Chapter 6 Carbohydrate Metabolism
I. Glycolysis and the Fate of Pyruvate
A. Overview
3. Glycolysis is regulated at three points: hexokinase, phosphofructokinase (PFK), and pyruvate kinase.
5. Glycolysis interfaces with glycogen metabolism, the pentose phosphate pathway, the formation of amino sugars, triglyceride synthesis (by means of glycerol 3-phosphate), the production of lactate (a dead-end reaction), and transamination with alanine.
6. Pyruvate dehydrogenase interfaces with other pathways such as the citric acid cycle or fat synthesis through its product, acetyl CoA.
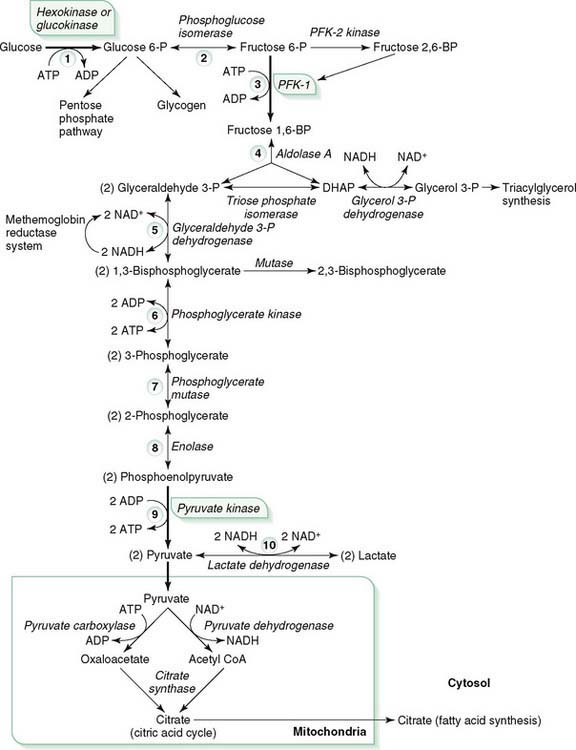
B. Glycolysis and pyruvate oxidation: pathway reaction steps (Fig. 6-1)
1. Step 1
a. Phosphorylation of glucose to glucose 6-phosphate, the first regulated step in glycolysis, is irreversible and traps glucose inside the cell.
c. The two enzymes that catalyze this step, hexokinase and glucokinase, are specialized to function under different conditions (Table 6-1).
d. Hexokinase, present in all tissues, is active at low glucose concentrations (low Km) and cannot rapidly phosphorylate large amounts of glucose (low Vmax).
TABLE 6-1 Comparison of Hexokinase and Glucokinase
| Characteristic | Hexokinase | Glucokinase |
|---|---|---|
| Tissue location | All | Liver and pancreatic β cells |
| Km | Low (high substrate affinity) | High (low substrate affinity) |
| Vmax | Low | High |
| Inhibited by glucose 6-phosphate | Yes | No |
| Inducible by insulin | No | Yes |
| Substrate specificity | Glucose, fructose, galactose | Glucose only |
| Physiologic role | Provides cells with basal level of glucose 6-phosphate needed for energy production | Permits accumulation of intracellular glucose for conversion to glycogen or triacylglycerols |
4. Step 4
b. Triose phosphate isomerase reversibly converts glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP).
c. DHAP is reversibly converted to glycerol 3-phosphate by glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, which uses NADH as a cofactor.
5. Step 5
a. Reversible conversion of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (1,3-BPG) by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase using NAD+ as a cofactor
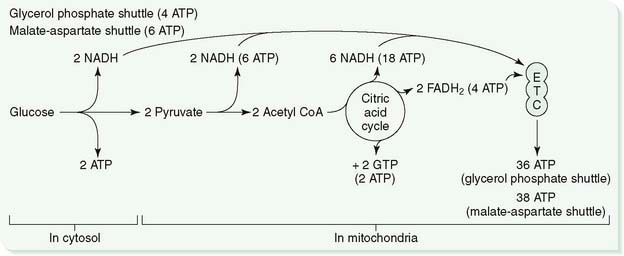
c. NADH is shuttled into the ETC by the glycerol phosphate shuttle or the malate-aspartate shuttle (see Chapter 5).
10. Step 10
11. Pyruvate dehydrogenase, a large multienzyme complex located in the mitochondrial matrix, acts on pyruvate to produce acetyl CoA and 2 NADH.
C. Glycolysis and pyruvate oxidation: regulated steps
2. Hexokinase versus glucokinase
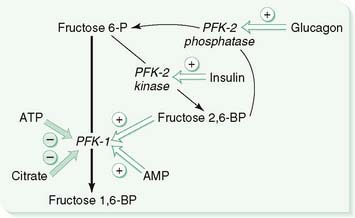
3. PFK-1
a. Inhibitors include ATP (indicates that energy stores are high) and citrate (indicates that the cell is actively making ATP).
b. Activators of PFK-1 include AMP (indicates that energy stores are depleted) and fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, which is formed by phosphofructokinase 2 (PFK-2).
c. The fructose 2,6-bisphosphate level is controlled by the insulin-to-glucagon ratio by its effect on PFK-2, which is a bifunctional enzyme that has different activities in the fed and fasting states (Fig. 6-3).
(1) In the fed state (i.e., high insulin, low glucagon), insulin dephosphorylates PFK-2, giving it kinase activity, which converts fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, leading to activation of PFK-1 and enhanced glycolysis.
4. Pyruvate kinase
5. Pyruvate dehydrogenase
a. Cycling between inactive and active forms of pyruvate dehydrogenase is catalyzed by a specific kinase (phosphorylates the enzyme) and phosphatase (dephosphorylates the enzyme).
D. Glycolysis and pyruvate oxidation: unique characteristics
1. Comparison of aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis
a. NADH produced in the glycolytic pathway must be oxidized to regenerate NAD+ for glycolysis to continue.
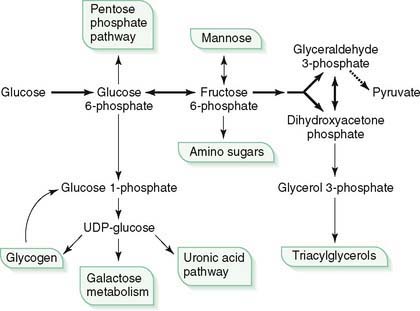
E. Glycolysis and pyruvate oxidation: interface with other pathways (Fig. 6-4)
1. Glucose 6-phosphate, the first product formed in glycolysis, connects the glycolytic pathway to the pentose phosphate pathway and to glycogen synthesis, galactose metabolism, and the uronic acid pathway.
2. Fructose 6-phosphate is the precursor for synthesis of amino sugars (e.g., glucosamine and galactosamine), which ultimately are incorporated into glycoproteins and glycosaminoglycans (e.g., chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid).
3. Glycerol 3-phosphate, derived from dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP), is used in the synthesis of triacylglycerols in the liver.
4. 1,3-BPG is converted by a mutase to 2,3-BPG in RBCs, which is the key substrate for shifting the O2-binding curve to the right (decreasing O2 affinity) (see Fig. 6-1).
5. In the RBC the reaction that converts glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 1,3-BPG, donates some of the NADH to be used by the methemoglobin reductase pathway to reduce methemoglobin (Fe3+), which cannot bind O2, to hemoglobin (Fe2+), which binds O2 to its heme iron (see Fig. 6-1, step 5).
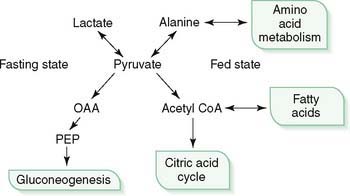
6. Pyruvate, the end product of aerobic glycolysis, is a key metabolic intermediate whose fate differs in the fed and fasting states (Fig. 6-5).
a. In the fed state, when glucose is plentiful, pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl CoA by pyruvate dehydrogenase.
F. Glycolysis and pyruvate oxidation: clinical relevance
1. Lactic acidosis (increased lactate in blood)
a. In aerobic glycolysis, electrons from NADH are transferred to the ETC by the glycerol phosphate shuttle or the malate-aspartate shuttle, and NAD+ is returned to the cytosol (see Figs. 5-9 and 5-10 in Chapter 5).
b. In anaerobic glycolysis, reduction of pyruvate to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase regenerates NAD+ (see Fig. 6-1).
II. Gluconeogenesis
A. Overview
2. Reciprocal regulation by the insulin-to-glucagon ratio ensures that glycolysis and gluconeogenesis are not stimulated simultaneously.
6. Gluconeogenic enzyme deficiencies result in fasting hypoglycemia.
TABLE 6-2 Hereditary Defects in Catabolism of Sugars
| Disease | Metabolic Effect | Clinical Features |
|---|---|---|
| Glucose and Pyruvate Metabolism | ||
| Pyruvate kinase deficiency (AR, most common enzyme deficiency in the glycolytic pathway) | Inadequate ATP for maintaining ion pumps in RBC membrane results in loss of H2O and membrane damage (produces RBCs with spikes) | Hemolytic anemia and jaundice begin at birth; anemia is somewhat offset by an increase in 2,3-BPG, which shifts the O2-binding curve to the right (decreased O2 affinity) |