Bronchioloalveolar Cell Carcinoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Bronchioloalveolar cell carcinoma (BAC)
Adenocarcinoma with BAC pattern and no evidence of stromal, vascular, or pleural invasion
Essentially, current definition is that of in situ adenocarcinoma
Etiology/Pathogenesis
BAC appears not to be associated with tobacco smoking
Macroscopic Features
Localized tumor mass: Usually < 3 cm in diameter
Multinodular pattern: Extensive areas of lung parenchyma are involved in miliary fashion
Diffuse pattern: No distinct tumor mass or nodule is present
Lung parenchyma appears congested, mimicking pneumonia
Top Differential Diagnoses
Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH)
Tumor nodule of < 0.5 cm in greatest dimension
Metastatic adenocarcinoma
Good clinical history and physical examination
Immunohistochemical studies may be helpful in determining primary site
Invasive adenocarcinoma
By definition, BAC is a tumor with no lymphatic, pleural, or interstitial invasion
Complete examination of tumor is required in order to rule out invasion
Presence of lymph node involvement rules out diagnosis of BAC
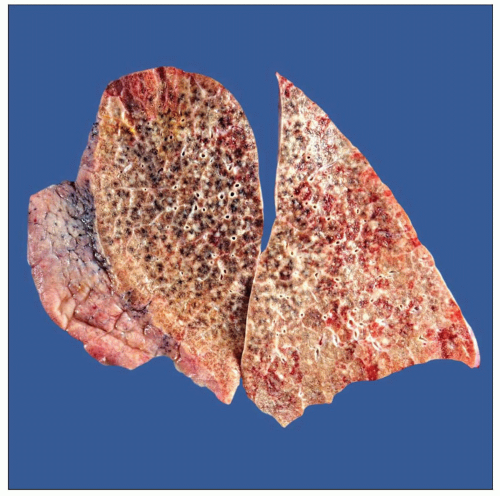 Gross photograph shows multiple small pulmonary nodules of different sizes. This represents the multinodular pattern of bronchioloalveolar cell carcinoma. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Bronchioloalveolar cell carcinoma (BAC)
Synonyms
Adenocarcinoma in situ, adenocarcinoma with bronchioloalveolar pattern
Definitions
Well-differentiated adenocarcinoma
Lesion with relatively bland cytologic features that arises in periphery of lung and spreads along the walls of distal air spaces
Subset of adenocarcinoma common and distinctive enough to warrant separation from other subtypes
Adenocarcinoma with BAC pattern
No evidence of stromal, vascular, or pleural invasion
Essentially, current definition is similar to that of in situ adenocarcinoma
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
BAC appears not to be associated with tobacco use
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Incidence of true BAC is not high and may represent less than 10% of all carcinomas of lung
Age
Tumor can occur at any age
Presentation
Cough
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Bronchorrhea
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Wedge resection, lobectomy, or pneumonectomy
Prognosis
As currently defined, BAC tumors of 2 cm or less are expected to do well
In those tumors that are multifocal, prognosis may not be as good
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Localized tumor mass: Usually < 3 cm in diameter
Multinodular pattern: Extensive areas of lung parenchyma are involved in miliary fashion
Diffuse pattern: No distinct tumor mass or nodule is present
Lung parenchyma appears congested, mimicking lobar pneumonia
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
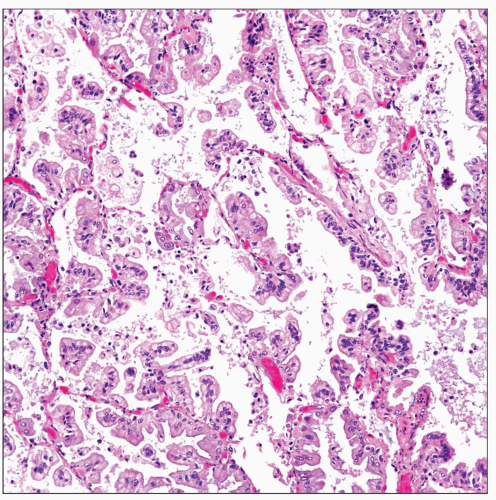
Histologic Features
Conventional type
Tumor cells are small and dark with hyperchromatic nuclei and scant cytoplasm
Tumor cells display prominent hobnail appearance and are devoid of nucleoli or mitotic figures
Mucinous type
Tumor cells are tall columnar and contain abundant mucinous cytoplasm
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree