Class
- Skeletal muscle relaxant, centrally acting
Carisoprodol
Commonly Prescribed for
(FDA approved in bold)
- Acute painful musculoskeletal conditions
- Muscle spasm
- Insomnia
Carisoprodol
 How the Drug Works
How the Drug Works
- Sedative, may block interneuronal activity in the descending reticular formation and spinal cord
Carisoprodol
How Long Until It Works
- Pain – as little as 30 minutes
Carisoprodol
If It Works
- Titrate to most effective tolerated dose
Carisoprodol
If It Doesn’t Work
- Increase dose. If ineffective, consider alternative medications
Carisoprodol
 Best Augmenting Combos for Partial Response or Treatment-Resistance
Best Augmenting Combos for Partial Response or Treatment-Resistance
- Botulinum toxin is effective, especially as an adjunct for focal spasticity, i.e., post-stroke or head injury affecting the upper limbs
- Use other centrally acting muscle relaxants with caution due to potential additive CNS depressant effect
Carisoprodol
Tests
- None required
Adverse Effects (AEs)
Carisoprodol
How Drug Causes AEs
- Most are related to sedative effects
Carisoprodol
Notable AEs
- Drowsiness, dizziness, vertigo, ataxia, depression, nausea/vomiting, tachycardia, postural hypotension, facial flushing
Carisoprodol
 Life-Threatening or Dangerous AEs
Life-Threatening or Dangerous AEs
- Hypersensitivity reactions rarely occur after the first dose. Symptoms include extreme weakness, ataxia, vision loss, dysarthria, and euphoria. Serious allergic reactions, such as erythema multiforme, eosinophilia, asthmatic episodes, fever, angioedema, and anaphylactoid shock have been reported
Carisoprodol
Weight Gain
- Unusual

Carisoprodol
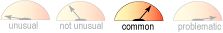
Sedation
- Common
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


