Central Hepatectomy
Aijun Li
Mengchao Wu
DEFINITION
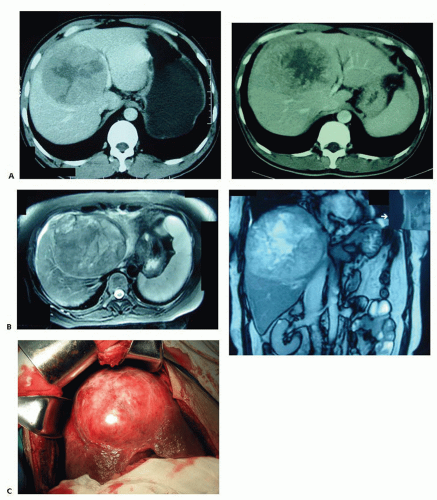
Central hepatectomy, alternatively referred to as mesohepatectomy, central bisegmentectomy, middle lobectomy, or central trisegmentectomy, is an operation that removes segments 1, 4, 5, and 8 en bloc (or lesser resections) while leaving the left lateral and right posterior lateral segments in situ (FIG 1).
It is a technically demanding operative procedure for large or deep-seated tumors located at the central part of the liver. It essentially requires two hepatic parenchymal dissections in close proximity to the hepatic veins and inferior vena cava (IVC) while preserving the portal pedicles to the remaining hepatic segments and results in two cut surfaces of the liver.
Because it conserves more liver parenchyma, central hepatectomy should be considered (vs. extended hepatectomy) in patients with centrally located tumors and compromised liver function (FIG 2).
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Resection of benign neoplasms of the central liver is indicated for one or more of three indications: (1) to relieve symptoms, (2) because the diagnosis is uncertain, or (3) to prevent malignant transformation (FIG 2).
Hemangioma
Adenoma, angiomyolipoma (AML)
Complex cysts
Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)
Liver resection remains the treatment of choice when appropriate for both primary and secondary central liver malignancies.
Hepatocellular cancer (HCC)
Metastatic cancers
Colorectal cancer
Breast cancer
Ovarian cancer
Lung cancer
Others
Sarcoma
PATIENT HISTORY AND PHYSICAL FINDINGS
Hepatic neoplasms may present with abdominal, flank, and/or shoulder pain. Other symptoms include early satiety, weight loss, or increasing abdominal girth.
With modern imaging, many hepatic lesions are an incidental finding in studies obtained as part of follow-up for a previously treated malignancy or for other unrelated indications.
A history of previous hepatitis or jaundice should be solicited.
A detailed history of alcohol consumption should be obtained.
Symptoms of liver failure should be queried including fatigue, lethargy, encephalopathy, and increasing abdominal girth.
The physical exam should focus on evidence of malnutrition including temporal and intrinsic hand muscle atrophy, the presence of ascites or peripheral edema, mental status changes of hepatic encephalopathy, asterixis, and telangiectasia.
IMAGING AND OTHER DIAGNOSTIC STUDIES
All potential liver surgery patients should undergo preoperative viral serologic testing, laboratory assessment of liver function including protein and coagulation profiles, and assessment of the Child-Pugh’s classification score.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or three-dimensional computed tomography (CT) reconstruction of the liver can help identify and map the variations of the intrahepatic vascular structures and their relationship to tumors (FIG 2).
CT with volumetric assessment is useful to determine if the planned hepatic remnant volume is adequate.1
Alternatively, hepatic functional reserve can be determined by indocyanine green (ICG) clearance or ICG 15 minutes retention (15-R). Central hepatectomy should be considered in patients with an ICG 15-R less than 20%.2
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
Preoperative Planning
A complete medical history is essential. In particular, underlying cardiac or pulmonary comorbidities should be thoroughly evaluated prior to determining whether a patient is a candidate for liver resection.
For malignant lesions, the evaluation for extrahepatic metastases should include a chest CT.
The risk of postoperative hepatic failure should be determined. Central hepatectomy is performed for patients with underlying liver disease. A preoperative liver biopsy to determine the extent of disease may be warranted in high-risk patients to avoid nontherapeutic laparotomy.
The Child-Pugh score is the most commonly employed clinical tool for selection of surgical candidates. Most patients
being considered for central hepatectomy will be classified as Child-Pugh A.
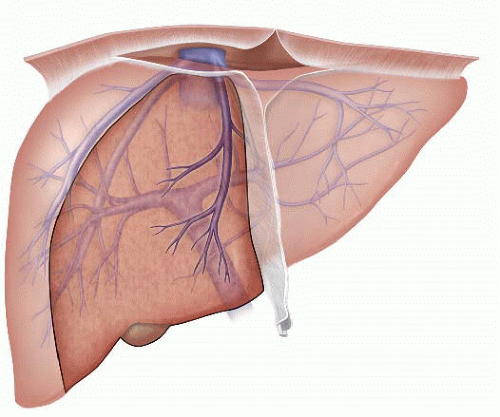
FIG 1 • Resection area: Central hepatectomy removing part or all of the left medial sector and right anterior sector.
For central hepatectomy, preoperative portal vein embolization is rarely employed as it is often difficult to determine which side of the portal vein should be embolized. Although preoperative transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) has been suggested for reducing HCC tumor size and for facilitating the subsequent resection, in patients who underwent preoperative TACE, cholecystitis and dense adhesions around the liver hilum developed, thus increasing the operative complexity.
Positioning
The patient should be positioned supine, in gentle reverse Trendelenburg, with both arms extended.
If suprahepatic control of the IVC is planned or possible, the right arm should be tucked and the chest included in the sterile field.
Arterial, central venous, and urethral catheters were inserted preoperatively to monitor vital signs, intravascular volume, and urine output during the operation.
TECHNIQUES
The essential principles of central hepatectomy are (1) control of inflow vessels, (2) control of outflow vessels, (3) parenchymal transection, (4) identifying and controlling potential sites of bile leak, and (5) preserving the vascular inflow and outflow of the hepatic remnant.
INCISION AND INITIAL EXPLORATION
The abdomen is entered through a right subcostal margin or a bilateral subcostal margin incision. Most surgeons use a bilateral subcostal incision extended vertically to the xiphoid process.
A right thoracoabdominal incision should be considered. This is particularly relevant when tumor is large and involving the dome of the liver. In this circumstance, control of the hepatic veins and the vena cava may prove very difficult. The morbidity of a thoracoabdominal incision is preferable to potentially catastrophic hemorrhage.
The liver is bimanually palpated; hepatic metastases and the degree of cirrhosis are determined. Extrahepatic metastases and potential portal adenopathy are assessed, and specimens obtained for frozen section if indicated.
Intraoperative ultrasonography is used to delineate the extent of the neoplasm, the relationship of the lesion to vital structures, and mark the plane of the parenchymal transection.
MOBILIZATION OF LIVER
The round ligament is divided and the falciform ligament incised and separated from the anterior abdominal wall.
The peritoneal reflections that form the triangular ligament are incised and the diaphragm fully mobilized from all attachments to the liver. If, in the course of mobilization, tumor is found to involve the diaphragm, the affected area of the diaphragm may be excised and subsequently repaired with pledgeted sutures.
The suprahepatic IVC and the hepatic veins above the liver are dissected to facilitate the subsequent approach to the hepatic veins.
The caudate lobe is fully dissected from the IVC, controlling the small hepatic veins that directly drain into the IVC with clips and/or ligatures. An accessory posterior right hepatic vein is often encountered and may require suture ligation to obtain reliable control of the vessel.
DISSECTION OF THE PORTA HEPATIS
The classic approach involves extrahepatic control of the inflow vessels (hepatic artery and portal vein) and biliary tree.
The sheath of the porta hepatis is opened laterally. The cystic duct and artery are ligated and divided. The gallbladder may be either removed or left attached to the liver to preserve a margin when appropriate.
The portal vein is followed cephalad up to and above the bifurcation. There is usually a small branch that passes posteriorly from the right portal vein to the caudate lobe. Control and division of this vessel is important during middle hepatectomy.
The right anterior branch and left medial branches of the portal vein and hepatic artery are circumferentially dissected, controlled with vessel loops, and then with vascular clamps prior to being divided and ligated (FIGS 3 and 4). These vessels supply the right lobe anterior segments (Couinaud’s segments 5 and 8) and the left medial segment (Couinaud’s segments 4a and 4b). The usual practice is to ligate the right anterior branch and left medial branch of the artery and portal vein (sometimes including hepatic duct), working from anterior to posterior.
Typically, unless the tumor involves the middle hepatic vein close to its junction with the IVC, the middle hepatic vein is not controlled extrahepatically. It is identified, controlled, and divided during the parenchymal dissection.
When feasible, the middle hepatic vein is extraparenchymally isolated, cross-clamped, and divided at its insertion (FIG 5). There are two methods for exposing the middle hepatic vein extrahepatically:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree