8 Biliary Diseases
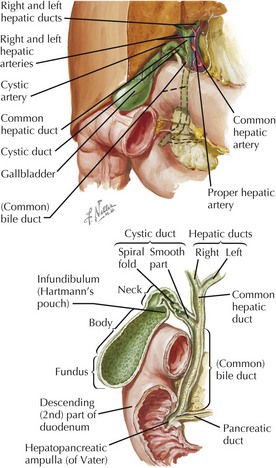
Anatomy of the Extrahepatic Biliary System
• Anatomy of the biliary system is highly variable, and this includes ducts, arteries, veins, and lymphatics.
Gallbladder
• Normally lies between hepatic segments IV and V, in a ventral fossa between the anatomical right and left lobes
• Parasympathetic preganglionic innervation from left (anterior) vagus fibers contracts gallbladder and relaxes bile duct sphincter.
• Postganglionic sympathetic fibers from the celiac ganglion are driven by preganglionic fibers from T7-T10 spinal segments traveling in greater splanchnic nerves.
Cystic Duct
• Typical cystic duct joins the common hepatic duct well below the right and left hepatic duct junction.
• Triangle of Calot: classic configuration (shown above) with cystic duct right, common bile duct left, liver above, and right hepatic artery passing through
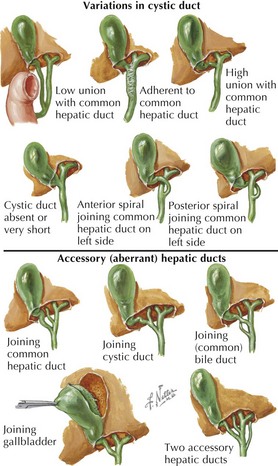
Cystohepatic Junction
• Variations
 Low insertion of cystic duct, crossing anterior to common hepatic duct, inserting behind the duodenum
Low insertion of cystic duct, crossing anterior to common hepatic duct, inserting behind the duodenum
 Low insertion of cystic duct, crossing anterior to common hepatic duct, inserting behind the duodenum
Low insertion of cystic duct, crossing anterior to common hepatic duct, inserting behind the duodenum(Common) Bile Duct
• Bile duct sphincter: smooth muscle surrounding the distal end of the duct, part of the complex sphincter of Oddi