Definitions
A burn is the response of the skin, mucous membranes and subcutaneous tissues to thermal injury. A partial thickness burn does not destroy the skin epithelium or destroys only part of it, sub-classified into superficial and deep partial thickness. A full thickness burn destroys all sources of skin epithelial regrowth.
Key Points
- Start resuscitation immediately in major burns.
- Calculate fluid requirement from the time of the burn.
- Examine for vital areas burns (airway/hands/face/perineum/circumferential).
- Assume that all burns in <5 years and >55 years are not superficial.
- Refer all major burns to a specialist burns centre.
- Remember tetanus prophylaxis.
Common Causes
- Thermal injury: dry – flame, hot metal, sunburn; moist – hot liquids or gases.
- Electricity (deep burns at entry and exit sites, may cause cardiac arrest).
- Chemicals (usually industrial accidents with acid or alkali).
- Radiation (partial thickness initially, chronic deeper injury later).
Clinical Features
General
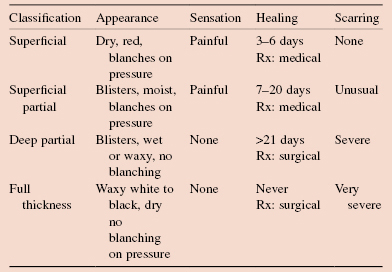
Specific
- Evidence of smoke inhalation (soot in nose or sputum, burns in the mouth, hoarseness).
- Eye or eyelid burns (early ophthalmological opinion).
- Circumferential burns (will need escharotomy).
- Hands, feet, genitalia, joints (will need specialist care).
Investigations
- FBC, U+E.
- If inhalation suspected: chest X-ray, arterial blood gases, CO estimation.
- Blood group and crossmatch.
- ECG/cardiac enzymes with electrical burns.
Complications
Immediate
- Smoke inhalation: commonest cause of death from burns.
- Circumferential burns → compartment syndrome (limbs → limb ischaemia; thorax → restrictive respiratory failure). Rx: escharotomy.
Early
- Hyperkalaemia (from cytolysis in large burns). Rx: insulin and dextrose.
- Acute renal failure (combination of hypovolaemia, sepsis, tissue toxins). Rx: aggressive early resuscitation, ensuring high GFR with fluid loading and diuretics, treat sepsis.
- Infection (Staphlococcus and MRSA, Streptococcus, E. coli, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, yeasts). Treat established infection (106 organisms present in wound biopsy) with systemic antibiotics. Early surgical excision.
- Stress ulceration (Curling’s ulcer). Prevent with PPI prophylaxis.
Late
Contractures.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


