Common Acquired Melanocytic Nevi
Christine J. Ko, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Majority develop in adolescence
Microscopic Pathology
Flat surface to slightly raised to polypoid
Epidermis varies (e.g., thin or seborrheic keratosis-like)
Well-circumscribed
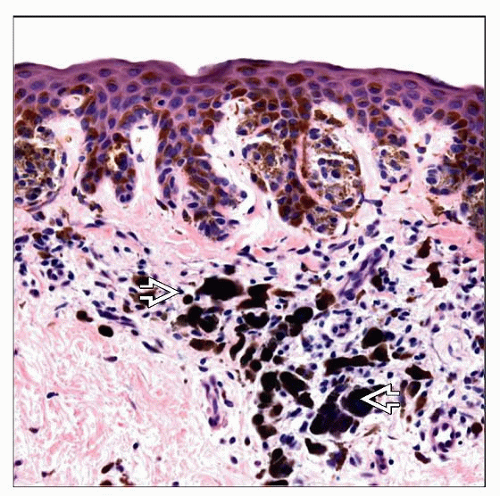
Melanocytes arranged in regular clusters/nests, particularly at junction of epidermis and dermis and superficial dermis
Nest defined as 3-5 clustered melanocytes
Generally symmetrical from side to side
Orderly arrangement of nests at junction and in superficial dermis
Mitoses generally absent
Melanin pigment often limited to junctional or superficial dermal nests
Dermal maturation: Type A nevus cells superficially, type B and C nevus cells with descent into dermis
Type A nevus cells: Epithelioid
Type B nevus cells: Lymphocytoid
Type C nevus cells: Spindled, neuroid
May see pseudonuclear inclusion: Lighter staining round area within nucleus
Top Differential Diagnoses
Atypical/”dysplastic”/Clark nevus
Congenital melanocytic nevus
DDx of junctional lentiginous melanocytic nevus
Lentigo (simple)
DDx of intradermal nevus (especially neurotized)
Neurofibroma
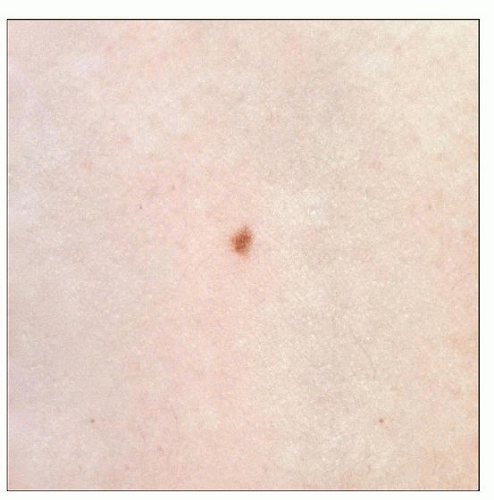 This junctional melanocytic nevus is an oval macule of even, light brown pigment. There is overall symmetry with a smooth border; the size was measured to be 2 × 1 mm. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Benign melanocytic nevus, junctional melanocytic nevus, compound melanocytic nevus, intradermal melanocytic nevus, common mole, common melanocytic nevus, nevocellular nevus
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Exact Etiology Unknown
Believed by some to arise from intraepidermal melanocytes
Others suggest that melanocytic nevi arise from nerves or pluripotential cells
Tumor vs. Hamartoma?
Still debated
Evidence for tumor
Studies showing that some nevi are clonal
Growth advantage of nevus cells over epidermal, dendritic melanocytes in cell culture
Similar expression of different markers by nevi and malignant melanoma
Presence of mutations in BRAF oncogene in majority of nevi
Evidence for hamartoma
Other proliferative elements: Epidermal, follicular, connective tissue
Studies showing that some nevi are polyclonal
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Number of acquired nevi
Increases with age up to 3rd decade
May be related to familial predisposition
Sun exposure in childhood also linked to development of nevi
More common in lighter skinned individuals
Age
Not present at birth
Majority develop in adolescence
Density of nevi generally decreases after 4th decade
Presentation
Junctional lesions
Flat to minimally raised macule/very thin papule
Generally < 6 mm, but may be larger
Color often a variation of brown
Compound lesions
Slightly raised papule
Variable color (brown, flesh-colored, pink)
May contain hair
Intradermal lesions
Papule, may be pedunculated
Variable color (brown, flesh-colored, pink)
May contain hair
Natural History
Abtropfung hypothesis of Unna
Melanocytes are initially junctional
With chronologic time (aging), melanocytes “drop off” into dermis, creating compound melanocytic lesions
With more time, the junctional melanocytes have all “dropped off,” creating intradermal melanocytic lesions
Intradermal melanocytic lesions may eventually “shed” or become acrochordons
Degenerative changes include balloon cell change and fatty change
Alternative hypothesis
Nevi begin in the dermis
Not all melanocytic nevi display progressive changes; some arrest at a given stage indefinitely
Treatment
Not necessary
Conservative removal (e.g., shave removal) generally sufficient
Residual dark pigment may remain
Pigment may recur irregularly within scar (recurrent nevus)
Prognosis
Benign
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Flat surface to slightly raised to polypoid
Well-circumscribed
Melanocytes arranged in nests, particularly at junction of epidermis and dermis and superficial dermis
Nest defined as cluster of at least 3 (some authors) or 5 (other authors) melanocytes
Generally symmetrical from side to side
Orderly arrangement of nests at junction and in superficial dermis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree