CHAPTER 10 Cardiovascular Disorders
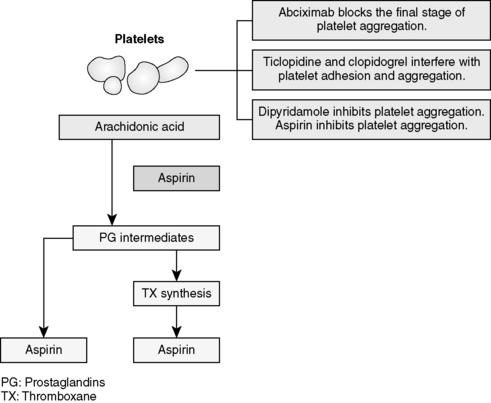
Figure 10-2 Action for antiplatelet drugs.
(Modified from Lilley LL, Harrington S, Snyder JS: Pharmacology and the nursing process, ed. 5, St. Louis, 2007, Mosby. In Mosou K, Snipe K: Pharmacology for pharmacy technicians. St. Louis, 2009, Mosby.)

Figure 10-3 Algorithm for digoxin therapy for heart failure.
(Modified from Morris S, Hatcher HF, Reddy DK: Digoxin therapy for heart failure: An update, American Family Physician, August 15, 2006. Available at: http://www.aafp.org/afp/20060815/613.html.)
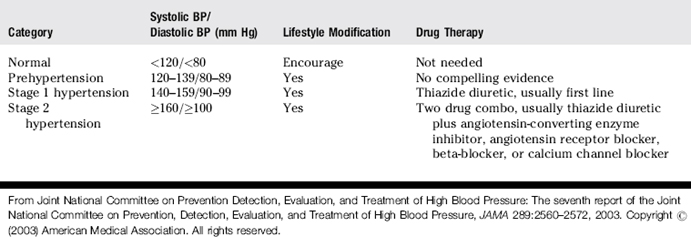
Fields L.E., Burt V.L., Cutler J.A., et al. The burden of adult hypertension in the United States 1999 to 2000: a rising tide. Hypertension. 2004;44:1-7.
Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection. Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA.. 2001;285:2486-2497.
Joint National Committee on Prevention Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. The seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. JAMA. 2003;289:2560-2572.
Vaughan Williams E.M. Classification of anti-arrhythmic drugs. Sandfte E., Flensted-Jensen E., editors. Symposium on Cardiac Arrhythmias. 1970 Sweden, AB ASTRA:Södertälje. 449-472
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree