Class
- Antiparkinson agent, anticholinergic
Benztropine
Commonly Prescribed for
(FDA approved in bold)
- Extrapyramidal disorders
- Parkinsonism
- Acute dystonic reactions
- Idiopathic generalized dystonia
- Focal dystonias
- Dopa-responsive dystonia
Benztropine
 How the Drug Works
How the Drug Works
- In PD, there is a relative excess of cholinergic input. Benztropine is a synthetic anticholinergic with relatively greater CNS activity than most other anticholinergics. May also inhibit the reuptake and storage of dopamine at central dopamine receptors, prolonging dopamine action
Benztropine
How Long Until It Works
- PD/extrapyramidal disorders – minutes-hours
Benztropine
If It Works
- PD – do not abruptly discontinue or change doses of other PD treatments. Usually most effective in combination with other medications
Benztropine
If It Doesn’t Work
- PD – Generally benztropine is an adjunctive medication for common PD symptoms, such as tremor, rigidity, and drooling. Other cardinal PD symptoms, such as bradykinesia and gait difficulties, are most likely to improve with other PD treatments, such as levodopa, dopamine agonists, amantadine, or MAO-B inhibitors
- Acute dystonic reactions – diphenhydramine is another option, if not effective consider benzodiazepines. If possible, discontinue the agent that precipitated the extrapyramidal AE
Benztropine
 Best Augmenting Combos for Partial Response or Treatment-Resistance
Best Augmenting Combos for Partial Response or Treatment-Resistance
- For bradykinesia or gait disturbances causing significant functional disturbance, levodopa is most effective. For idiopathic PD patients, especially younger patients with normal cognition and milder disability, dopamine agonists are a good first choice. Amantadine and MAO-B inhibitors may also be useful
- Depression is common in PD and may respond to low dose SSRIs
Benztropine
Tests
- None
Adverse Effects (AEs)
Benztropine
How Drug Causes AEs
- Prevents the action of acetylcholine on muscarinic receptors
Benztropine
Notable AEs
- Dry mouth, tachycardia, palpitations, hypotension, disorientation, confusion, hallucinations, constipation, nausea/vomiting, dilation of colon, rash, blurred vision, diplopia, urinary retention, elevated temperature, decreased sweating, erectile dysfunction
Benztropine
 Life-Threatening or Dangerous AEs
Life-Threatening or Dangerous AEs
- May precipitate narrow-angle glaucoma. Risk of heat stroke, especially in elderly patients. Can cause tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmias and hypotension in susceptible patients. May cause urinary retention in patients with prostate hypertrophy
Benztropine
Weight Gain
- Unusual

Benztropine
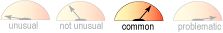
Sedation
- Common
Benztropine
What to Do About AEs
- Confusion, hallucinations – stop benztropine and any other anticholinergics
- Sedation – can take entire dose at night or lower dose
- Dry mouth – chewing gum or water can help
- Urinary retention: if drug cannot be discontinued, obtain urological evaluation
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


