Muscles of the Leg
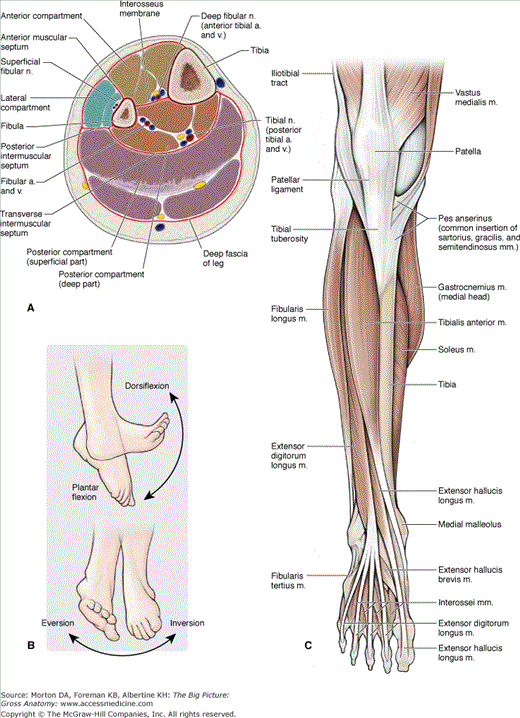
The leg consists of the tibia and fibula. Proximally, the tibia of the leg articulates with the femur of the thigh through the knee joint. Distally, the tibia and fibula of the leg articulate with the talus bone of the foot through the ankle joint. The muscles of the leg that act on the knee and ankle as well as on the joints of the foot are organized into three fascial compartments, similar to those of the thigh muscles (Figure 37-1A). The anterior compartment primarily contains muscles that produce extension (dorsiflexion) and inversion; the posterior compartment primarily contains muscles that produce flexion (plantarflexion) and inversion; and the lateral compartment primarily contains muscles that produce flexion (plantarflexion) and eversion.
The ankle (talocrural) joint consists of articulations between the tibia and talus (tibiotalar joint) and the fibula and talus (talofibular joint) and allows for motion primarily in the saittal plane, as (Figure 37-1B) follows:
- Plantar flexion (flexion). Movement in which the angle between the leg and foot increases.
- Dorsiflexion (extension). Movement in which the angle between the leg and foot decreases.
The subtalar joint is formed by articulations between the talus and the calcaneus and allows for motion primarily in the coronal plane, as follows:
- Inversion (prontation). Movement in which the plantar surface of the foot faces medially.
- Eversion (supination). Movement in which the plantar surface of the foot faces laterally.
The muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg produce numerous actions because some muscles cross the ankle, foot, and digits, and perhaps a combination of each of these joints (Table 37-1). The muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg have the following similar features:
- Common innervation. Deep fibular nerve.
- Common action. Dorsiflexion.
- Common vascular supply. Anterior tibial artery.
Muscle | Proximal Attachment | Distal Attachment | Action | Innervation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Anterior compartment of the leg | ||||
Tibialis anterior | Tibia and interosseous membrane | Medial cuneiform and base of metatarsal 1 | Dorsiflexion of foot at ankle joint; inversion of foot | Deep fibular n. (L4, L5) |
Extensor digitorum longus | Fibula and lateral tibial condyle | Via dorsal digital expansions into digits 2–5 | Extension of lateral digits 2–5 and dorsiflexion of foot | Deep fibular n. (L5, S1) |
Extensor hallucis longus | Fibula and interosseous membrane | Distal phalanx of great toe | Extension of great tow and dorsiflexion of foot | |
Fibularis (peroneus) tertius | Distal part of fibula | Base of metatarsal 5 | Dorsiflexion and eversion of foot | |
Lateral compartment of the leg | ||||
Fibularis (peroneus) longus | Upper surface of fibula | Medial cuneiform and base of metatarsal 1 | Eversion and plantarflexion of foot | Superficial fibular n. (L5, S1, S2) |
Fibularis (peroneus) brevis | Lower surface of fibula | Base of metatarsal 5 | ||
Posterior compartment of the leg (superficial group) | ||||
Gastrocnemius | Medial head: superior to medial femoral condyle Lateral head: superior to lateral femoral condyle | Via calcaneal tendon to posterior surface of calcaneus bone | Plantarflexes foot and flexes knee | Tibial n. (S1, S2) |
Plantaris | Superior to lateral femoral condyle | |||
Soleus | Posterior aspect of tibia (soleal line) and posterior aspect of fibular head and shaft | Plantarflexes the foot | ||
Posterior compartment of the leg (deep group) | ||||
Popliteus | Posterior surface of proximal tibia | Lateral femoral condyle | Unlocks knee joint; laterally rotates femur on fixed tibia | Tibial n. (L4, L5, S1) |
Flexor hallucis longus | Posterior surface of fibula and interosseous membrane | Distal phalanx of great toe | Flexes great toe | Tibial n. (S2, S3) |
Flexor digitorum longus | Tibia | Distal phalanges of digits 2–5 | Flexes digits 2–5 | |
Tibialis posterior | Interosseous membrane, tibia, and fibula | Navicular, all cuneiform bones, and metatarsals 2–4 | Inversion and plantarflexion of foot; support of medial arch of foot during walking | Tibial n. (L4, L5) |
The following muscles are located in the anterior compartment of the leg (Figure 37-1C):
- Tibialis anterior muscle. Attaches proximally to the tibia and interosseous membrane; distally, it attaches to the medial cuneiform and the base of metatarsal 1. The tibialis anterior muscle dorsiflexes the foot at the ankle joint and inverts the foot. The deep fibular nerve (L4 and L5) innervates this muscle.
- Extensor digitorum longus muscle. Attaches proximally on the fibula and lateral tibial condyle; distally, it attaches to the dorsal digital expansions into digits 2 to 5. The extensor digitorum longus muscle extends lateral digits 2 to 4 and dorsiflexes the foot at the ankle joint. The deep fibular nerve (L5 and S1) innervates this muscle.
- Extensor hallucis longus muscle. Attaches proximally on the fibula and interosseous membrane; distally, it attaches to the distal phalanx of the great toe. The extensor hallucis longus muscle extends the great toe and dorsiflexes the foot. The deep fibular nerve (L5 and S1) innervates this muscle.
- Fibularis (peroneus) tertius muscle. Attaches proximally to the distal part of the fibula; distally, it attaches to the base of metatarsal 5. The fibularis tertius muscle dorsiflexes and everts the foot. The deep fibular nerve (L5 and S1) innervates this muscle.
Muscles and their associated tendons cross the anterior surface of the ankle and insert in the foot. In addition, the following intrinsic muscles are located on the dorsal surface of the foot:
- Extensor digitorum brevis muscle. Attaches proximally to the lateral calcaneus; distally, it attaches to the dorsal surface of digits 2 to 4. The extensor digitorum brevis muscle extends digits 2 to 4. The deep fibular nerve (S1 and S2) innervates this muscle.
- Extensor hallucis brevis muscle. Attaches proximally to the lateral calcaneus; distally, it attaches to the dorsal surface of the great toe. The extensor hallucis brevis muscle extends the great toe. The deep fibular nerve (S1 and S2) innervates this muscle.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree