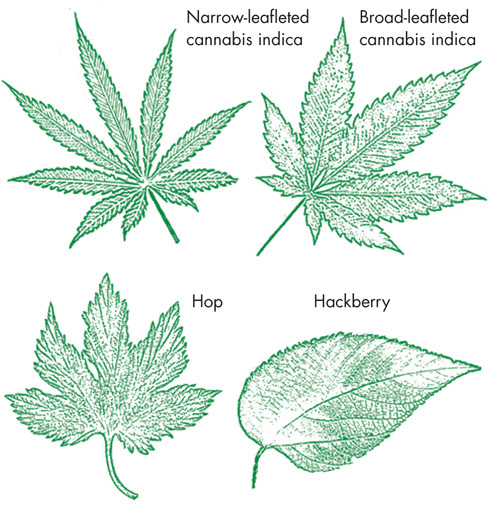
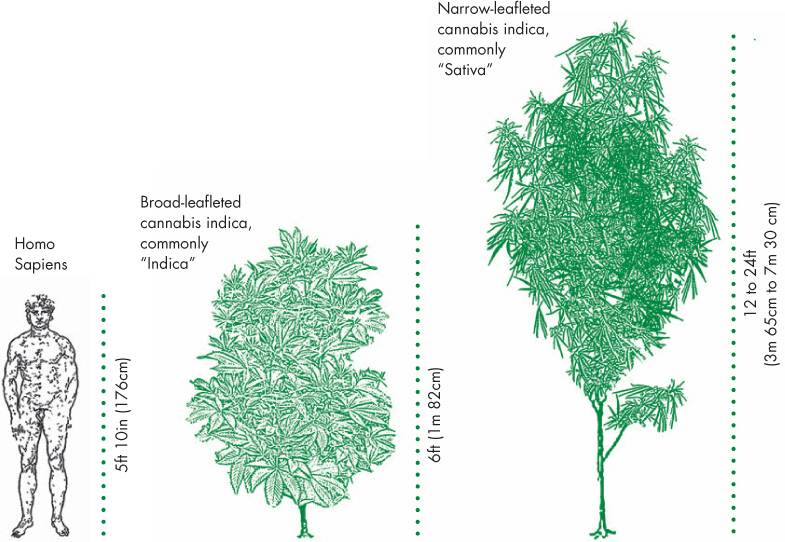
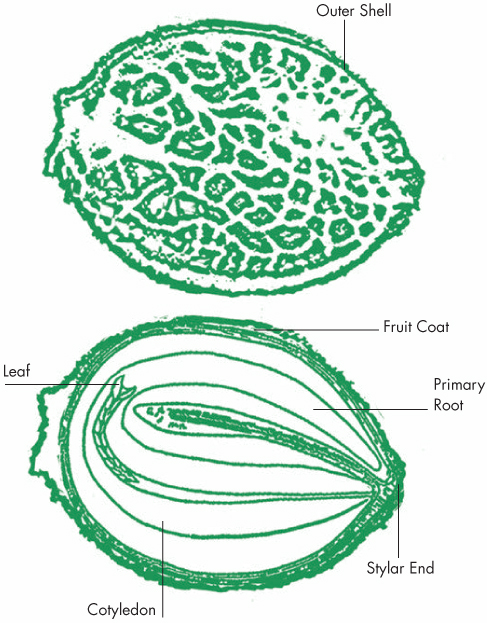
Current genetic understanding places cannabis within the plant family Cannabaceae. This small family consists of flowering plants that originated within the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Besides cannabis, the Cannabaceae family includes two species of hops, whose female flowers are used for making beer. The leaves of hop plants share their palmate (finger-shaped) form with cannabis. More recently, the Cannabaceae family has broadened to include 70 species of hackberry trees, previously thought to be part of the related Ulmaceae family, which also includes elm trees. Genetic evidence supports the argument for cannabis appearing to have split into two species: sativa and indica. Sativa is the fiber type of cannabis that produces more CBD and typically less than 1 percent THC. Indica is the drug-rich cannabis, whose THC content can reach 25 percent of the plant’s dry weight. In common parlance, sativa is used to describe narrow-leafleted and taller drug varieties from more tropical climes, while indica is applied to the broad-leafleted and shorter drug varieties from Afghanistan and Pakistan. While the Afghan plants rarely grow to more than 6½ feet (2 meters) in height, their Southeast Asian counterparts, for example in Vietnam, have been reported to exceed 27 feet (7 meters) in height. Cannabis is a truly multipurpose plant. Its extraordinarily strong fibers have been used to make hemp cloth and paper for thousands of years. The Vikings used hemp to make sails for their ships to voyage from Scandinavia to Nova Scotia. Betsy Ross sewed the first United States flag from hempen cloth. The American Declaration of Independence was written on hemp paper, and deutsche marks—now obsolete German currency—were once printed on hemp paper. In the Netherlands, windmills were often built to crush hemp stalks.13 As already mentioned, cannabis’ potential as a food source is likely what first drew early humans’ attention. Cannabis seed (hempseed)—which is strictly speaking a nut rather than a seed—is exceptionally rich in polyunsaturated fats, essential fatty acids, and proteins (see this page). This composition qualifies it as a functional food (that is, a food that can benefit a person’s health in ways other than purely nutritional) and indeed hempseed has been used in Asian cultures as both a food and a medicine for three millennia. Despite the sweeping American prohibition of cannabis products, over the last two decades hempseed has been permitted in the U.S. for use in food.14 Cannabis resin’s utility as a drug, both for medicinal and psychoactive use, has encouraged breeding favoring the plant’s production of resin (see this page). Breeding for increased resin production has produced a range of cannabis drug chemotypes regionally around the globe, with some cultivars producing only THC, other cultivars producing THC and CBD, and a few cultivars expressing propyl THCV and/or CBDV (see this page). Cannabis is dioecious, meaning that it produces male and female flowers on separate plants. By contrast, the majority of flowering plants exhibit both male and female reproductive organs on the same plant, developing mechanisms that are geared to reduce inbreeding and self-pollination. Cannabis likely evolved two sexes to encourage a wider genetic diversity.15 Molecular genetic markers have been found within cannabis, meaning that the plant’s sex can be determined before any visible signs are observed.16 Cannabis is an annual plant, which means that it completes its life cycle within a single year. Most cannabis seeds will germinate three to seven days after planting. During the first three months of the cannabis life cycle, the plant undergoes a rapid vegetative growth phase, producing leaf mass for optimal photosynthesis. Following the vegetative phase, longer nights after the summer solstice trigger the cannabis flowering cycle within both male and female cannabis plants. Depending on the latitude, cannabis flowering requires 10 to 12 hours of night. Flowering cannabis produces fewer leaflets (small leaves) as the plant shifts its metabolic resources toward reproduction.17 A typical female cannabis plant will produce hundreds of tiny flowers. At the top of the plant these flowers are clustered in a huge mass that in Spanish is called a “cola.” Colas of outdoor female cannabis plants can exceed 4 feet (1.2 meters) at harvest time.
THE CANNABIS PLANT
Cannabis for Everything
The Sexes of Cannabis
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree