Cardiovascular System
Atif Ahmed
▪ Questions and Answers
1. Which of the following statements is true about the human heart?
a. It develops from two tubes that later divide into four chambers.
b. It is first recognizable at 15 days of gestation.
c. It starts to pump at 8 weeks of gestation.
d. Tetralogy of Fallot is the most common congenital anomaly.
e. Congenital heart defects are present in 6 per 100,000 live births.
View Answer
1. b. The heart develops from a single tube and is first recognizable at 15 days of gestation. Congenital heart diseases have an incidence of 6 per 1,000 live births. Chamber septal defects are the most common congenital heart anomaly.
2. The most common chromosomal abnormality associated with congenital heart disease is:
a. 46,XY inv (3)(p21q22)
b. Deletions in chromosomal region 22q11.2
c. 45XO chromosomal karyotype
d. Trisomy 21
e. Trisomy 18
View Answer
2. d. Trisomy 21 is the most common cytogenetic abnormality and is specifically associated with complete atrioventricular canal defect and left ventricular outflow obstruction. Turner syndrome (45XO) is commonly associated with bicuspid aortic valve and coarctation of the aorta and DiGeorge syndrome (deletions in chromosomal region 22q11.2) is associated with persistent truncus arteriosus.
3. The most common valvular abnormality in the United States is:
a. Mitral valve prolapse
b. Aortic valve disease
c. Subaortic stenosis
d. Pulmonic stenosis
e. Rheumatic mitral stenosis
View Answer
3. a. Mitral valve prolapse occurs in 1% to 3% of the population and is most commonly seen in Marfan syndrome. Other common valvular disease includes congenital aortic valve disease, which commonly presents at 50 to 70 years of age and manifests as stenosis in most cases.
4. Congenital heart anomalies LEAST frequently associated with microdeletions in chromosome 22q11 include:
a. Persistent truncus arteriosus
b. Tetralogy of Fallot
c. Interrupted aortic arch
d. Patent ductus arteriosus
e. Right-sided aortic arch
View Answer
4. d. Conotruncal malformations, commonly associated with velocardiofacial syndrome (deletions in 22q11), include persistent truncus arteriosus, absent ductus arteriosus, interrupted aortic arch, tetralogy of Fallot, and right-sided aortic arch. Coarctation of the aorta is less common. Patent ductus arteriosus, on the other hand, is commonly associated with trisomy 21 and congenital rubella infection.
5. In complete transposition of the great vessels, there is:
a. Atrioventricular (AV) discordance with ventriculoarterial concordance
b. AV discordance associated with ventriculoarterial discordance
c. AV concordance associated with ventriculoarterial discordance
d. AV concordance associated with ventriculoarterial concordance
View Answer
5. c. This is the typical scenario of complete transposition: the aorta ascends parallel and to the right of the pulmonary artery. There is AV concordance because the right atrium communicates with the right ventricle from which the aorta arises and the left atrium is in continuity with the left ventricle from which the pulmonary artery arises.
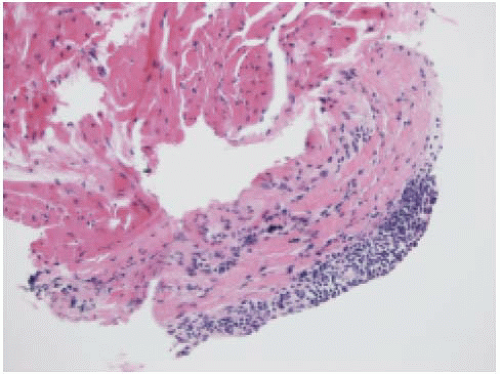
6. What is the most likely cause of this lesion (Fig. 9.1), which is seen in endomyocardial biopsy of a heart transplant recipient patient?
a. Effect of chemotherapy
b. Recurrent Chagas disease of the heart
c. Direct effect from placement of pacemaker wires
d. Acute transplant rejection
e. Restrictive cardiomyopathy
View Answer
6. d. The image shows “Quilty lesion,” which is a dense endocardial collection of lymphocytes. This phenomenon is seen in heart-transplant patients receiving cyclosporine therapy and is not related to rejection.
7. What is the most common metastatic tumor to the heart?
a. Prostatic carcinoma
b. Carcinoma of the lung
c. Rhabdomyosarcoma
d. Melanoma
e. Colon carcinoma
View Answer
7. b. Carcinoma of the lung is the most frequent metastatic tumor to heart, followed by lymphoma, breast carcinoma, and other tumors.
8. What is the most common cardiovascular abnormality seen in patients with congenital rubella syndrome?
a. Patent ductus arteriosus
b. Interrupted aortic arch
c. Coarctation of the aorta
d. Ventricular septal defect
e. Transposition of the great vessels
View Answer
8. a. Congenital heart defects result from rubella infection in the first 3 months of gestation. The most common anatomic defects include patent ductus arteriosus, pulmonary artery stenosis, and systemic arterial hypoplasia.
9. Brown-Brenn is a special stain that is used in which of the following conditions?
a. To delineate loss of elastic tissue in Marfan syndrome patients
b. To highlight intracellular lipid
c. To stain Gram-positive bacteria
d. Is a stain for myxoid degeneration in heart valves
e. To stain mycobacterial organisms
View Answer
9. c. Brown-Brenn stain is a modified Gram stain for bacteria. This stain is indicated in cases of infective endocarditis endocardial vegetations.
10. These are histologic sections of a tumor identified in the heart of a 37-year-old woman with signs of mitral valve stenosis (Fig. 9.2). Which of the following statements best describes this lesion?
a. It is the most common primary heart tumor found in this age group.
b. It is most commonly located in the right ventricle.
c. It can regress spontaneously without treatment.
d. It is an aggressive tumor with potential for metastasis and high mortality.
e. It is a hamartomatous lesion.
View Answer
10. a. Cardiac myxoma is the most common primary tumor of the heart and constitutes 50% to 80% of primary heart tumors. It is most commonly located in the atrium and characteristically presents as a heart murmur that changes with time and position.
11. What is the most common artificial heart valve used in surgical practice?
a. Bioprosthetic heart valve
b. Björk-Shiley valve
c. Medtronic-Hall tilting disk valve
d. St. Jude valve
e. Starr-Edwards valve
View Answer
11. a. The most common artificial heart valves are bioprosthetic valves. The remaining choices are examples of mechanical valves.
12. All of the following morphologic cardiomyopathic changes are associated with Adriamycin therapy EXCEPT:
a. Loss of cross striations in the myocytes
b. Inflammatory infiltrate of mononuclear cells
c. Myocytolysis
d. Loss of cytoplasmic myofilaments
e. Vacuolization of cardiac myocytes
View Answer
12. b. Cardiomyopathy related to Adriamycin is characterized by myofibrillar loss and vacuolar degeneration of heart myocytes. Electron microscopy reveals distension and swelling of the endoplasmic reticulum. Inflammation is notably minimal to absent.
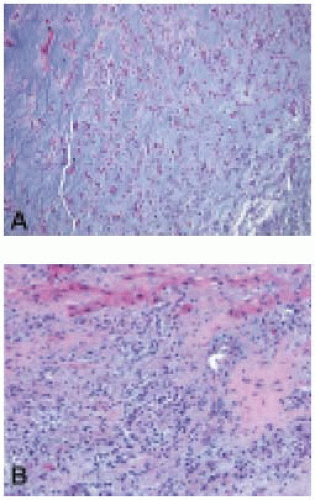
13. A heart transplant recipient has undergone an endomyocardial biopsy 2 months after the transplant (Fig. 9.3). Additional significant histologic findings to look for in the biopsy that will determine the management of this patient include the identification of:
a. Nodular subendocardial lymphocytic infiltrate
b. Interstitial fibrosis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree