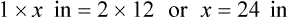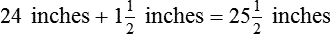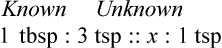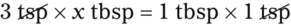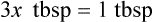Chapter 4 • Know standard abbreviations for the household, metric, and apothecary systems used in the medical field • Identify, convert, and calculate using household measurements of length, weight, and volume found in the medical field • Identify, convert, and calculate using International System of Units (SI), or metric, measurements of length, weight, and volume found in the medical field • Identify, convert, and calculate using apothecary system measurements of weight and volume found in the medical field U.S. customary system (household system) System of measurement based on common kitchen measuring devices Length is used in household and metric systems to measure height or body circumference as well as length of a suture line. In pharmacy, length is only used to measure medications that require application to the body that must be measured in inches or centimeters or millimeters. In this case, the means of application is usually premarked on a dispensing paper for ease in ensuring that the correct amount of medication is being administered, such as with nitroglycerin ointment. Another pharmaceutical use of length is in finding body surface area (BSA) in which height and weight are compared for dosage calculation (BSA is discussed in Chapter 10). Length measurements also include inches, feet, centimeters, meters, kilometers, yards, and miles. Some of the previously mentioned measurements are those you use daily, whereas others may be foreign and need explanation. This chapter covers the basic measurements per system, which are essential for learning conversions in Chapter 5. Household measurements are expressed in Arabic numbers with the abbreviation for each following the number, such as 5 tsp or TABLE 4.1 Household Measurements of Weight Some medication labels include household measurements as well as metric measurements as seen on the label for Retrovir (Figure 4-1). Table 4-2 gives the measurements of length often seen in the medical setting. A mile is also a measurement of length but is not used in pharmaceutical calculations. TABLE 4.2 Household Measurements of Length Table 4-3 shows the household measurements of volume or liquid used most frequently in the home and in pharmaceutical calculations. Always remember that the size of a drop is totally dependent on the size of the opening in the dropper and viscosity of the liquid; therefore the 60 drops per teaspoon often found in measurement tables for household measurements is only an approximation. Drops used with intravenous therapy are stated in invariable amounts in the metric system as will be seen in later chapters. Also, household utensils are not necessarily accurate, so the amounts measured in these utensils should be considered only approximations. TABLE 4.3 Household Measurements of Volume NOTE: tbsp may be cancelled because both equivalents of the same measurement are known.
Comparisons of Measurement Systems
Introduction
Household Or U.S. Customary System
 pt. Table 4-1 provides the basic household measurements for weight accompanied by abbreviations and equivalents as appropriate.
pt. Table 4-1 provides the basic household measurements for weight accompanied by abbreviations and equivalents as appropriate.
MEASUREMENT UNIT
ABBREVIATION
EQUIVALENT
Ounce
oz
—
Pound
lb, #
16 oz
Ton
T
2000#

MEASUREMENT UNIT
ABBREVIATION
EQUIVALENTS
Inch
in, ″
—
Foot
ft, ′
12 inches
Yard
yd
36 inches, 3 feet
MEASUREMENT UNIT
ABBREVIATION
EQUIVALENTS
Drops
gtts
—
Teaspoon
tsp, Tsp, t
60 drops (depending on the size of the dropper and the viscosity of the medication)
Tablespoon
tbsp, Tbsp, tbs, T
3 teaspoons
Ounce
oz
2 tbsp or 6 tsp
Cup
C, c
8 oz
Pint
pt
2 c, 16 oz
Quart
qt
2 pt, 4 c, 32 oz
Gallon
gal
4 qt, 8 pt, 16 c, 128 oz
Using Fractional Method for Finding Equivalency in Household Measurements
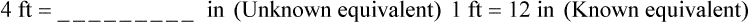
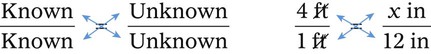
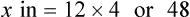
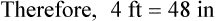
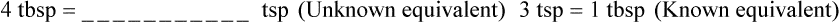
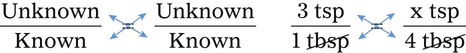
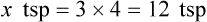
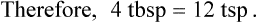
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Comparisons of Measurement Systems

 _____________________
_____________________ _____________________
_____________________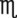 _____________________
_____________________ viii =
viii = 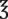 _____________________
_____________________ ii =
ii = 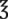 _____________________
_____________________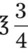 =
=  _____________________
_____________________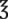 iv =
iv =  _____________________
_____________________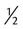 ,
, 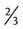 , or
, or 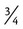 . For example, a teaspoon and a half would be expressed as
. For example, a teaspoon and a half would be expressed as 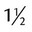 tsp. You will later learn that the apothecary system also uses fractions, whereas the metric system uses decimal values.
tsp. You will later learn that the apothecary system also uses fractions, whereas the metric system uses decimal values.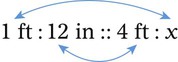
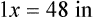
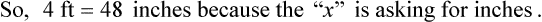

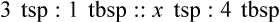
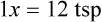
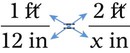
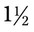 ″. What would this be in inches? (1 ft = 12 inches)
″. What would this be in inches? (1 ft = 12 inches)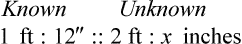
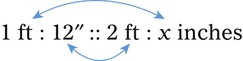
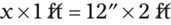
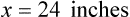
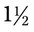 ″ to the 24″ as indicated in the problem.
″ to the 24″ as indicated in the problem.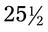 ″.
″.