Caroli Disease
Joseph Misdraji, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Congenital segmental dilatation of intrahepatic bile ducts
Caroli syndrome when associated with congenital hepatic fibrosis
Clinical Issues
Characterized by cholangitis, hepatolithiasis, abscess, and sepsis
Associated with ARPKD
Cholangiocarcinoma develops in 7-24% of cases
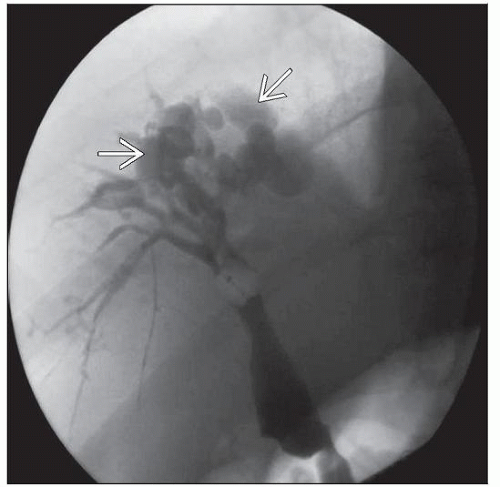
Image Findings
Cholangiogram shows intrahepatic saccular duct dilatation
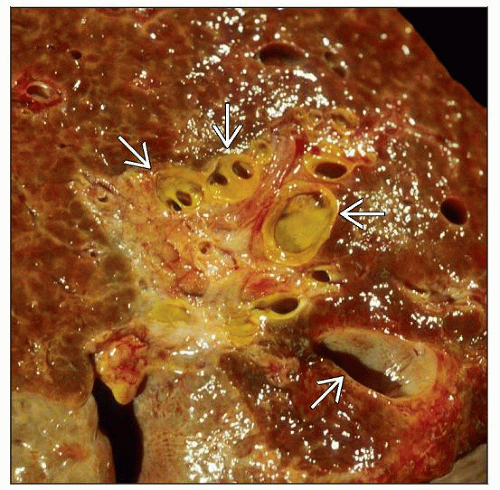
Microscopic Pathology
Dilated intrahepatic bile ducts may show periductal fibrosis, inflammation, or frank abscesses
Background liver can show congenital hepatic fibrosis
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Congenital cystic dilatation of intrahepatic biliary tree
Communicating cavernous ectasia
Type V choledochal cyst
Definitions
Caroli disease: Congenital segmental dilatation of larger intrahepatic bile ducts
Caroli syndrome: Congenital segmental dilatation of larger intrahepatic bile ducts in conjunction with congenital hepatic fibrosis (CHF)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Developmental Anomaly
Total or partial arrest of remodeling of ductal plate of larger intrahepatic bile ducts
Caroli disease
Only larger ducts affected
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree