Capillary Hemangiomatosis
Key Facts
Terminology
Benign condition characterized by proliferation of small capillaries in pulmonary interstitium
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Possible autosomal recessive inheritance has been mentioned
May also appear as an incidental finding
Clinical Issues
Unusual occurrence
It may occur in any age group
Most cases appear to be more commonly diagnosed in 3rd or 4th decade of life
Symptoms
Cough
Hemoptysis
Respiratory distress
Chest pain
Pulmonary hypertension
Interstitial lung disease
Prognosis
Good if diagnosed earlier
Can be fatal in advanced stages
Top Differential Diagnoses
Capillaritis
Cavernous hemangioma
Capillary hemangioma
Pulmonary hemorrhage
Angiosarcoma
Normal lung parenchyma
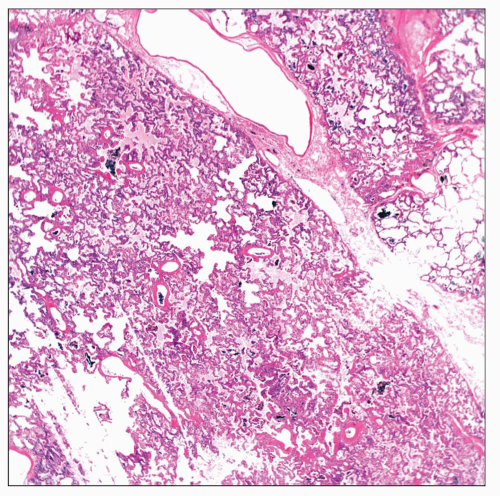 Low-power view shows a lung section with capillary hemangiomatosis. At this power, the lung may look within normal limits, and in a cursory review, the pathological process can be easily missed. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Capillary hemangiomatosis (CH)
Definitions
Benign condition characterized by proliferation of small capillaries in pulmonary interstitium
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Possible autosomal recessive inheritance has been observed
May also appear as an incidental finding
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Unusual occurrence
Age
It may occur in any age group
Most cases appear to be more commonly diagnosed in 3rd or 4th decade of life
Gender
No gender predilection
Ethnicity
No ethnic predilection
Site
Pulmonary interstitium
Presentation
Cough
Hemoptysis
Respiratory distress
Chest pain
Pulmonary hypertension
Interstitial lung disease
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Due to extensive nature of process, radical approach may be necessary
Lobectomy or pneumonectomy
Drugs
Interferon α-2a
Prognosis
Good if diagnosed earlier and if the process is less diffuse
Can be fatal due to pulmonary hemorrhage
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Congested lung parenchyma
Sponge-like appearance
Multicystic changes in lung parenchyma
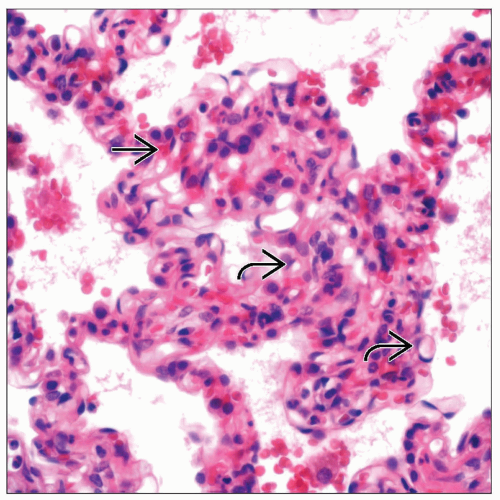
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Interstitial congestion
Proliferation of small capillaries
Capillaries may infiltrate into bronchi and larger vessels
Presence of double capillaries
Lack of cytologic atypia
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Capillaritis
In cases of capillaritis, there is usually inflammatory reaction associated with the process
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree