Blastomycosis
Key Facts
Terminology
Pulmonary infection caused by inhalation of the fungus Blastomyces dermatidis
Clinical Issues
Geographic distribution in the USA: Mississippi, Missouri, and Ohio River valleys
Acute infection is usually self-limited and may simulate bacterial pneumonia
Microscopic Pathology
Typical reaction of lung parenchyma to B. dermatidis is suppuration with abscess formation
Advanced stages show necrotizing palisading granulomas
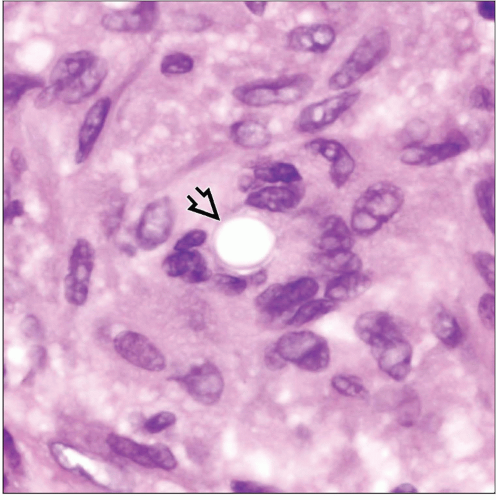
Organisms are round to oval budding yeasts measuring 8-15 µm with thick, refractile cell walls
Organisms stain positive with GMS and may also stain positive for PAS
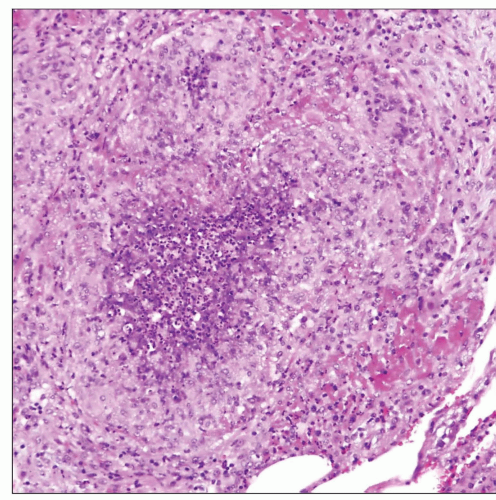 Scanning magnification of a suppurative, epithelioid granuloma in pulmonary blastomycosis shows a dense collection of epithelioid histiocytes with central necrosis and neutrophilic infiltrates. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
North American blastomycosis
Definitions
Pulmonary infection caused by inhalation of the fungus Blastomyces dermatidis
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Natural habitat for the fungus is most likely wood
CLINICAL ISSUES