Colchicine Effect
Elizabeth A. Montgomery, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
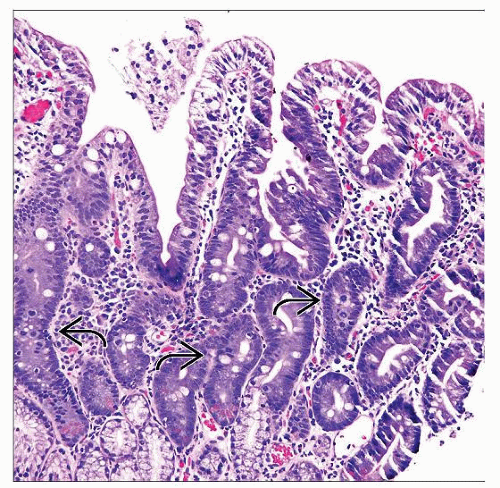
GI symptoms associated with mitotic arrest restricted to proliferative compartment of mucosa
Best seen in small bowel and gastric antrum
Clinical Issues
Serum levels can be monitored clinically
Colchicine has long half-life
Patients with renal failure or liver disease most prone to toxicity
Alkaloid
Used to treat gout and many rheumatologic disorders
Microscopic Pathology
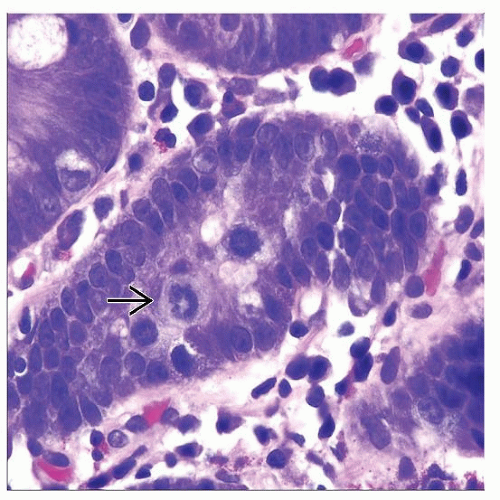
Abundant mitotic figures arrested in metaphase (ring mitoses) restricted to proliferative compartment
Apoptosis and atrophic villi
Reactive epithelial changes
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Colchicine toxicity
Definitions
GI symptoms associated with mitotic arrest restricted to proliferative compartment of mucosa
Seen best in small bowel and gastric antrum
Colchicine effect can be seen in neoplasms of patients taking therapeutic doses but only seen in normal mucosa when patients have toxic serum levels
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Seen in patients taking colchicine
Alkaloid
Used to treat gout and many unrelated rheumatologic disorders
Familial Mediterranean fever
Binds to tubulin and inhibits formation of microtubules
Thus inhibits degranulation, chemotaxis, mitosis, spermatogenesis
Gastrointestinal manifestations of toxicity
Cramping, abdominal pain, diarrhea
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree