Bronchocentric Granulomatosis
Key Facts
Terminology
Reaction pattern of lung parenchyma characterized by broncho- and bronchiolocentric necrotizing granulomatous inflammation
Clinical Issues
Most cases of BCG are allergic and associated with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
About 50% of patients have history of chronic asthma
Frequent finding is mucoid impaction with “allergic” mucin
Noninfectious cases occur mainly in asthmatic patients with mucus impaction
Infectious cases show more variable findings, ranging from localized consolidation to nodular parenchymal lesions
Microscopic Pathology
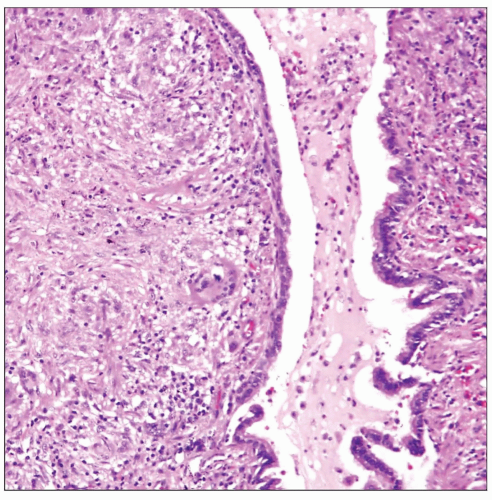
Destruction of walls of small bronchi and bronchioles by necrotizing granulomatous inflammation
Bronchial walls are replaced by palisading histiocytic reaction
Abundant necrotic debris seen in lumens of bronchioles with numerous neutrophils and eosinophils
Impaction of proximal airways by allergic mucin
Eosinophils are particularly prominent in cases associated with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
Multinucleated giant cells may be present, particularly around necrotic debris
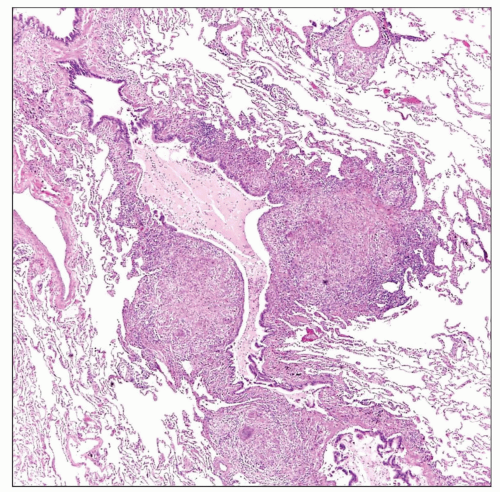 Bronchocentric granulomatosis shows multiple epithelioid granulomas composed of epithelioid histiocytes circumscribing a bronchus. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Bronchocentric granulomatosis (BCG)
Definitions
Reaction pattern of lung parenchyma characterized by broncho- and bronchiolocentric necrotizing granulomatous inflammation
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Process can be related to infectious and noninfectious causes
Infections associated with BCG include mycobacteria, fungi (Aspergillus, Histoplasma, etc.), and parasites (Echinococcus)
Noninfectious causes of BCG include Wegener granulomatosis and rheumatoid arthritis
Allergic causes of BCG include allergic aspergillosis in association with mucoid impaction
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Most cases of BCG are allergic and associated with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
About 50% of patients have history of chronic asthma
Age
No particular age distribution
Site
BCG affects mostly larger bronchi but may also involve more distant bronchioles
Presentation
Fever
Cough
Wheezing
Peripheral eosinophilia
Mucoid impaction
Endoscopic Findings
Frequent finding is mucoid impaction with “allergic” mucin
Laboratory Tests
Elevated IgE levels and serum precipitins to Aspergillus are important clues in allergic cases
Antinuclear antibody testing is helpful to rule out Wegener granulomatosis
Cultures are important to rule out specific infectious agents
Natural History
Noninfectious cases occur mainly in asthmatic patients with mucus impaction
Infectious cases show more variable findings, ranging from localized consolidation to nodular parenchymal lesions
Cavitation is most often encountered in cases associated with infectious etiology
Treatment
Steroids are treatment of choice for both infectious and noninfectious BCG
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree