Collagenous Colitis
Julianne K. Purdy, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Middle-aged to elderly women
Chronic nonbloody diarrhea
Normal colonoscopy
Microscopic Pathology
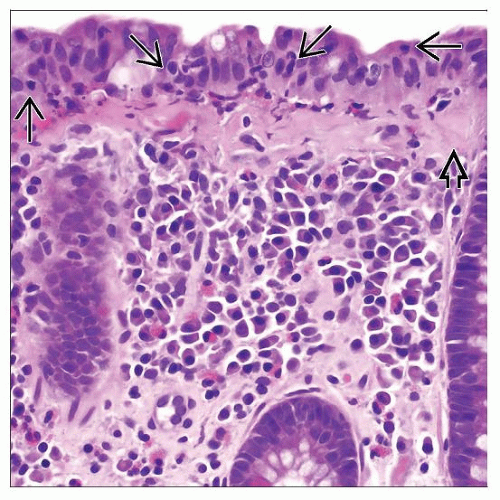
Patchy subepithelial increased collagen
Most reliable biopsies from transverse colon
Irregular collagen band extends entraps capillaries, inflammatory cells, and fibroblast nuclei
Increased intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs)
> 10-20 IELs/100 surface epithelial cells
Chronic or mixed inflammation in lamina propria
Increased eosinophils (may be marked)
Detachment of surface epithelial cells from collagen band
Normal crypt size and shape; rare distortion
Rarely giant cells or focal IBD-like changes (Paneth cell metaplasia, cryptitis, crypt abscesses, branched crypts)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Lymphocytic colitis
No increased subepithelial collagen
Inflammatory bowel disease
Erosion/ulceration, crypt architectural distortion, basal plasmacytosis
Amyloidosis
Stains with Congo red, not trichrome
Tangential sectioning
Ischemic/radiation colitis
No ↑ intraepithelial or lamina propria lymphocytes
Entities mimicking thickened collagen
Tangential sectioning of tissue, hyperplastic polyp
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Collagenous colitis (CC)
Definitions
Form of microscopic colitis with abnormal subepithelial collagen deposition and normal colonoscopy
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Abnormal immunologic response to intraluminal bacteria/toxin in predisposed individuals
Ileostomy with diversion of fecal stream → cessation of symptoms and histologic remission
Infection
Antibodies to Yersinia more common in CC patients
Development after C. difficile infection
No definite infectious agent identified
Drugs: NSAIDs, lansoprazole, cimetidine, ticlopidine, simvastatin
NSAID use: 39% of CC patients
Mechanisms not elucidated
Prior ulceration/inflammation → stimulation of collagen synthesis or resulting defect in regulation
Genetic Factors
Familial cases exist; HLA data inconclusive
Autoimmune Pathogenesis
Often coexisting autoimmune disease (17-40%)
Celiac disease (8-17%), thyroid disorders, diabetes, collagen vascular diseases
Causality not proven
Responds to steroids but no immune complex deposits identified
Abnormal Collagen Metabolism
Impaired degradation of extracellular matrix (vs. increased fibrogenesis) → increased collagen accumulation
↑ pericryptal fibroblast turnover and activation → increased/premature collagen formation
↑ expression of fibrogenic genes by myofibroblasts
Transforming growth factor β-1 (TGF-β-1) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) alter balance of fibrogenesis and fibrinolysis
Possibly ↑ basic fibroblast growth factor → differentiation of fibroblasts
Unknown Etiology
Likely multifactorial
CLINICAL ISSUES