP) test in amniotic fluid and maternal serum
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Highest in Finland
1:10,000-1:80,000 births (gene frequency 1:200)
Fin-major accounts for 78% of Finnish cases
Fin-minor accounts for 22% of Finnish cases
Occurs worldwide at lower frequency
61% of nephrotic syndrome in first 3 months of life
Numerous other point mutations are described in non-Finnish patients, resulting in variable nephrin synthesis
Age
Onset < 3 months: Homozygous mutation
Onset 6 months to 5 years: Compound heterozygous mutation
Rare cases of adult onset FSGS attributed to NPHS1 mutations
Presentation
Massive proteinuria-nephrotic syndrome
Elevated AFP in amniotic fluid and maternal serum
Laboratory Tests
AFP elevated in maternal plasma and amniotic fluid (in utero nephrotic syndrome)
Antinephrin antibodies post transplant
Treatment
Supportive therapy
Transplantation once patient weight is > 8 kg
Patients who are transplanted have 30% rate of recurrent nephrotic syndrome
Not a recurrence but instead secondary to anti-nephrin antibodies
Plasmapheresis, cyclophosphamide, and methylprednisolone prolongs graft survival in patients with antinephrin antibodies
Prognosis
Mean time to ESRD = 32 months
Rate of progression is variable
Somewhat slower in females (40 months) than males (21 months)
Patients with Fin-major have earliest onset and most rapid course
Patients with Fin-minor have later onset and delayed progression
Many severely affected infants with FN die from infection
Compound heterozygotes develop ESRD later at 6-15 years of age
Fetal carriers of NPHS1 mutations are normal post birth
IMAGE FINDINGS
Ultrasonographic Findings
Echogenic kidneys with symmetric distribution of microcysts
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree