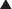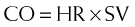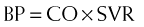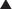Chapter 11 Cardiology
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACEIs)
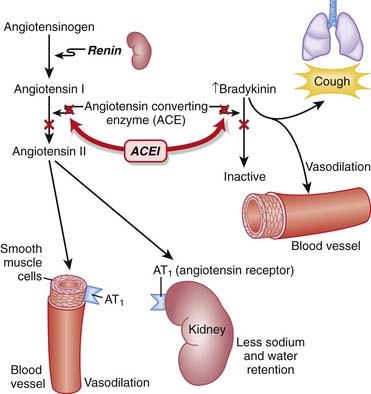
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Through inhibition of ACE with an ACEI, the following effects occur:
Through inhibition of ACE with an ACEI, the following effects occur: Net result: Because angiotensin II levels are lower and bradykinin levels are higher, there is more vasodilation; SVR (systemic vascular resistance) and afterload are lowered. Because aldosterone levels are lower, less Na and water are reabsorbed in the kidney; therefore preload is reduced (Figure 11-1).
Net result: Because angiotensin II levels are lower and bradykinin levels are higher, there is more vasodilation; SVR (systemic vascular resistance) and afterload are lowered. Because aldosterone levels are lower, less Na and water are reabsorbed in the kidney; therefore preload is reduced (Figure 11-1).Pharmacokinetics
 Most ACEIs are cleared predominantly by the kidneys. Dose adjustment should be considered in renal impairment.
Most ACEIs are cleared predominantly by the kidneys. Dose adjustment should be considered in renal impairment.Contraindications
 Pregnancy: During the second and third trimesters, the teratogenic effects are thought to be caused in part by fetal hypotension.
Pregnancy: During the second and third trimesters, the teratogenic effects are thought to be caused in part by fetal hypotension.Side Effects
 Dry cough: Attributed to increased bradykinin levels. Can be persistent enough to affect compliance and may lead to discontinuation.
Dry cough: Attributed to increased bradykinin levels. Can be persistent enough to affect compliance and may lead to discontinuation. Hyperkalemia: Particularly in combination with K+-sparing diuretics. Hyperkalemia occurs via the reduction in aldosterone but is usually clinically significant only with the addition of oral K+ or in patients with renal dysfunction.
Hyperkalemia: Particularly in combination with K+-sparing diuretics. Hyperkalemia occurs via the reduction in aldosterone but is usually clinically significant only with the addition of oral K+ or in patients with renal dysfunction. Hypotension: Caused by vasodilation from lower levels of angiotensin II. Patients with ventricular dysfunction (low ejection fraction) are at greater risk.
Hypotension: Caused by vasodilation from lower levels of angiotensin II. Patients with ventricular dysfunction (low ejection fraction) are at greater risk. Renal dysfunction: Angiotensin II plays an important role in maintaining glomerular filtration rate (GFR) by constricting the efferent (outgoing) arteriole of the glomerulus. This is particularly important when the blood flow to the kidneys has been compromised. ACEIs cause vasodilation of the efferent arteriole. This decreases the glomerular pressure and reduces GFR. Volume depletion amplifies this effect.
Renal dysfunction: Angiotensin II plays an important role in maintaining glomerular filtration rate (GFR) by constricting the efferent (outgoing) arteriole of the glomerulus. This is particularly important when the blood flow to the kidneys has been compromised. ACEIs cause vasodilation of the efferent arteriole. This decreases the glomerular pressure and reduces GFR. Volume depletion amplifies this effect. Angioedema: A rare but serious adverse effect, often attributed to the increased bradykinin levels, although a definitive mechanism has not been established. Angioedema is edema caused by pathologically leaky blood vessels. It can cause swollen lips or tongue, and death can also result from airway obstruction.
Angioedema: A rare but serious adverse effect, often attributed to the increased bradykinin levels, although a definitive mechanism has not been established. Angioedema is edema caused by pathologically leaky blood vessels. It can cause swollen lips or tongue, and death can also result from airway obstruction.Important Notes
 The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) plays an important role in the body’s compensation for a failing heart. Activation of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) leads to the release of renin, which in turn increases vascular tone and sodium and water retention.
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) plays an important role in the body’s compensation for a failing heart. Activation of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) leads to the release of renin, which in turn increases vascular tone and sodium and water retention. ACEIs might be of particular use in the management of HTN in the diabetic patient, as they may delay the development of diabetic nephropathy. This is primarily because of a reduction in intraglomerular pressure, through relaxation of the efferent arteriole and the overall reduction in systemic blood pressure (BP).
ACEIs might be of particular use in the management of HTN in the diabetic patient, as they may delay the development of diabetic nephropathy. This is primarily because of a reduction in intraglomerular pressure, through relaxation of the efferent arteriole and the overall reduction in systemic blood pressure (BP).Advanced
 In addition to the beneficial effects of RAS inhibitors in diabetic nephropathy, there is emerging evidence that RAS inhibitors may reduce the incidence of new-onset diabetes. Potential mechanisms for this effect include improvements in blood flow that improve the delivery of insulin and glucose to skeletal muscle, as well as effects on glucose transport and insulin signaling. If this preventative effect of RAS inhibition in diabetes becomes established, it could change the way these agents are used.
In addition to the beneficial effects of RAS inhibitors in diabetic nephropathy, there is emerging evidence that RAS inhibitors may reduce the incidence of new-onset diabetes. Potential mechanisms for this effect include improvements in blood flow that improve the delivery of insulin and glucose to skeletal muscle, as well as effects on glucose transport and insulin signaling. If this preventative effect of RAS inhibition in diabetes becomes established, it could change the way these agents are used. ONTARGET (Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in Combination with Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial) was a large (approximately 8500 patients per arm), long-term (median follow-up of 56 months) study comparing an angiotensin-receptor blocker (ARB), an ACEI, and a combination of the two in patients with vascular disease or high-risk diabetes. The study found that the combination of ARB and ACEI failed to demonstrate benefit versus either agent alone, with an increased incidence of adverse events in this population.
ONTARGET (Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in Combination with Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial) was a large (approximately 8500 patients per arm), long-term (median follow-up of 56 months) study comparing an angiotensin-receptor blocker (ARB), an ACEI, and a combination of the two in patients with vascular disease or high-risk diabetes. The study found that the combination of ARB and ACEI failed to demonstrate benefit versus either agent alone, with an increased incidence of adverse events in this population.Evidence
Hypertension
 A 2009 Cochrane review (24 trials, N = 58,040 participants) compared benefits and harms of first-line antihypertensives with those of placebo or no treatment over a minimum of 1 year in patients with hypertension. ACEIs (three trials) reduced mortality (relative risk [RR] 0.83), stroke (RR 0.65), coronary heart disease (RR 0.81), and cardiovascular events (RR 0.76).
A 2009 Cochrane review (24 trials, N = 58,040 participants) compared benefits and harms of first-line antihypertensives with those of placebo or no treatment over a minimum of 1 year in patients with hypertension. ACEIs (three trials) reduced mortality (relative risk [RR] 0.83), stroke (RR 0.65), coronary heart disease (RR 0.81), and cardiovascular events (RR 0.76).FYI Notes
 Brady means slow (e.g., bradycardia). Bradykinin is so named because it causes slow contractions of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
Brady means slow (e.g., bradycardia). Bradykinin is so named because it causes slow contractions of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Bradykinin is also implicated in the edema that accompanies sepsis, allergic reactions, and carcinoid syndrome. Angioedema is associated with a deficiency of C1 esterase, an enzyme that cleaves bradykinin.
Bradykinin is also implicated in the edema that accompanies sepsis, allergic reactions, and carcinoid syndrome. Angioedema is associated with a deficiency of C1 esterase, an enzyme that cleaves bradykinin.Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
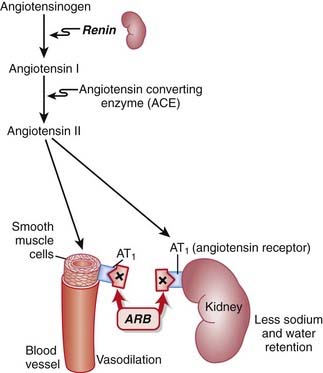
 ARBs are antagonists of the angiotensin-1 (AT1) receptor. Therefore they block the actions of angiotensin II.
ARBs are antagonists of the angiotensin-1 (AT1) receptor. Therefore they block the actions of angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a vasoactive hormone that induces vasoconstriction and stimulates the secretion of aldosterone by the adrenal cortex, which results in sodium and water retention.
Angiotensin II is a vasoactive hormone that induces vasoconstriction and stimulates the secretion of aldosterone by the adrenal cortex, which results in sodium and water retention. Blocking AT1 results in vasodilation, natriuresis (renal loss of sodium), and diuresis (renal loss of water).
Blocking AT1 results in vasodilation, natriuresis (renal loss of sodium), and diuresis (renal loss of water). ACEIs block the degradation of bradykinins. ARBs have no effect on bradykinin levels. Because bradykinins are vasodilators, ARBs might not produce as much vasodilation as ACEIs.
ACEIs block the degradation of bradykinins. ARBs have no effect on bradykinin levels. Because bradykinins are vasodilators, ARBs might not produce as much vasodilation as ACEIs. Conversely, ACE is not the only enzyme that forms angiotensin II. Thus ARBs might provide more complete inhibition of the vasopressor activity of angiotensin II compared with ACEIs (Figure 11-2).
Conversely, ACE is not the only enzyme that forms angiotensin II. Thus ARBs might provide more complete inhibition of the vasopressor activity of angiotensin II compared with ACEIs (Figure 11-2).Pharmacokinetics
 All ARBs have intermediate (12 to 24 hour) half-lives and thus provide the advantage of once-daily dosing.
All ARBs have intermediate (12 to 24 hour) half-lives and thus provide the advantage of once-daily dosing.Side Effects
 Renal failure can occur in patients whose renal function is marginal or highly dependent on the RAS, because of the same mechanism seen with ACEIs.
Renal failure can occur in patients whose renal function is marginal or highly dependent on the RAS, because of the same mechanism seen with ACEIs.Important Notes
 Perhaps because of the lack of increased bradykinin levels, ARBs are not typically associated with the side effect of cough, which can be a significant limitation to the use of ACEIs.
Perhaps because of the lack of increased bradykinin levels, ARBs are not typically associated with the side effect of cough, which can be a significant limitation to the use of ACEIs.Advanced
 In addition to the beneficial effects of RAS inhibitors in diabetic nephropathy, there is emerging evidence that RAS inhibitors may reduce the incidence of new-onset diabetes. Potential mechanisms for this effect include improvements in blood flow that improve the delivery of insulin and glucose to skeletal muscle, as well as effects on glucose transport and insulin signaling. If this preventative effect of RAS inhibition in diabetes becomes established, it could change the way these agents are used.
In addition to the beneficial effects of RAS inhibitors in diabetic nephropathy, there is emerging evidence that RAS inhibitors may reduce the incidence of new-onset diabetes. Potential mechanisms for this effect include improvements in blood flow that improve the delivery of insulin and glucose to skeletal muscle, as well as effects on glucose transport and insulin signaling. If this preventative effect of RAS inhibition in diabetes becomes established, it could change the way these agents are used. ACEIs reduce the effect of both AT1 and AT2 receptors by lowering levels of angiotensin II; only AT1 receptors are inhibited by ARBs. Chronic stimulation of the AT2 receptor may be beneficial in providing neuroprotection in older patients with HTN and thus could mean that ARBs have a potential advantage in this patient subset.
ACEIs reduce the effect of both AT1 and AT2 receptors by lowering levels of angiotensin II; only AT1 receptors are inhibited by ARBs. Chronic stimulation of the AT2 receptor may be beneficial in providing neuroprotection in older patients with HTN and thus could mean that ARBs have a potential advantage in this patient subset. ONTARGET (Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in Combination with Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial) was a large (approximately 8500 patients per arm), long-term (median follow-up of 56 months) study comparing an ARB, an ACEI, and a combination of the two in patients with vascular disease or high-risk diabetes. The study found that the combination of ARB and ACEI failed to demonstrate benefit versus either agent alone, with an increased incidence of adverse events in this population.
ONTARGET (Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in Combination with Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial) was a large (approximately 8500 patients per arm), long-term (median follow-up of 56 months) study comparing an ARB, an ACEI, and a combination of the two in patients with vascular disease or high-risk diabetes. The study found that the combination of ARB and ACEI failed to demonstrate benefit versus either agent alone, with an increased incidence of adverse events in this population.Direct Renin Inhibitors
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
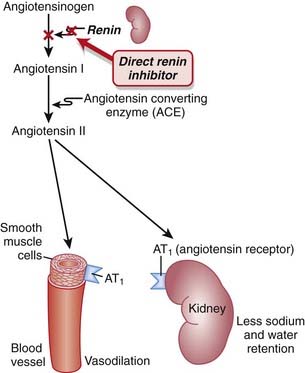
 Renin is an enzyme released from the kidneys that converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I. It is considered to be the rate-limiting step in the eventual formation of angiotensin II.
Renin is an enzyme released from the kidneys that converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I. It is considered to be the rate-limiting step in the eventual formation of angiotensin II. Renin and its inactive precursor, prorenin, are stored in the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney. Renin is released in response to three different stimuli:
Renin and its inactive precursor, prorenin, are stored in the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney. Renin is released in response to three different stimuli: Other agents that target the RAS, such as the ACEIs and ARBs, elicit a compensatory increase in plasma renin activity, resulting in increased binding of angiotensin II to AT1 receptors and other AT receptors.
Other agents that target the RAS, such as the ACEIs and ARBs, elicit a compensatory increase in plasma renin activity, resulting in increased binding of angiotensin II to AT1 receptors and other AT receptors. Therefore, one potential advantage of renin antagonists over ACEIs and ARBs is avoiding the compensatory increase in the RAS. It is yet to be established whether these theoretical advantages translate into clinically meaningful advantages (Figure 11-3).
Therefore, one potential advantage of renin antagonists over ACEIs and ARBs is avoiding the compensatory increase in the RAS. It is yet to be established whether these theoretical advantages translate into clinically meaningful advantages (Figure 11-3).Evidence
Blood-Pressure Lowering Efficacy versus Placebo
 A 2008 Cochrane review (six trials, 3694 participants) compared the blood-pressure–lowering efficacy of renin inhibitors versus placebo in primary HTN. The authors found that aliskiren elicits a dose-dependent reduction in both systolic and diastolic pressure similar to that seen with ACEIs or ARBs. In the included trials, aliskiren did not increase withdrawals due to adverse events versus placebo.
A 2008 Cochrane review (six trials, 3694 participants) compared the blood-pressure–lowering efficacy of renin inhibitors versus placebo in primary HTN. The authors found that aliskiren elicits a dose-dependent reduction in both systolic and diastolic pressure similar to that seen with ACEIs or ARBs. In the included trials, aliskiren did not increase withdrawals due to adverse events versus placebo.FYI Notes
 Renin was first identified in 1898, when it was extracted from kidneys and discovered to have pressor properties. It would be another 40 years before it was determined that renin was an enzyme that catalyzed the formation of a pressor substance (angiotensin II), rather than being the pressor itself.
Renin was first identified in 1898, when it was extracted from kidneys and discovered to have pressor properties. It would be another 40 years before it was determined that renin was an enzyme that catalyzed the formation of a pressor substance (angiotensin II), rather than being the pressor itself. Although renin inhibitors were considered to be the most obvious target for inhibition of the RAS, it took several decades to develop the first direct renin inhibitor. Two main hurdles were finding an agent with sufficient bioavailability and an agent with high affinity for the active site of the renin enzyme.
Although renin inhibitors were considered to be the most obvious target for inhibition of the RAS, it took several decades to develop the first direct renin inhibitor. Two main hurdles were finding an agent with sufficient bioavailability and an agent with high affinity for the active site of the renin enzyme.Sodium Channel Blockers (Class I Antiarrhythmics)
Description
Na channel blockers are Vaughan Williams class I antiarrhythmics. There are three subclasses: Ia, Ib, and Ic. The use of Na channel blockers as local anesthetics is discussed in the discussion of local anesthetics in Chapter 21.
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
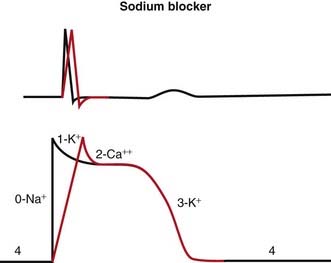
 Na channels are blocked, so Na ion movement during phase 0 of the action potential is inhibited. The result is a “slow” phase 0, which results in a wider (and slower) QRS wave on the electrocardiogram (ECG). The net result is slower conduction (Figure 11-4).
Na channels are blocked, so Na ion movement during phase 0 of the action potential is inhibited. The result is a “slow” phase 0, which results in a wider (and slower) QRS wave on the electrocardiogram (ECG). The net result is slower conduction (Figure 11-4). Phase 3 can be longer or shorter, depending on the subclass (a, b, or c). This is omitted in the diagram for simplicity.
Phase 3 can be longer or shorter, depending on the subclass (a, b, or c). This is omitted in the diagram for simplicity. Changing the duration of the action potential (not shown in diagram) influences the QT interval (distance from the QRS to the T wave). This distance can be thought of as the refractory period of the ECG. Therefore changing the action potential durations will change the refractory times of atrial, Purkinje or ventricular tissues.
Changing the duration of the action potential (not shown in diagram) influences the QT interval (distance from the QRS to the T wave). This distance can be thought of as the refractory period of the ECG. Therefore changing the action potential durations will change the refractory times of atrial, Purkinje or ventricular tissues. Because abnormal electrical circuits require a delicate balance between conduction speed and refractory times, changing these parameters will sometimes terminate dysrhythmias or create new ones.
Because abnormal electrical circuits require a delicate balance between conduction speed and refractory times, changing these parameters will sometimes terminate dysrhythmias or create new ones.Pharmacokinetics
 Quinidine interacts with digoxin (CP450). This can result in increased levels of digoxin, a toxic drug with a narrow therapeutic index. Both drugs are antiarrhythmic drugs and have the potential to be coadministered.
Quinidine interacts with digoxin (CP450). This can result in increased levels of digoxin, a toxic drug with a narrow therapeutic index. Both drugs are antiarrhythmic drugs and have the potential to be coadministered.Side Effects
 Proarrhythmic: As with all antiarrhythmics, changing the delicate balance of conduction speed and refractory times might provoke another area of the conducting system into developing a dysrhythmia.
Proarrhythmic: As with all antiarrhythmics, changing the delicate balance of conduction speed and refractory times might provoke another area of the conducting system into developing a dysrhythmia. Nervous system dysfunction: Na channels are required for nerve function. Numbness and tingling of the lips and tongue, ringing in the ear, inappropriate behavior, decreased consciousness, and seizures can all occur.
Nervous system dysfunction: Na channels are required for nerve function. Numbness and tingling of the lips and tongue, ringing in the ear, inappropriate behavior, decreased consciousness, and seizures can all occur.Evidence
 Atrial fibrillation and prevention of recurrence: A Cochrane review in 2007 (45 studies, 12,559 patients) evaluated the efficacy and safety of multiple different antiarrhythmics in patients who had previously experienced atrial fibrillation (a very common arrhythmia). Class Ia antiarrhythmics were associated with increased mortality compared with controls (odds ratio [OR] 2.39; number needed to harm [NNH] 109). Class Ia and Ic were associated with reduced occurrences of atrial fibrillation (OR 0.19 to 0.6). There were many withdrawals from treatment because of side effects for all antiarrhythmics (NNH 17 to 36).
Atrial fibrillation and prevention of recurrence: A Cochrane review in 2007 (45 studies, 12,559 patients) evaluated the efficacy and safety of multiple different antiarrhythmics in patients who had previously experienced atrial fibrillation (a very common arrhythmia). Class Ia antiarrhythmics were associated with increased mortality compared with controls (odds ratio [OR] 2.39; number needed to harm [NNH] 109). Class Ia and Ic were associated with reduced occurrences of atrial fibrillation (OR 0.19 to 0.6). There were many withdrawals from treatment because of side effects for all antiarrhythmics (NNH 17 to 36).β Antagonists (β-Blockers)
Prototype and Common Drugs
 β-Blockers are a heterogeneous family and can be subclassified according to the receptors they antagonize (it is important to know which are β1 selective):
β-Blockers are a heterogeneous family and can be subclassified according to the receptors they antagonize (it is important to know which are β1 selective):MOA (Mechanism of Action)
To understand β-blockers, you must understand the effects of the adrenergic system and which effects are mediated via β receptors. β-Blockers competitively antagonize the action of catecholamines at β receptors. There are many cardiac and noncardiac consequences of β-blockade. More details on the autonomic nervous system are described in Chapter 3.
Hypertension
 Cardiac output (CO) is therefore reduced, which leads to a reduction in BP. Recall:
Cardiac output (CO) is therefore reduced, which leads to a reduction in BP. Recall: where SVR = systemic vascular resistance.
 In addition, β1 antagonism leads to a reduction in renin secretion, which in turn reduces production of angiotensin II, a hormone that induces vasoconstriction and, via aldosterone, sodium retention.
In addition, β1 antagonism leads to a reduction in renin secretion, which in turn reduces production of angiotensin II, a hormone that induces vasoconstriction and, via aldosterone, sodium retention. The utility of β-blockers in myocardial ischemia and infarction results from their ability to reduce HR and contractility and therefore lower O2 demand. They have also proven useful after a MI for the same reason, reducing the workload of the heart.
The utility of β-blockers in myocardial ischemia and infarction results from their ability to reduce HR and contractility and therefore lower O2 demand. They have also proven useful after a MI for the same reason, reducing the workload of the heart.Tachycardia and Arrhythmia
The properties of β-blockers that make them antitachycardics include the following:
1 Depression of the sinoatrial (SA) node (slows automaticity)
 Catecholamine β1 stimulation results in an increase in the slow Na+ current (If) of the action potential phase 4 in the SA node. This results in a faster rising (and shorter) phase 4, a shorter time to the next heartbeat, and thus a faster HR. β-Blockers will oppose this action, slowing the SA pacemaker rate.
Catecholamine β1 stimulation results in an increase in the slow Na+ current (If) of the action potential phase 4 in the SA node. This results in a faster rising (and shorter) phase 4, a shorter time to the next heartbeat, and thus a faster HR. β-Blockers will oppose this action, slowing the SA pacemaker rate.
 Catecholamine β1 stimulation results in an increase in the slow Na+ current (If) of the action potential phase 4 in the SA node. This results in a faster rising (and shorter) phase 4, a shorter time to the next heartbeat, and thus a faster HR. β-Blockers will oppose this action, slowing the SA pacemaker rate.
Catecholamine β1 stimulation results in an increase in the slow Na+ current (If) of the action potential phase 4 in the SA node. This results in a faster rising (and shorter) phase 4, a shorter time to the next heartbeat, and thus a faster HR. β-Blockers will oppose this action, slowing the SA pacemaker rate.2 Depression of the AV node (prolongs the refractory period)
 Same mechanism as SA node: a decrease in the slow Na+ current (If) leaves the AV node in a refractory state longer.
Same mechanism as SA node: a decrease in the slow Na+ current (If) leaves the AV node in a refractory state longer.
 This mechanism is useful in making the AV node a protector of the ventricles. In situations (atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter) in which the AV node is bombarded by electrical signals from the atria, the depressed AV node can permit only a fraction of these signals to enter into the ventricular conducting system, controlling the ventricular rate.
This mechanism is useful in making the AV node a protector of the ventricles. In situations (atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter) in which the AV node is bombarded by electrical signals from the atria, the depressed AV node can permit only a fraction of these signals to enter into the ventricular conducting system, controlling the ventricular rate.
 Same mechanism as SA node: a decrease in the slow Na+ current (If) leaves the AV node in a refractory state longer.
Same mechanism as SA node: a decrease in the slow Na+ current (If) leaves the AV node in a refractory state longer. This mechanism is useful in making the AV node a protector of the ventricles. In situations (atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter) in which the AV node is bombarded by electrical signals from the atria, the depressed AV node can permit only a fraction of these signals to enter into the ventricular conducting system, controlling the ventricular rate.
This mechanism is useful in making the AV node a protector of the ventricles. In situations (atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter) in which the AV node is bombarded by electrical signals from the atria, the depressed AV node can permit only a fraction of these signals to enter into the ventricular conducting system, controlling the ventricular rate.Myocardial Ischemia and Infarction
Chronic Congestive Heart Failure
 Patients with a dysfunctional cardiovascular system have an inefficient system and thus require extra support; this support is in the form of increased levels of SNS activation, renin-angiotensin activity, endothelin activity, and many other compensatory mechanisms.
Patients with a dysfunctional cardiovascular system have an inefficient system and thus require extra support; this support is in the form of increased levels of SNS activation, renin-angiotensin activity, endothelin activity, and many other compensatory mechanisms. Sustained activation of the SNS results in fibrosis and apoptosis of myocytes. Through low level blockade of the SNS, the fibrosis and apoptosis (and other damaging mechanisms) are slowed or inhibited.
Sustained activation of the SNS results in fibrosis and apoptosis of myocytes. Through low level blockade of the SNS, the fibrosis and apoptosis (and other damaging mechanisms) are slowed or inhibited.Pharmacokinetics
 Shorter half-lives (3 to 4 hours): propranolol, metoprolol (sustained-release forms with longer half-lives are available)
Shorter half-lives (3 to 4 hours): propranolol, metoprolol (sustained-release forms with longer half-lives are available) Distribution to the central nervous system (CNS) has been implicated as a source of drug-induced confusion with some β-blockers. Specifically, metoprolol is lipid soluble and therefore crosses the blood-brain barrier, whereas atenolol, another selective β1 blocker does not.
Distribution to the central nervous system (CNS) has been implicated as a source of drug-induced confusion with some β-blockers. Specifically, metoprolol is lipid soluble and therefore crosses the blood-brain barrier, whereas atenolol, another selective β1 blocker does not.Contraindications
 Asthmatics should not use nonselective (β1, β2) β-blockers, as blocking β2 receptors may lead to bronchoconstriction. Stimulation of β2 receptors in the airways causes smooth muscle relaxation of the bronchioles and is the basis of bronchodilators that are β2 agonists.
Asthmatics should not use nonselective (β1, β2) β-blockers, as blocking β2 receptors may lead to bronchoconstriction. Stimulation of β2 receptors in the airways causes smooth muscle relaxation of the bronchioles and is the basis of bronchodilators that are β2 agonists. Second-degree heart block: It can be converted to third-degree heart block, resulting in very low HRs.
Second-degree heart block: It can be converted to third-degree heart block, resulting in very low HRs. Bradycardia: β-Blockers could make the already slow heart so slow that CO and BP fall below levels that are required by the body for adequate perfusion.
Bradycardia: β-Blockers could make the already slow heart so slow that CO and BP fall below levels that are required by the body for adequate perfusion. Acute heart failure: Note that chronic heart failure is an indication for β-blockers, and acute heart failure is a contraindication. In acute heart failure the patient is decompensated and probably being kept alive by the SNS being ramped up. Blocking the effects of the flight-or-fight response would further decompensate the patient and potentially kill him or her.
Acute heart failure: Note that chronic heart failure is an indication for β-blockers, and acute heart failure is a contraindication. In acute heart failure the patient is decompensated and probably being kept alive by the SNS being ramped up. Blocking the effects of the flight-or-fight response would further decompensate the patient and potentially kill him or her.Side Effects
 Raynaud’s phenomenon: Cold extremities (fingers in particular) may result from antagonism of β2 receptors, leading to vasoconstriction in the periphery.
Raynaud’s phenomenon: Cold extremities (fingers in particular) may result from antagonism of β2 receptors, leading to vasoconstriction in the periphery. Impotence: Erectile function is dependent on changes in blood flow and vasodilation in the corpora cavernosa, and these mechanisms can be blocked by β-blockers.
Impotence: Erectile function is dependent on changes in blood flow and vasodilation in the corpora cavernosa, and these mechanisms can be blocked by β-blockers. Hypoglycemia: Nonselective β-blockers may interfere with recovery from hypoglycemia in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes, as they antagonize the ability of catecholamines to promote glycogenolysis and mobilize glucose. Also, in diabetics, the β-blockade prevents symptoms caused by hypoglycemia and so masks early mild hypoglycemia, which can then deteriorate.
Hypoglycemia: Nonselective β-blockers may interfere with recovery from hypoglycemia in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes, as they antagonize the ability of catecholamines to promote glycogenolysis and mobilize glucose. Also, in diabetics, the β-blockade prevents symptoms caused by hypoglycemia and so masks early mild hypoglycemia, which can then deteriorate. CNS effects: Insomnia, nightmares, and depression are side effects. The mechanism is not well understood, but in theory these effects should occur more frequently with lipophilic drugs that cross the blood-brain barrier, such as propranolol and metoprolol.
CNS effects: Insomnia, nightmares, and depression are side effects. The mechanism is not well understood, but in theory these effects should occur more frequently with lipophilic drugs that cross the blood-brain barrier, such as propranolol and metoprolol.Important Notes
 β-blockers should not be discontinued abruptly, because of a rebound effect that might result in tachycardia and exacerbate the symptoms of coronary artery disease or might induce a hypertensive effect. The rebound appears to be an overactivity of the SNS, caused perhaps by receptor up-regulation.
β-blockers should not be discontinued abruptly, because of a rebound effect that might result in tachycardia and exacerbate the symptoms of coronary artery disease or might induce a hypertensive effect. The rebound appears to be an overactivity of the SNS, caused perhaps by receptor up-regulation. The use of β-blockers for HTN is generally avoided in elderly patients, whereas younger hypertensive patients tend to respond well to these agents.
The use of β-blockers for HTN is generally avoided in elderly patients, whereas younger hypertensive patients tend to respond well to these agents. Not only might β-blockers impair the response to hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes, but the negative chronotropic effects of these agents may mask the tachycardia that normally provides an important indicator of hypoglycemia to the diabetic. Despite these concerns, β-blockers have proven effective in the treatment of people with type 1 diabetes who have experienced an MI, and thus the decision whether to use them is one of risk versus benefit in this population.
Not only might β-blockers impair the response to hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes, but the negative chronotropic effects of these agents may mask the tachycardia that normally provides an important indicator of hypoglycemia to the diabetic. Despite these concerns, β-blockers have proven effective in the treatment of people with type 1 diabetes who have experienced an MI, and thus the decision whether to use them is one of risk versus benefit in this population. β-blockers were once contraindicated in chronic heart failure, but current evidence is very strong that they reduce mortality. It is very important to note that β-blockers are contraindicated in patients with acute decompensated heart failure.
β-blockers were once contraindicated in chronic heart failure, but current evidence is very strong that they reduce mortality. It is very important to note that β-blockers are contraindicated in patients with acute decompensated heart failure.Evidence
After Myocardial Infarction
 Evidence for the role of β-blockers in secondary prevention after an MI comes from several trials and was summarized in a 1999 systematic review (82 trials, N = 54,234 patients). There was a 23% reduction in the odds of death in long-term trials but only a 4% reduction in short-term trials. The review found that the number needed to treat (NNT) to avoid a fatality over the course of 2 years is 42. The greatest amount of evidence available was for propranolol, timolol, and metoprolol.
Evidence for the role of β-blockers in secondary prevention after an MI comes from several trials and was summarized in a 1999 systematic review (82 trials, N = 54,234 patients). There was a 23% reduction in the odds of death in long-term trials but only a 4% reduction in short-term trials. The review found that the number needed to treat (NNT) to avoid a fatality over the course of 2 years is 42. The greatest amount of evidence available was for propranolol, timolol, and metoprolol.Hypertension and Associated Stroke and Coronary Artery Disease
 A Cochrane review in 2007 (13 studies, N = 91,561 patients) compared β-blockers with other agents for HTN. Atenolol was the β-blocker most frequently used. The authors found that β-blockers had only weak effects in reducing stroke and no effect on coronary heart disease versus placebo. There was also a trend toward worse outcomes when compared with calcium channel blockers (CCBs), RAS inhibitors, and thiazides, prompting the authors to suggest that β-blockers should not be considered as first-line agents for HTN.
A Cochrane review in 2007 (13 studies, N = 91,561 patients) compared β-blockers with other agents for HTN. Atenolol was the β-blocker most frequently used. The authors found that β-blockers had only weak effects in reducing stroke and no effect on coronary heart disease versus placebo. There was also a trend toward worse outcomes when compared with calcium channel blockers (CCBs), RAS inhibitors, and thiazides, prompting the authors to suggest that β-blockers should not be considered as first-line agents for HTN.Obstructive Airway Disease (Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
 A Cochrane review in 2002 (29 studies, N = 381 patients) examined the impact of single-dose or short-term selective β1-blockers in patients with mild to moderate obstructive airway disease. There were no differences in pulmonary flow measurements compared with placebo except for a small decrease in FEV1 after the first treatment—an effect that disappeared with subsequent doses.
A Cochrane review in 2002 (29 studies, N = 381 patients) examined the impact of single-dose or short-term selective β1-blockers in patients with mild to moderate obstructive airway disease. There were no differences in pulmonary flow measurements compared with placebo except for a small decrease in FEV1 after the first treatment—an effect that disappeared with subsequent doses.Potassium Channel Blockers (Class III Antiarrhythmics)
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Blocking K channels in phase 3 of the action potential slows the efflux of K back out of the myocyte, which slows the rate at which the cell repolarizes and therefore lengthens the plateau phase of the action potential. This increases the refractory period of atrial, ventricular, and Purkinje cells. This also increases the QT interval on the ECG (Figure 11-5).
Blocking K channels in phase 3 of the action potential slows the efflux of K back out of the myocyte, which slows the rate at which the cell repolarizes and therefore lengthens the plateau phase of the action potential. This increases the refractory period of atrial, ventricular, and Purkinje cells. This also increases the QT interval on the ECG (Figure 11-5). Amiodarone contains multiple antiarrhythmic properties and is an Na blocker, a K blocker, a Ca blocker, and β-blocker, all rolled into one chemical. However, it is primarily referred to as a class III drug.
Amiodarone contains multiple antiarrhythmic properties and is an Na blocker, a K blocker, a Ca blocker, and β-blocker, all rolled into one chemical. However, it is primarily referred to as a class III drug.Pharmacokinetics
 Drug interactions:
Drug interactions: Amiodarone and dronedarone are metabolized by and are inhibitors of CYP3A4; this is important because other drugs used in the control of dysrhythmias, including verapamil and diltiazem, are also metabolized by CYP3A4, and drug levels can be increased when drugs are coadministered.
Amiodarone and dronedarone are metabolized by and are inhibitors of CYP3A4; this is important because other drugs used in the control of dysrhythmias, including verapamil and diltiazem, are also metabolized by CYP3A4, and drug levels can be increased when drugs are coadministered. There is an interaction with digoxin, another drug used for treatment of arrhythmias: levels of digoxin can be increased up to 2.5 times as a result of P-glycoprotein interactions at the kidney.
There is an interaction with digoxin, another drug used for treatment of arrhythmias: levels of digoxin can be increased up to 2.5 times as a result of P-glycoprotein interactions at the kidney.