Classification of Tubulointerstitial Diseases
Robert B. Colvin, MD
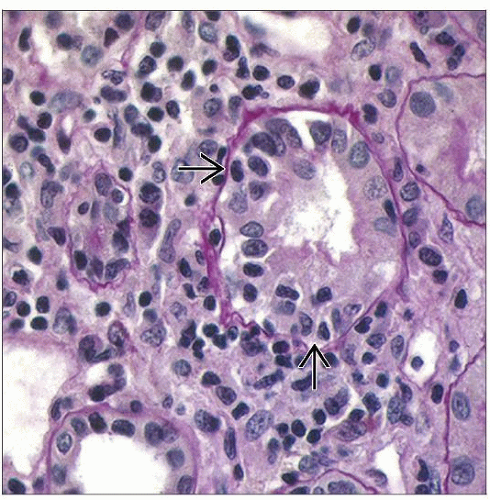
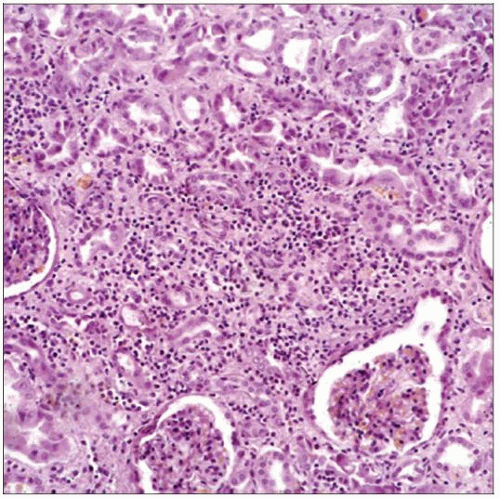 Acute interstitial nephritis was originally described in 1898 by William Councilman as a systemic response to certain extrarenal infections (here an untreated streptococcal infection). |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Acute interstitial nephritis (AIN)
Chronic interstitial nephritis (CIN)
Acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
Acute tubular injury (ATI)
Synonyms
Tubulointerstitial nephritis
Interstitial nephritis
Definitions
Group of diseases primarily manifested by inflammation &/or injury of renal tubules and interstitium
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Genetic
Storage diseases, crystal deposition, transport abnormalities, mitochondrionopathies
Infection
Direct infection of kidney by bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, rickettsia
Indirect effects of systemic infection
C. diphtheriae, Streptococcus, and many other organisms
Toxic
Heavy metals, biologic toxins, organic compounds
Metabolic
Monoclonal protein deposition, milk alkali syndrome, hypokalemia
Immunologic
Autoimmune, drug allergy, allograft rejection
Ischemia
Shock
Hypovolemia