Carcinoid
Satish K. Tickoo, MD
Victor E. Reuter, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Well-differentiated neuroendocrine neoplasm arising within kidney
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Up to 20% of primary renal carcinoids arise in “horseshoe” kidneys
Clinical Issues
Approximately 1/2 of cases < 50 years at diagnosis
Clinical signs or symptoms of carcinoid syndrome extremely uncommon
Regional lymph node metastasis often present in cases undergoing lymph node resection with nephrectomy
Most patients with metastasis have protracted clinical course, with only rare reported deaths due to disease
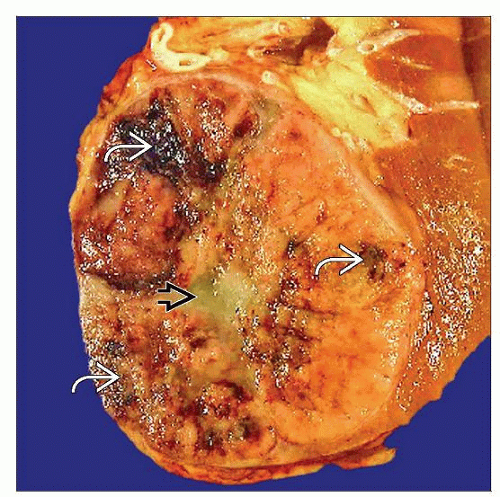
Macroscopic Features
Solitary tumor, usually well circumscribed
Necrosis very uncommon
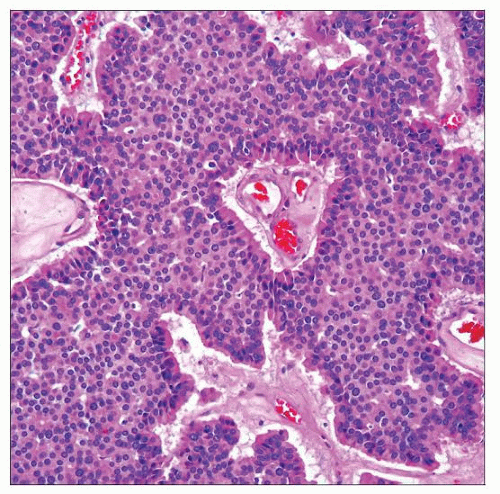
Microscopic Pathology
Tumor-renal parenchymal junctions sharply defined in most cases, with focal infiltration in occasional case
Morphologically similar to carcinoid tumors at other sites
Invasion into perinephric fat was observed in > 40% cases in a recent study (largest to date)
Often positive for metastasis to lymph nodes (> 1/3 of cases)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Carcinoid tumor metastatic to kidney
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Renal carcinoid tumor (RCT)
Definitions
Well-differentiated primary neuroendocrine neoplasm arising within kidney
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Developmental Anomaly
Up to 20% of primary renal carcinoids arise in “horseshoe” kidneys
Pathogenesis of this association not clear
Association With Renal Teratoma
Rarely reported to arise in renal teratoma or “teratoid tumors,” both extremely uncommon tumors in kidney
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Very rare tumor of kidney
Approximately 80 cases reported in literature
After the gonads, kidney is 2nd most common site for genitourinary carcinoids in both sexes
Age
Range: 27-78 years (mean: 52 years)
Approximately 1/2 of cases < 50 years at diagnosis
Presentation
Approximately 40% present with tumor-related symptoms, including back or flank pain, hematuria, or enlarging abdominal mass
Clinical signs or symptoms of carcinoid syndrome are extremely uncommon
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Nephron-sparing surgery for organ-confined tumors is preferred surgical approach
Adjuvant therapy
Because of usual prolonged clinical course even in widely metastatic disease
Role of adjuvant therapies uncertain; effective therapies are unavailable
Value of anti-angiogenic targeted therapies in widely metastatic settings is currently suggested
Prognosis
Regional lymph node metastasis often present in cases undergoing lymph node resection with nephrectomy
Lung, liver, and bone are other reported metastatic sites
Most patients with metastasis have protracted clinical course, with only rare reported deaths due to disease
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree