Cartilaginous Hamartoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Benign mesenchymoma
Clinical Issues
Intrapulmonary coin lesion of variable size
Central or peripheral tumor
Complete surgical resection
Excellent prognosis
Macroscopic Features
Well-circumscribed lesion
Firm with mucoid and cartilaginous areas
Usually a single lesion
Rarely hamartomas may present as multiple intrapulmonary lesions
Top Differential Diagnoses
Bronchial chondromas
Do not show invaginations of respiratory epithelium
May be associated with other conditions, such as gastric smooth muscle tumors
Pleomorphic adenoma
Shows presence of epithelial component that immunophenotypically is myoepithelial
PA in the lung rarely will show mature cartilage
Also lacks presence of invaginations of respiratory epithelium
Chondrosarcoma
Will display more cellular atypia
Does not have admixture of adipose tissue
Lacks presence of invaginations of respiratory epithelium
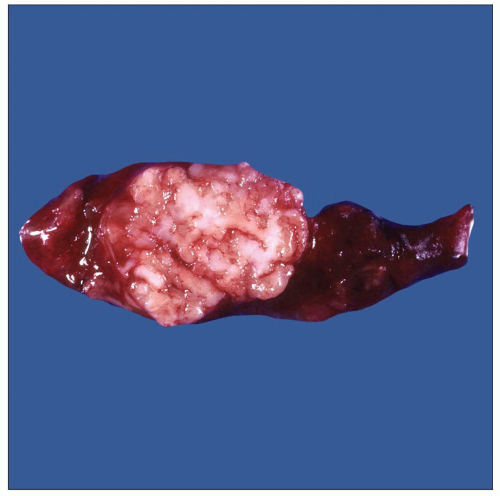 Gross photograph shows a well-circumscribed intrapulmonary tumor, slightly lobulated with a cartilaginous appearance. These features are classical for cartilaginous hamartoma. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Cartilaginous hamartoma (CH)
Synonyms
Benign mesenchymoma
Definitions
Benign mesenchymal tumor of the lung
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Pathogenesis
It is not clear whether CH represents a true tumor or hamartomatous lesion
Thus, both terms, benign mesenchymoma and hamartoma, have been used interchangeably
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Intrapulmonary coin lesion of variable size
Central or peripheral tumor
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete surgical resection
Prognosis
Excellent prognosis; cured by simple excision
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Well-circumscribed lesion
Firm with mucoid and cartilaginous areas
Usually solitary
Rarely hamartomas may present as multiple intrapulmonary lesions
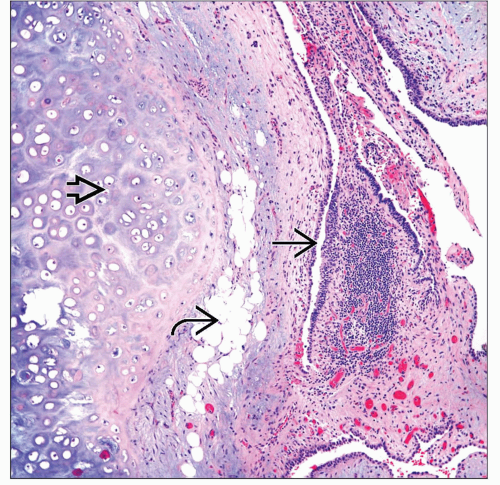
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Mature cartilage
Adipose tissue
Myxoid stroma
Invaginations of respiratory epithelium
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Chondromyxoid
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Cartilaginous
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Bronchial Chondroma
Does not show invaginations of respiratory epithelium
Branchial chondroma rarely will show additional adipose tissue
May be associated with other conditions, such as gastric smooth muscle tumors
Pleomorphic Adenoma (PA)
Shows presence of epithelial component that immunophenotypically is myoepithelial
PA in the lung rarely shows mature cartilage
Also lacks presence of invaginations of respiratory epithelium
Chondrosarcoma, Primary or Metastatic
Displays more cellular atypia
Does not have admixture of adipose tissue
Lacks presence of invaginations of respiratory epithelium
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree