Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma
Jesse K. McKenney, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Some cases arise in background of typical urothelial carcinoma
Subset of CCC in females arise in association with endometriosis or ectopic Müllerian glands
Clinical Issues
Extremely rare
Female predominance
Hematuria and dysuria
Deeply invasive CCC is highly aggressive
Microscopic Pathology
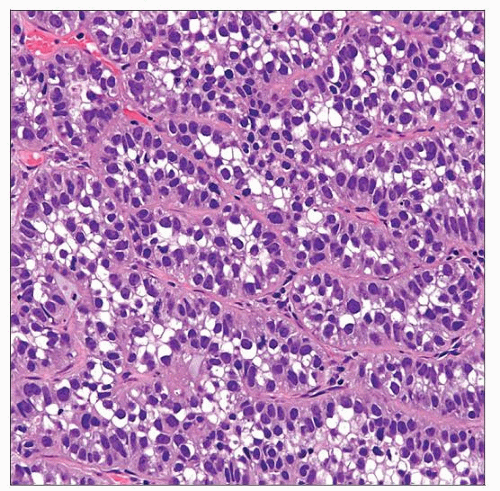
Mixed tubulocystic, papillary, and solid/diffuse patterns
Tumor cells typically range from flat to cuboidal
Mixed clear and eosinophilic cytoplasm
“Hobnail” arrangement of cells can be seen
Papillae may have densely hyalinized cores
Cytologic atypia usually moderate to severe
Mitotic figures are frequent
Ancillary Tests
Positive for CK7, CEA, and CA125; occasionally for CK20
Also express pax-8 and AMACR
Top Differential Diagnoses
Nephrogenic adenoma
Secondary involvement (direct extension) from gynecologic tract CCC
Urothelial carcinoma with clear cytoplasm
Urothelial carcinoma with glandular differentiation
Renal cell carcinoma
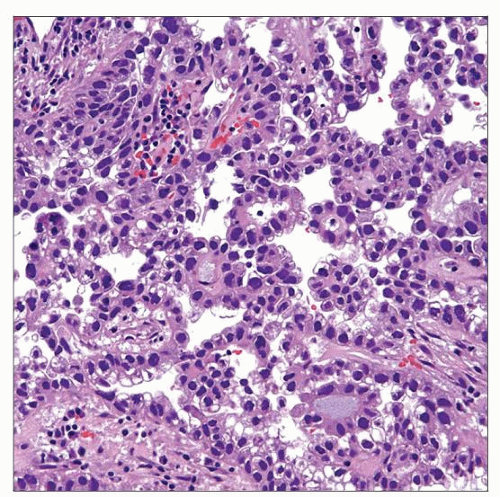 Clear cell adenocarcinoma of the bladder is characterized by papillary architecture with cuboidal lining cells showing clear to eosinophilic cytoplasm and multiple areas with a “hobnail” arrangement. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Clear cell adenocarcinoma (CCC)
Synonyms
Mesonephric adenocarcinoma
Definitions
Distinct morphologic variant of bladder adenocarcinoma
Identical to Müllerian-type clear cell adenocarcinoma of female genital tract
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Urothelial Origin
Some cases arise in background of typical urothelial carcinoma
Represents alternative differentiation
Müllerian Origin
Subset of CCC in females arise in association with endometriosis or ectopic Müllerian glands
Unknown
In many cases, origin cannot be determined
No immunohistochemical stains aid in this determination
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Extremely rare
Age
Wide age range (22-83 years)
Gender
Female predominance
Presentation
Hematuria and dysuria
Prognosis
Stage dependent
Deeply invasive CCC is highly aggressive
Noninvasive exophytic tumors may have long-term survival
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Papillary &/or polypoid mass
Rarely ulcerative
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Mixed tubulocystic, papillary, and solid/diffuse patterns
Tumor cells typically range from flat to cuboidal
Neoplastic cells may have clear to eosinophilic cytoplasm
Papillae may have densely hyalinized cores
“Hobnail” arrangement of cells may be seen
Cytologic atypia is usually moderate to severe
Mitotic figures are frequent
Level of cytologic atypia may be heterogeneous
Foci may closely resemble nephrogenic adenoma
Typically have obvious invasion
Associated myxoid stroma is also common
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Neoplastic
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Glandular
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunohistochemistry
Usually positive for CK7, CEA, and CA125
Occasionally positive for CK20
No immunoreactivity for PSA, ER, or PR
Also expresses pax-2, pax-8, and AMACR
Frequently shows nuclear p53 expression
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Nephrogenic Adenoma
Low-power architecture may be identical to CCC
Mixed tubulocystic and papillary
Solid, diffuse pattern rare but well described
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree